5115 Case Hardening Steel - 1.7131 - 16MnCr5 - SAE 5115

5115 Case Hardening Steel - 1.7131 - 16MnCr5 - SAE 5115
Back to Steel Overview
5115 STEEL PRICE CHART
5115 STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Chemical name:
16MnCr5
Working hardness:
58 HRC (surface) - 60 HRC
Delivery condition:
max. 217 HB
16MnCr5
58 HRC (surface) - 60 HRC
max. 217 HB

5115 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
5115, also known as 16MnCr5 or EC80, is a cold work case hardening steel with a high surface hardness, a tough core and higher sulfur for better machining.
5115 case hardening steel finds its uses in automotive and mechanical engineering, for example for bushings and connecting rods. It is commonly used for parts that need a good core strength and high wear resistance.
Introducing approx. 0.8% carbon into the surface layer through case hardening, carburization or carbonitriding (diffusion process) will leave the material with a hard and wear resistant surface layer and a tough core able to absorb impact stresses without breaking.
The 5115 has a core strength of approx. 116-145 KSI (800-1000 N/mm2).
Stainless steel has a mass fraction of 10.5% of chromium which makes it a corrosion resistant steel. The 5115 has a mass fraction of 0.8 - 1.1% and is therefore not a corrosion resistant steel. The chromium content in this grade enhances the hardenability and wear resistance of this material grade. When corrosion resistance is a high priority it would be advisable to use a steel grade with a higher chromium content like a stainless steel.
As a ferromagnetic steel the 5115 can be magnetized.
