HSS M2 High Speed Steel - 1.3343 - HS6-5-2C - JIS ~SKH 51

HSS M2 High Speed Steel - 1.3343 - HS6-5-2C - JIS ~SKH 51
Back to Steel Overview
HSS M2 STEEL PRICE CHART
HSS M2 STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
W
HS6-5-2C
62 HRC - 65 HRC
max. 270 HB
HS6-5-2C
62 HRC - 65 HRC
max. 270 HB

HSS M2 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
HSS M2, one of the most used high speed steel, is suitable for cold forming tools e.g. cold extrusion rams, its elevated wear resistance makes it suitable for e.g. plastic molds and can also be used for certain hot work applications. The added tungsten and molybdenum give this high speed steel the excellent combination of toughness, wear resistance, red hot hardness and the good edge retention, which make it suitable to a wide variety of applications.
HSS M2 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Typically the density of High Speed Steel M2 is 0.293 lb/in3 (8.12g/cm3) at room temperature.
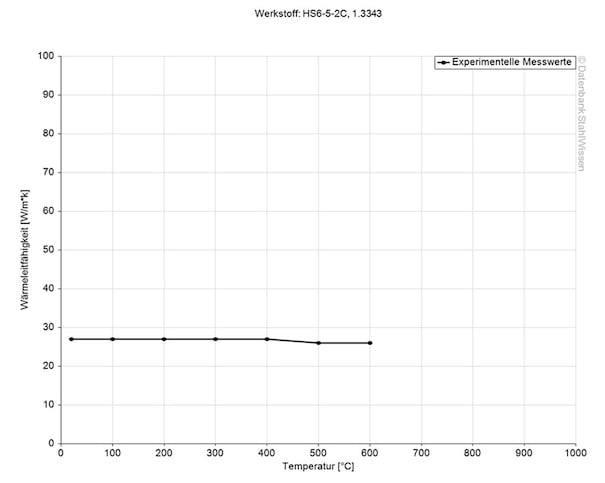
The heat conductivity for HSS M2 is at 32.8 W/(m*K) (227 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
32.8 | 68°F |
23.5 | 662°F |
25.5 | 1292°F |
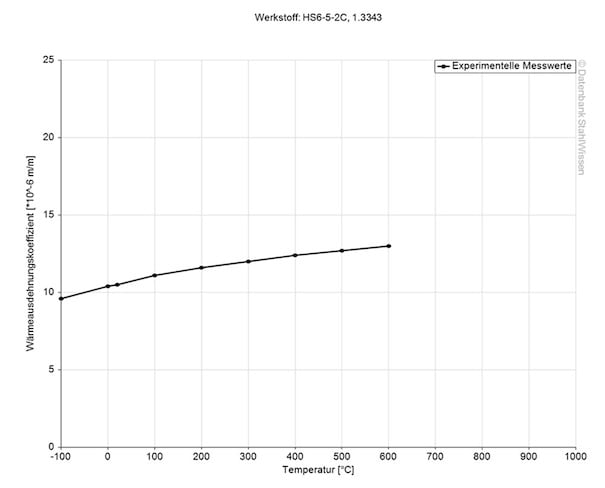
This diagram shows how much the HSS M2 might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.8 | 68 - 212°F |
11.8 | 68 - 392°F |
12.0 | 68 - 572°F |
12.5 | 68 - 752°F |
The following table shows the electrical resistivity of HSS M2.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.524 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |
0.581 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 212°F |
0.664 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 392°F |
0.751 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 572°F |

M2 AS $MART FLAT STOCK OR DRILL ROD.


