P20+Ni Tool Steel - ~1.2738 - ~40CrMnNiMo8-6-4 - Properties

P20+Ni Tool Steel - ~1.2738 - ~40CrMnNiMo8-6-4 - Properties
Back to Steel Overview
P20+Ni STEEL PRICE CHART
P20+Ni STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
Ni
~40CrMnNiMo8-6-4
32 HRC (delivery condition, quenched and tempered) - 50 HRC
max. 325 HB
~40CrMnNiMo8-6-4
32 HRC (delivery condition, quenched and tempered) - 50 HRC
max. 325 HB

P20+Ni PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
The P20+Ni is a plastic mold steel due to its good machinability and excellent polishability. The added nickel in this tool steel grade ensures a more uniform hardness throughout the material. P20+Ni can be used in a wide variety of applications as it has a good balance of hardness and toughness which gives it an advantage resisting cracking and breaking when used for impact applications or applications that will apply high stresses.
To be classed as a stainless steel the material has to have a mass fraction of a minimum of 10.5% of chromium. The P20+Ni has a mass fraction of 1.8 - 2.1% of chromium and can therefore not be classed as stainless steel.
Tool steel P20+Ni has some corrosion resistance though to be fully corrosion resistant the material needs to have a mass fraction of a minimum of 10.5% which the P20+Ni does not have with a chromium content of 1.8 - 21%.
P20+Ni is a ferromagnetic steel that can be magnetized, due to the nickel content the magnetizability can be slightly reduced.
The wear resistance for tool steel P20+Ni is 3 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
P20+Ni TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
P20+Ni can be used for knife making as it has a good balance of toughness and hardness, good wear resistance and is good to machine. Knives made from P20+Ni can withstand impact, do not easily chip, have good edge retention and can be sharpened relatively easy. Knives made from this material should receive additional surface treatment or coating to prevent rusting when used in a corrosive or wet environment.
The working hardness for the P20+Ni is in the range of 300 BHN (delivery condition, quenched and tempered) - 469 BHN (32 HRC (delivery condition, quenched and tempered) - 50 HRC).
Typically the density of P20 tool steel is 0.281 lb/in3 (7.80g/cm3) at room temperature.
Tool steel P20+Ni has a tensile strength of approx. 159.5 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
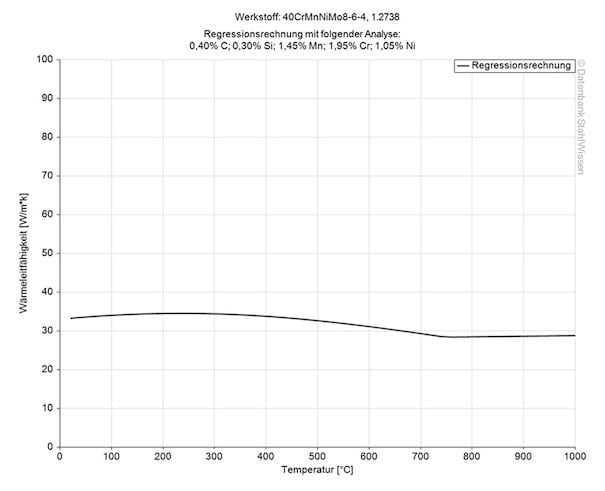
The heat conductivity for P20+Ni is at 34.5 W/(m*K) (239 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
34.5 | 68°F |
33.5 | 662°F |
32.0 | 1292°F |
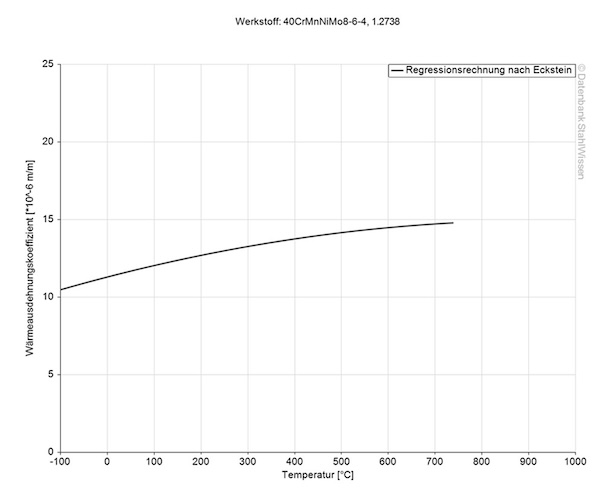
This diagram shows how much tool steel P20+Ni might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
11.1 | 68 - 212°F |
12.9 | 68 - 392°F |
13.4 | 68 - 572°F |
13.8 | 68 - 752°F |
14.2 | 68 - 932°F |
14.6 | 68 - 1112°F |
14.9 | 68 - 1292°F |
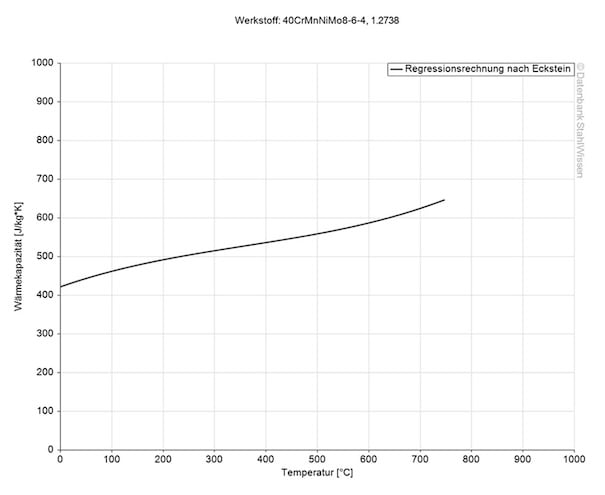
The specific heat capacity of tool steel at room temperature is 460 J/g-°C (0.109 BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.