5115 case hardening steel can be hot worked at a temperature range of 2012-1562°F (1100-850°C).
5115 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
The working hardness for the SAE 5115 is 601 - 627 BHN (58 - 60 HRC) on the surface.
Typically the density of 5115 is 0.284 lb/in3 (7.85g/cm3) at room temperature.
5115 has a tensile strength of approx. 104.4 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The yield strength for this steel alloy is approx. at 50 - 70 KSI (345 - 490MPa).
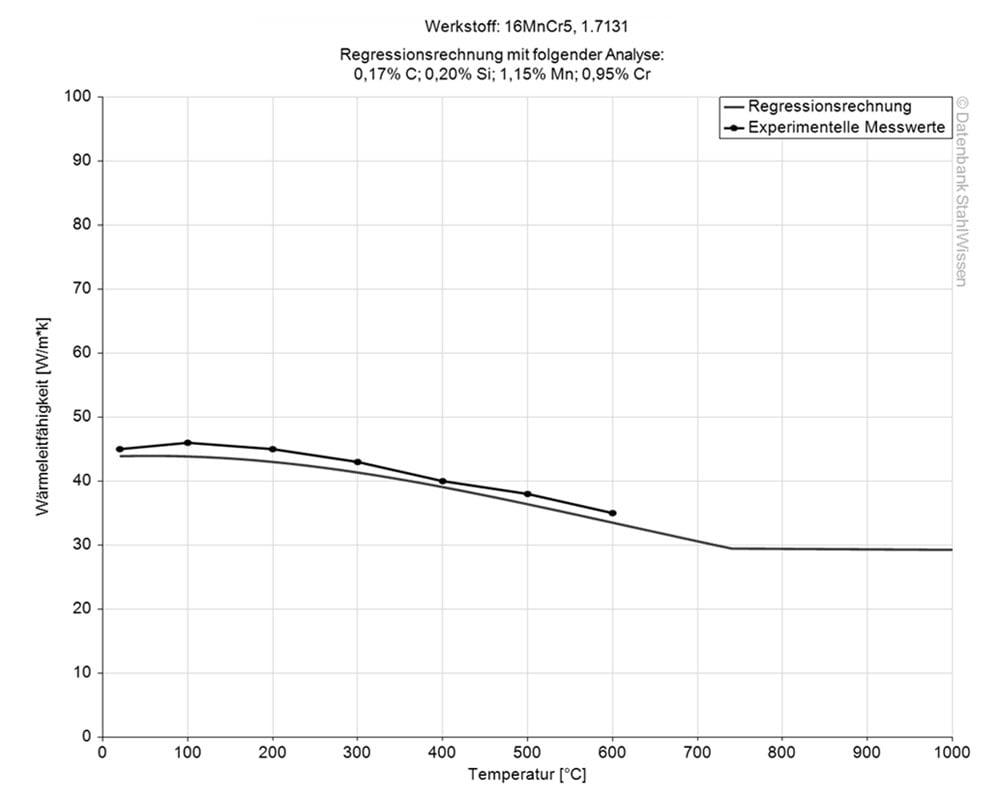
The heat conductivity for 5115 is at 44 W/(m*K) (25440 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
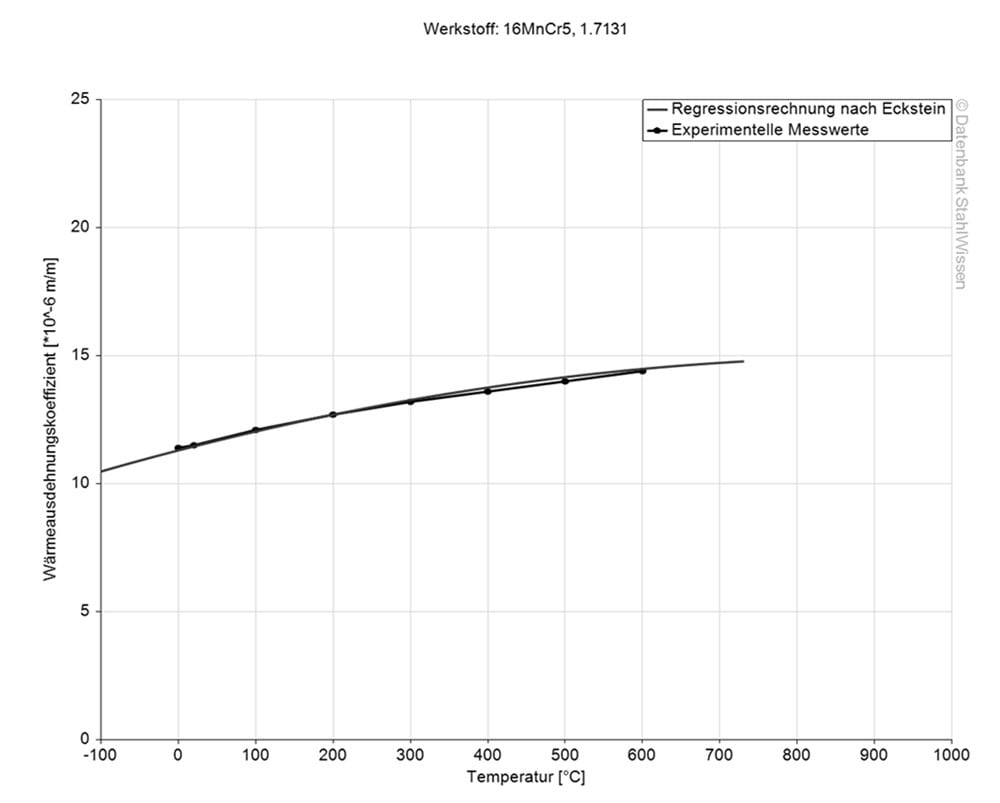
The following table shows expansion or contraction at various temperatures, which may be very important for high temperature works or when working with high temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
11.5 | 68 - 212°F |
12.5 | 68 - 392°F |
13.3 | 68 - 572°F |
13.9 | 68 - 752°F |
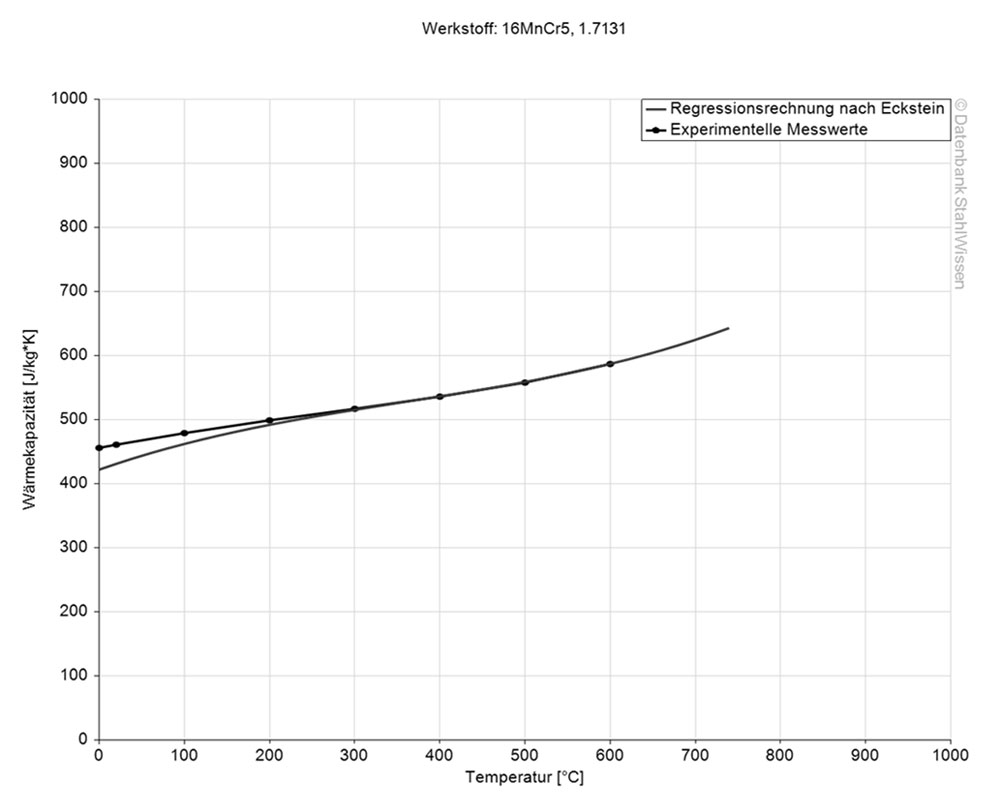
The specific heat conductivity for this steel grade is 0.470J/g-°C (0.112BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.

SHARPLY CALCULATED PRICES FOR PREMIUM-CUSTOMERS!


5115 PROCEDURE
Heat the material uniformly to a temperature of 1202 - 1292°F (650 - 700°C) and soak for 2 - 5 hours. Cool slowly in the furnace followed by further cooling in air.
Heat the parts uniformly to a temperature of 1562 - 1616°F (850 - 880°C), then cool in air.
Cooling the material fast will refine the grain structure and give it a more even and fine pearlitic structure. This improved structure improves the AISI 5115 steel's mechanical properties.
Heat to a curing temperature of 1490-1544°F (810-840°C) and quench the material in oil or water (water is being used for simple shaped large components only) to a temperature of 320-482°F (160-250°C).
Heat to a curing temperature of 1436-1508°F (780-820°C) and quench the material in oil or water (water is being used for simple shaped large components only) to a temperature of 320-482°F (160-250°C). After this process the material/parts have a hard, wear resistant surface layer with a relatively tough core which is able to absorb impact stresses without breaking.
Quenching, the 5115 case hardening steel, achieves the desired properties for this grade. Typically oil is used as the quenching medium, it provides a cooling rate that may help to reduce cracking and warping.
-
Oil
-
Water (for simple shaped larger components)
-
Salt bath
Temper parts for 1 hour per 25/32 inch (20 mm) of thickness but a minimum of 2 hours at a temperature of 302-392°F (150-200°C). The tempering temperature depends on the desired strength. The higher the tempering temperature the softer hardened steel turns. To avoid cracking, tempering should be done as soon as possible after hardening.
The 5115 can be treated in sub-zero temperatures. This will increase the hardness and wear resistance by transforming left austenite to martensite. This treatment might increase the risk of cracking and embrittlement if it is not done correctly and therefore the procedure should be done with the necessary care and consideration.