HSS M2 PROCEDURE
- • Salt bath – quench to a temperature of 1000 - 1100°F (538 - 593°C), then cool further to 150°F (66°C). After the quench the material has to be tempered immediately.
- • Vacuum – quench to a temperature below 1000°F (538°C) at a rate of 50°F (10°C), then cool to ambient temperature.
- • Air
Sub-Zero treatment can have many advantages like increased wear resistance, increased hardness, enhanced dimensional stability, refined microstructure and stress relief. It can bring some disadvantages like brittleness and when not done correctly cracking due to thermal shock too. The process should be carefully considered and controlled to receive the best possible outcome.
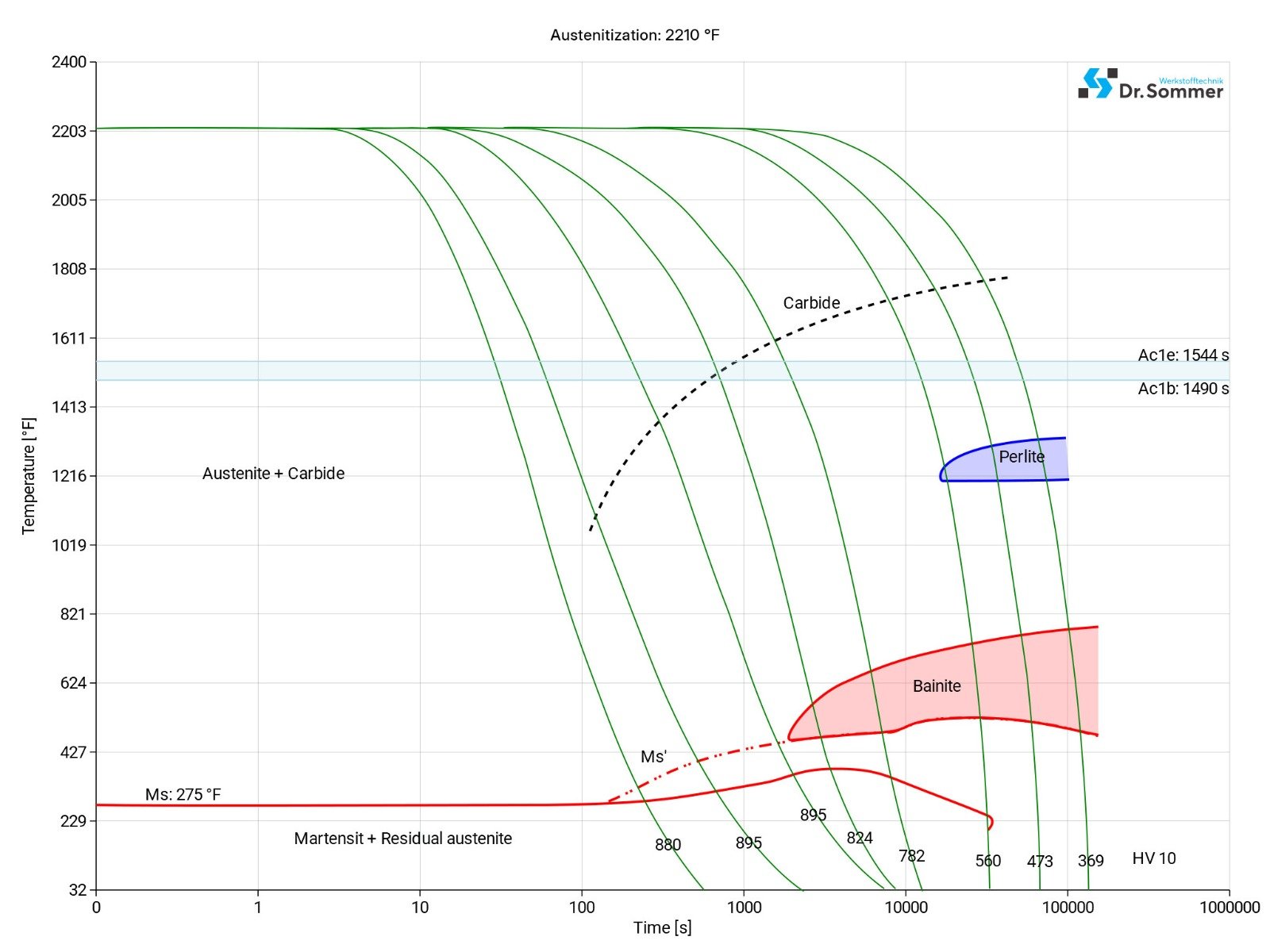
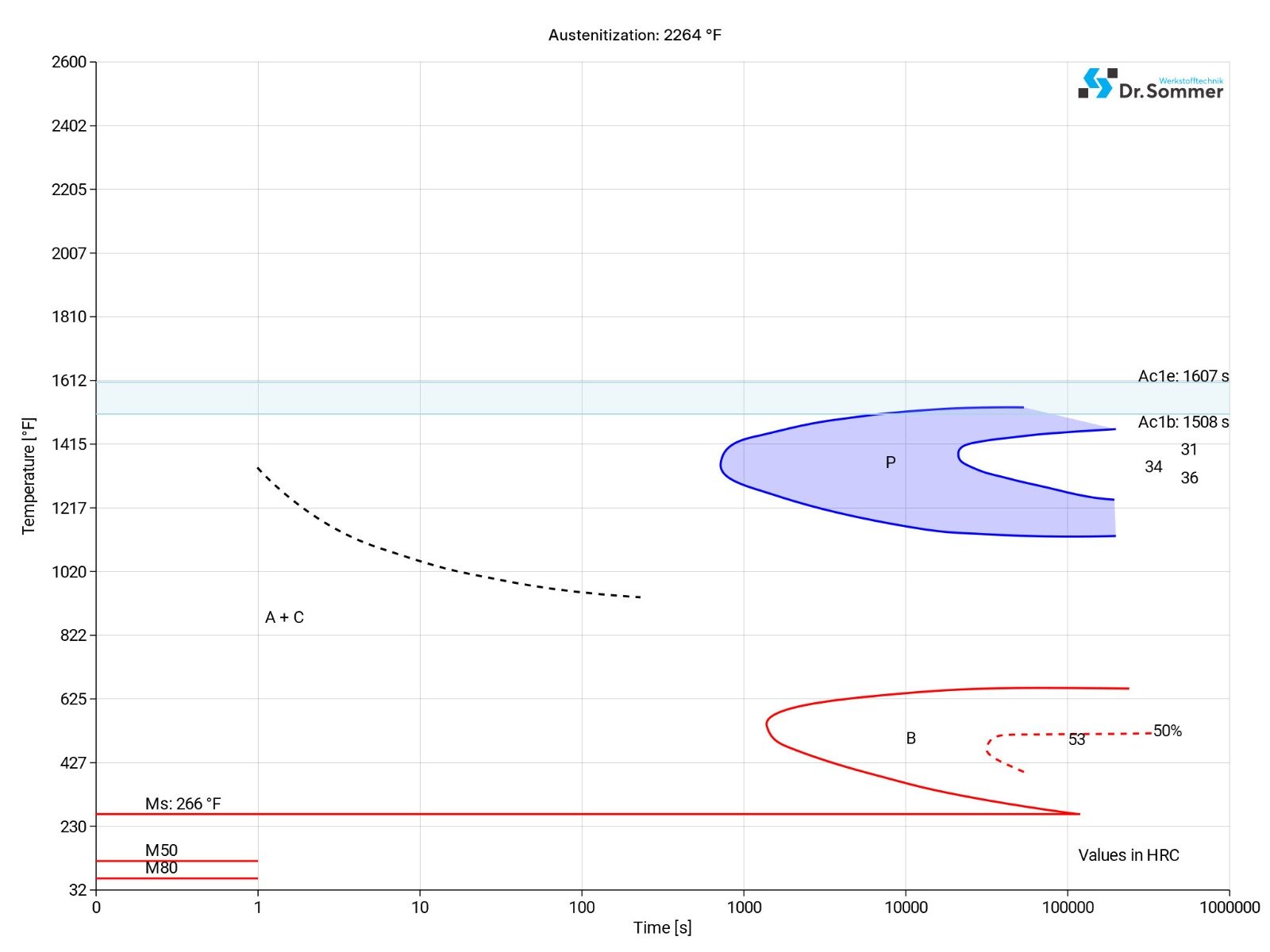
HSS M2 SURFACE TREATMENT
The choice of surface treatment should always take in consideration which application it will be used for and if it will benefit this. Following are a few examples for surface treatments and their benefits for High Speed Steel M2.
Different coatings, applying a thin layer onto the surface of the material, like TiN (Titanium Nitride), TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride), AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) or Diamond coating can enhance surface hardness, wear resistance, prolong tool life and reduce friction.
Chrome plating puts a thin layer of chrome onto the surface often used for aesthetic reasons but also to enhance wear resistance, strength and corrosion resistance.
HSS M2 PROCESSING
In its annealed condition, M2 is considered a “medium” machinability steel with poor grindability capabilities.
EDM is used for parts made from one individual piece, for cutting dies or when making intricate shapes. As a non contact, thermal energy based machining process it can be used for hard materials like the M2. Electrodes, surface finish and heat affected zones should be considered before EDM is used for this material grade. Afterwards the material should be checked thoroughly as due to thermal stresses micro cracks might occur in the heat affected zones which might, undetected, lead to tool or part failure.
Chrome plating puts a thin layer of chrome onto the surface often used for aesthetic reasons but also to enhance wear resistance, strength and corrosion resistance.