PRECISION!


P20+Ni PROCEDURE
As this steel grade comes quenched and tempered, heat treatment is usually not required. Should a higher hardness or rehardening be required, please follow the steps below. The goal of the heat treatment is to increase hardness and wear resistance, the process should be executed with care as not to introduce or reintroduce stresses or other defects.
Heat the parts to the temperature of 1310 - 1364°F (710 - 740°C) and hold for 2 - 5 hours. Holding time is generally approx. 1 hour per 1 inch (25.4 mm). Then slowly cool the parts in the furnace by 50 - 68°F (10 - 20°C) per hour to 1112°F (600°C). From there further cool down in air.
Heat the workpiece uniformly to a temperature of 1022 - 1112°F (550 - 600°C) , hold for 1 - 2 hours in a neutral atmosphere and cool slowly in the furnace. Slowly cooling the workpieces can prevent the reintroduction of stresses in the workpieces. Stress relieving can help to maintain its dimensional stability and enhance tool life.
Heat the material uniformly to a temperature of 1544 - 1598°F (840 - 870°C), soak for 15 - 30 minutes, then quench.
This plastic mold steel can be flame or induction hardened to reduce surface damage and is able to reach a hardness of approx. 469 BHN (50 HRC).
Flame hardening should be carried out after rough machining and should be evenly done as uneven heating may cause warping or cracking.
Induction hardening is a more controlled, faster and deeper hardening compared to flame hardening.
It is recommended to temper tool steel P20+Ni after flame or induction hardening as shown above under the topic “Tempering”. To achieve the best results and to maintain the entirety of offered properties these processes should be controlled and properly executed.
Quenching tool steel P20+Ni will transform austenite back to martensite which is a very brittle phase and the P20+Ni should be tempered after quenching to relieve stresses and reduce brittleness.
• Polymer
• Oil
Choose the appropriate tempering temperature and slowly heat to that temperature immediately after hardening. Hold for one hour per inch (25.4 mm) thickness but for a minimum of at least 2 hours, then cool in air.
Choosing the right tempering temperature will determine the balance of hardness and toughness. When a higher temperature is applied it will give the workpieces a greater toughness but will lower the hardness of it.
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
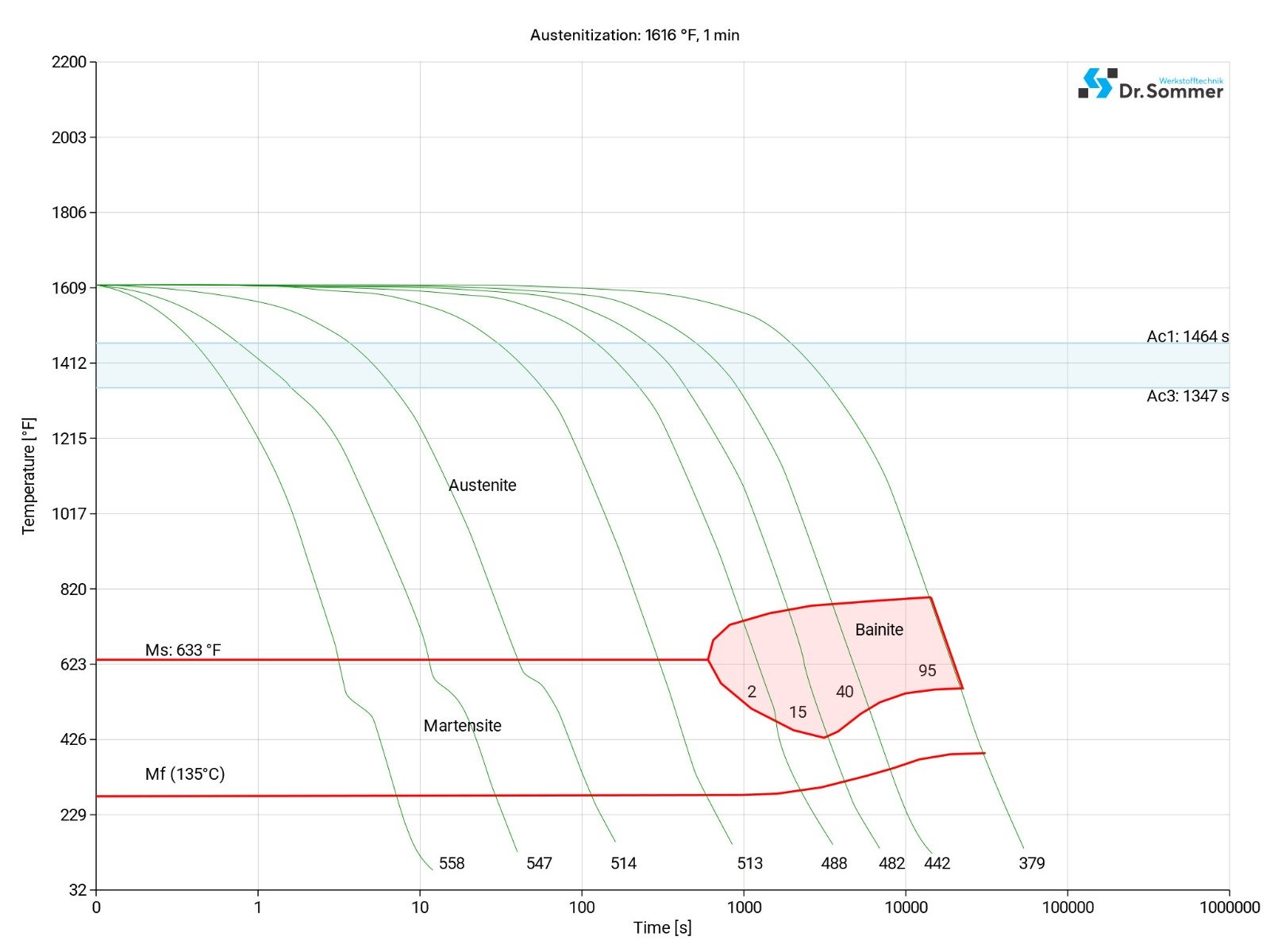
P20+Ni SURFACE TREATMENT
Following are a few examples for surface treatments for tool steel P20+Ni.
P20+Ni can subsequently be nitrated to increase the surface hardness and resistance to wear and erosion, as well, nitriding the surface increases corrosion resistance. In order to nitrate the material, it should be rough machined, stress relieved and ground before it is nitrated.