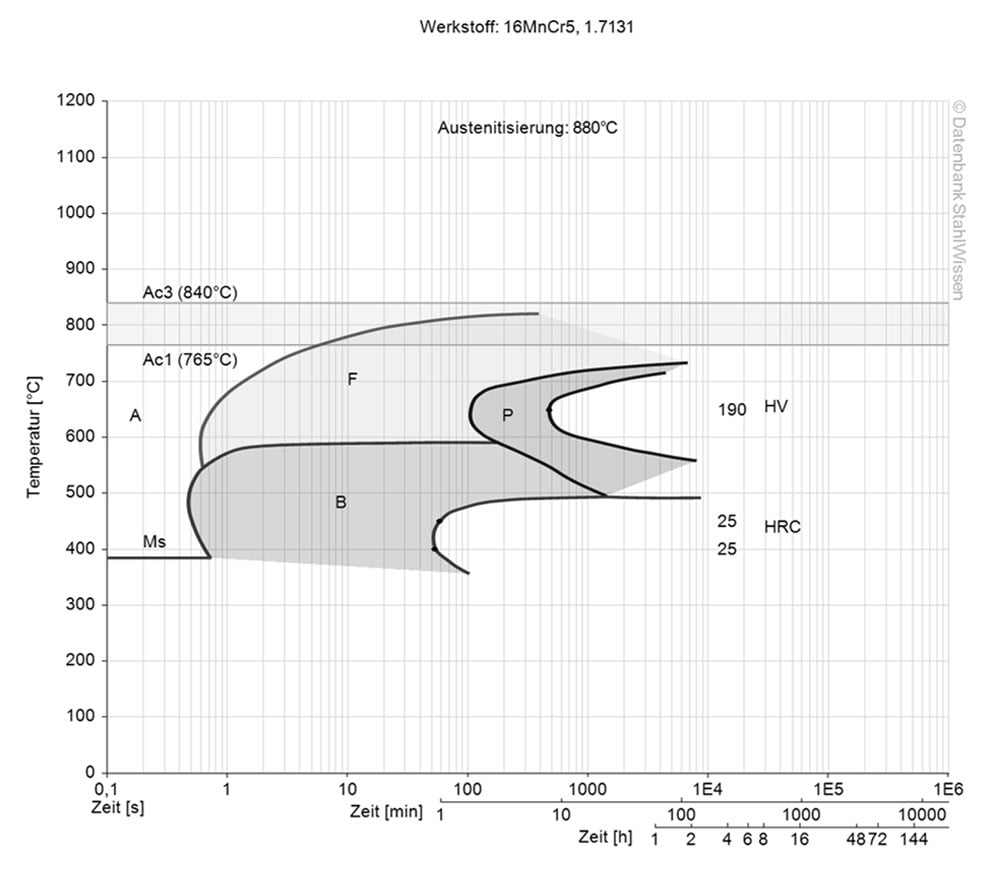
This diagram shows micro changes over time at different temperatures. Those are important during heat treatment as they show information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
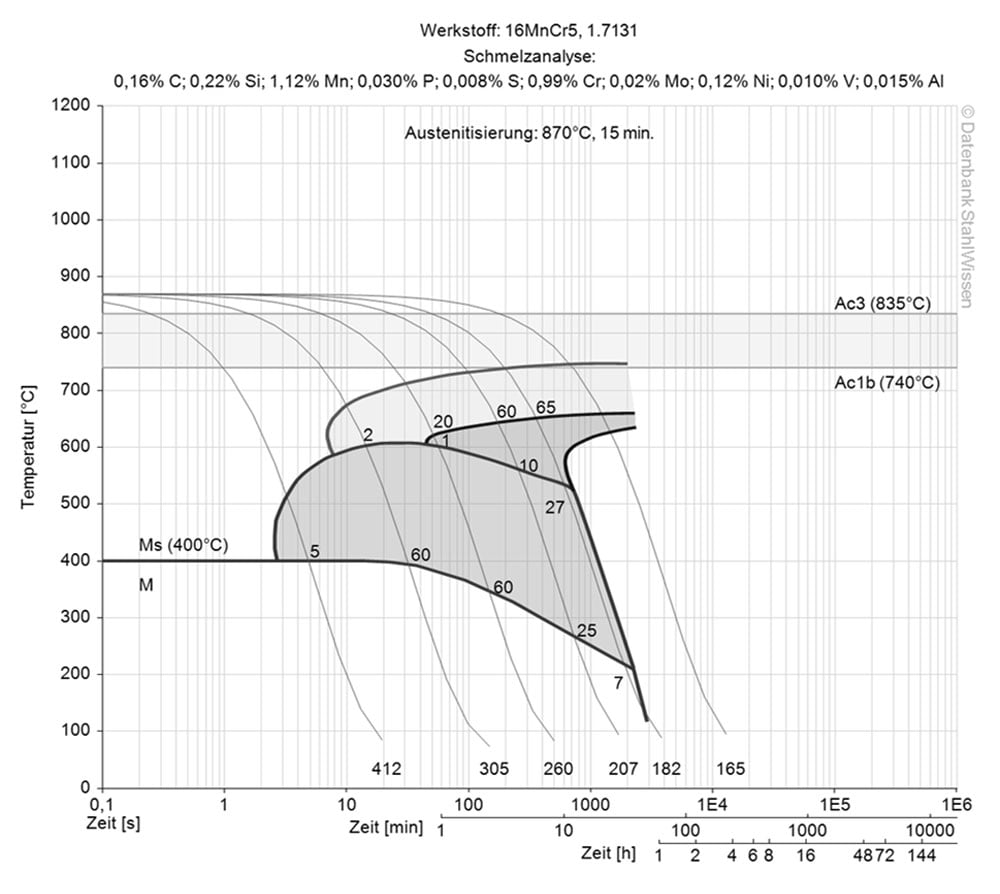