Preheat the material slowly to 1562 - 1652°F (850 - 900°C) and then continue to increase the temperature more quickly to the forging temperature of 1922 - 2102°F (1050 - 1150°C). Do not let the temperature drop below 1616 - 1652°F (880 - 900°C) and larger parts can be cooled slowly in the furnace when finished forging. Small and uncomplicated forgings can be cooled in lime or ashes.
Note, this is not an annealing, when cooled down properly, the parts should be annealed.
HSS M2 APPLICATION OPTIONS
High Speed Steel a high alloyed tool steel, often used for drills, taps, turning tools and broaches, has a 3 - 4 times higher cutting speed without losing its hardness up to a temperature of 1112°F (600°C).
In comparison, ordinary cold work tool steel loses its hardness at about 392°F (200°C). The foundation for its abilities can be found in its alloys as well as its martensitic microstructure.
• Milling cutters
• Twist drills
• Screw taps
• Reamers
• Broaching tools
• Rotary knives
• Planer knives
• Gear shaper cutters
• Circular saw segments
• Metal saws
• Woodworking tools
• Screw dies
• Countersinks
• Chasers
• Cold extrusion punches
• Precision cutting tools
• Dies
• Punches
• Plastic molds with high wear resistance

HSS M2 CONCLUSION
HSS M2 is ideal to use for high speed and high wear applications. It has great wear resistance, high impact toughness and good compression strength. Care has to be taken when the material is EDM’ed or welded as these processes can lead to brittleness in those areas and can lead to entry points for rust as well as weak spots where the material can crack. With a good surface treatment the material can be made even harder on the surface as well as reduce friction which is needed when using the material for example for taps or drills. With the right maintenance and use this material can be used for a large variety of applications.
Practically, this means:
- High wear resistance
- High impact strength
- Good compressive strength
- High heat resistance
- Good edge strength
- Nitridable
- Can be eroded, but caution is advised
- Working hardness is 62 - 65 HRC
We offer this steel as M2 Flat Stock and M2 Drill Rods.

HSSS M2 ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
HSS M2 DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