This steel grade is suitable to be chrome plated. Temper the material after hard plating at a temperature of 350°F (180°C) for approx. 4 hours. To avoid hydrogen embrittlement tempering should be done within 4 hours of plating.
P20+Ni has a good polishability in the delivered condition (quenched and tempered). Care should be taken not to over polish the parts with high pressure and a too long polishing time may lead to unwanted defects like discoloration, orange peel or pitting. Preparation is very important as well, tools and parts should be dust free and paste should be added to the tool for manual polishing or the parts if using machine polishing. If the material is not prepared to be dust free, particles can enter the surface during polishing and can cause pitting and/or scratches on the surface. Scratches and pitting can in turn be the entry point of moisture resulting in corrosion over time.
P20+Ni PROCESSING
P20+Ni is easy to machine and it can achieve a great surface finish. Cutting speeds and feeds should be considered due to hardness of the material and coolants should be used to reduce overheating and tool wear.
Dimensional changes can occur during rapid heating and cooling, stress relieving, machining and welding. All those processes should be done with care, control and evenly to prevent warping and distortion.
P20+Ni can be welded using all conventional methods. Preheat the material to a temperature of 600 - 700°F (316 - 371°C). Do not drop the welding temperature below 600°F (316°C). Fillers should be matched to the hardness of the base metal. Cool slowly to 100 - 150°F, then post heat to a temperature of 1000°F (538°C) for one hour per inch (25.4 mm) per weld depth and do not exceed 1050°F (566°C) as this will result in losing hardness. Double temper if possible.
P20+Ni APPLICATION OPTIONS
Its increased hardness, wear resistance, edge stability, good machinability and excellent polisability make the P20+Ni a good choice for molds and dies and high precision tooling. P20+Ni has a longer service life with its uniform strength and high toughness.
• Plastic molds
• Molding frames
• Die casting molds
• Dies
• Forging tools
• Metal extrusion tools
• Tube presses
• Hydroforming tools

P20+Ni CONCLUSION
P20+Ni has a good combination of properties giving it the right blend of hardness, toughness and machinability. These properties make the P20+Ni a great choice for molds and precision tools.
- Tool steel (pre-tempered)
- Focus on plastic mold construction
- Better through-hardenability due to nickel addition
- Low sulphur
- Good polishability
- Grainable
- Hard chromium platable
We offer this steel as P20+Ni Flat Stock.

P20+Ni ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
P20+Ni DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