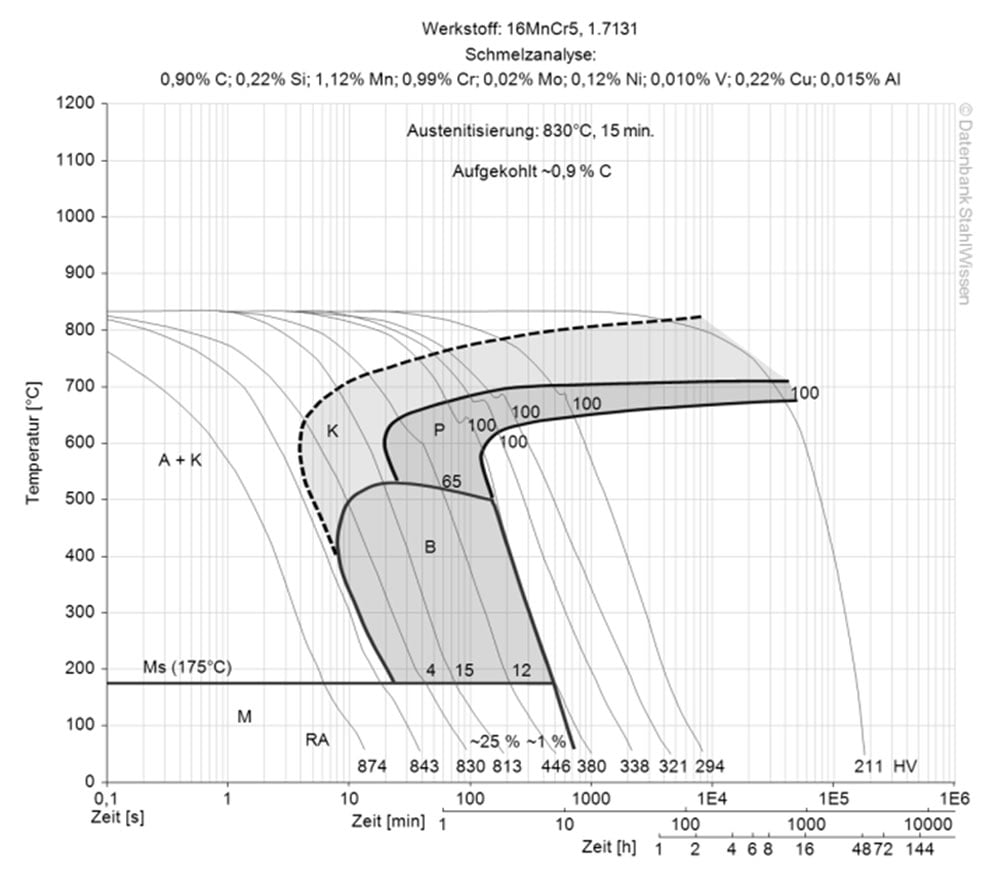
This diagram shows the structural changes at micro level over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperature and after what time different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite or bainite start to build.
5115 SURFACE TREATMENT
Nitriding introduces nitrogen into the surface of the material, this will give parts a harder surface but they will maintain a tough and ductile center.
As the 5115 will lose hardness, it is not usually nitrided in its hardened condition.
The material is heated to a temperature range of 1616-1796°F (880-980°C). To choose the right temperature it is important to consider the temperature, time, medium and equipment as well as the intended process and required microstructure. In general, carburizing takes place below 1742°F (950°C) during direct hardening. In special cases, carburizing temperatures up to 1832°F (1000°C) are used.
The parts are heated to the austenitic range and then the carbon and nitrogen diffused into the material. Carbonitriding will achieve a deeper case hardening depth compared to nitrocarburizing. This process increases the wear resistance and fatigue strength.
Nitrocarburizing also introduces carbon and nitrogen into the surface though in this process there is more nitrogen introduced than when carbonitriding. The case hardening depth is not as deep as for carbonitriding but it decreases corrosion and enhances appearance. Where carbonitriding may take a few hours to a few days, nitrocarburizing only takes a few hours.
5115 PROCESSING
Cold work and plastic mold steel (group of case hardening steel) with the objective of high surface hardness with core toughness. Excellent machinability, good cold hobbing and polishing properties. The tensile strength is a result of the combination of hardened surface and tough core.
EDM is used for parts made from one individual piece, for cutting dies or when making intricate shapes. There are various methods to erode various materials, some of them are for example wire erosion, spark erosion or die sink erosion.
Even if the 5115 is surface hardened EDM can be used on this material and gives the 5115 a smooth surface finish.
Based on the thermal coefficient expansion during heating and cooling phases are predictable. As this is a physical change the material will revert back to its former state.
Carburization, stress relief distortion, decarburization and phase changes may also lead to dimensional changes. To minimize or prevent these changes pre heating or post heating treatments should be considered as well as a controlled atmosphere during heat treatment.
Forging should be done at a temperature range of 2102-1562°F (1150-850°C). Overheating can result in grain growth and reduce mechanical properties. Do not let the forging temperature drop below 1562°F (850°C). Slowly cool the parts down to avoid possible stresses and unwanted microstructures.
5115 has limited weldability and should only be done before the heat treatment. Preheat the part to 482-662°F (250-350°C), post heat treatment is based on the heat treatment of the base metal.
5115 APPLICATION OPTIONS
The 5115 case hardening steel is often used in the automotive industry but also for bearings, gears, machine parts, fasteners and many more. It can withstand stress and wear due to the hard surface and tough core.
• Jig construction
• Plant engineering
• Apparatus Engineering
• Plastic processing
• Synthetic resin molds
• Base plates
• Bending bars
• Guide columns

5115 CONCLUSION
5115 is a cold work and plastic mold steel that belongs to the group of case-hardening steels. It is often used as a surface hardener for mechanically stressed parts, but can also be through-hardened.
- Case-hardening steel
- Plastic mold steel
- Cold work steel
- Good machinability
- Good cold sinkability
- Good polishability
- Surface hardenability
- Through hardenability
- Hard surface, tough core → good structural tensile strength
- Erodible
- Nitridable
- Etchable
We offer this steel as Metric 5115 Precision Ground Flat Stock and 5115 Flat Stock.

5115 ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
5115 DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

