S7 Tool Steel - DIN 1.2357 - 50CrMoV13-1 - Shock Resisting

S7 Tool Steel - DIN 1.2357 - 50CrMoV13-1 - Shock Resisting
Back to Steel Overview
S7 STEEL PRICE CHART
S7 STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
50CrMoV13-1
56 HRC - 60 HRC
max. 225 HB
50CrMoV13-1
56 HRC - 60 HRC
max. 225 HB

S7 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
S7 is an air hardening tool steel. The medium carbon content combined with moderate amounts of chromium and molybdenum provide the excellent properties, which make this steel grade suitable for applications where shock resistance, easy machining as well as medium hot work properties are important.
The excellent resistance to deformation during air hardening as well as the easiness of heat treatment are further advantages of this material. As its properties are well balanced the S7 is suitable for both hot and cold work, though is more often used for cold work.
To enhance the corrosion resistance the surface can additionally be treated or coated by nitriding or black oxide.
As for all steels, regular maintenance, applying a protective coating, and keeping the tools in dry and clean conditions can give them a longer life span.
S7 can be used for hot work applications involving high impact and shock. For hot work tools, temper in the high range up to 1000°F (538°C) but make sure the working temperature of the tool does not exceed 1000°F (538°C).
S7 can be used for cold work tools like shear blades, punches and chisels and other tools requiring high shock resistance.
S7 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Typically the density of S7 tool steel is 0.282 lb/in3 (7.8g/cm3) at room temperature.
The heat conductivity for the S7 is at 31.0 W/(m*K) (215 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
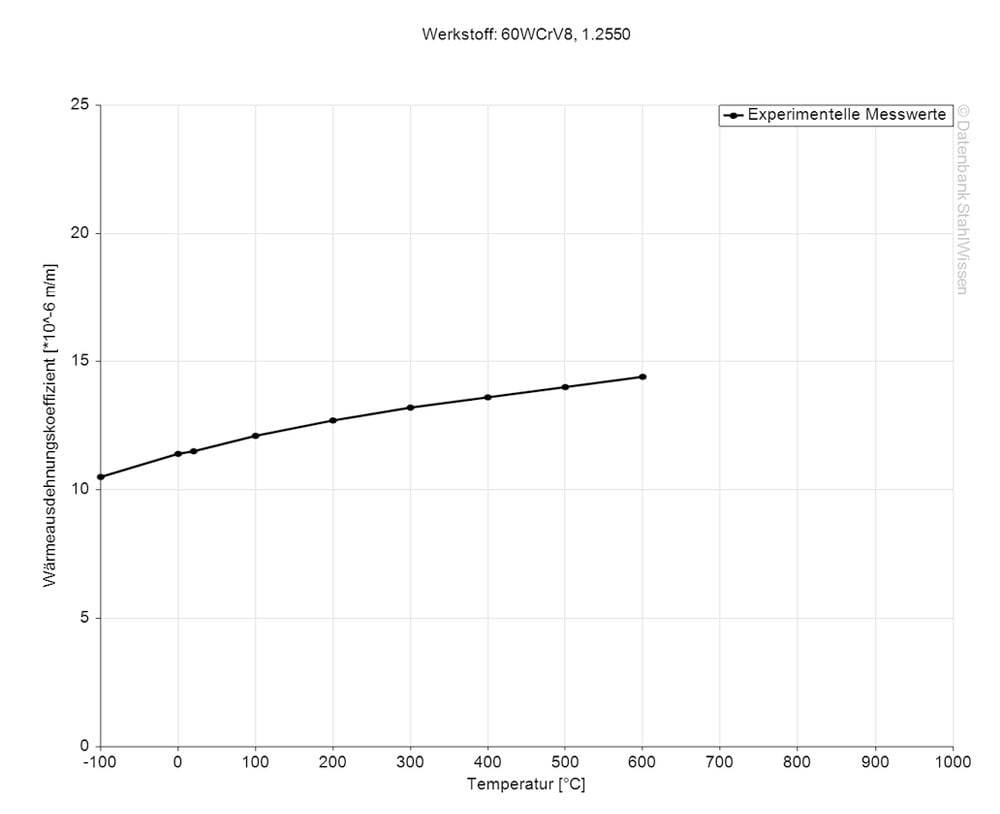
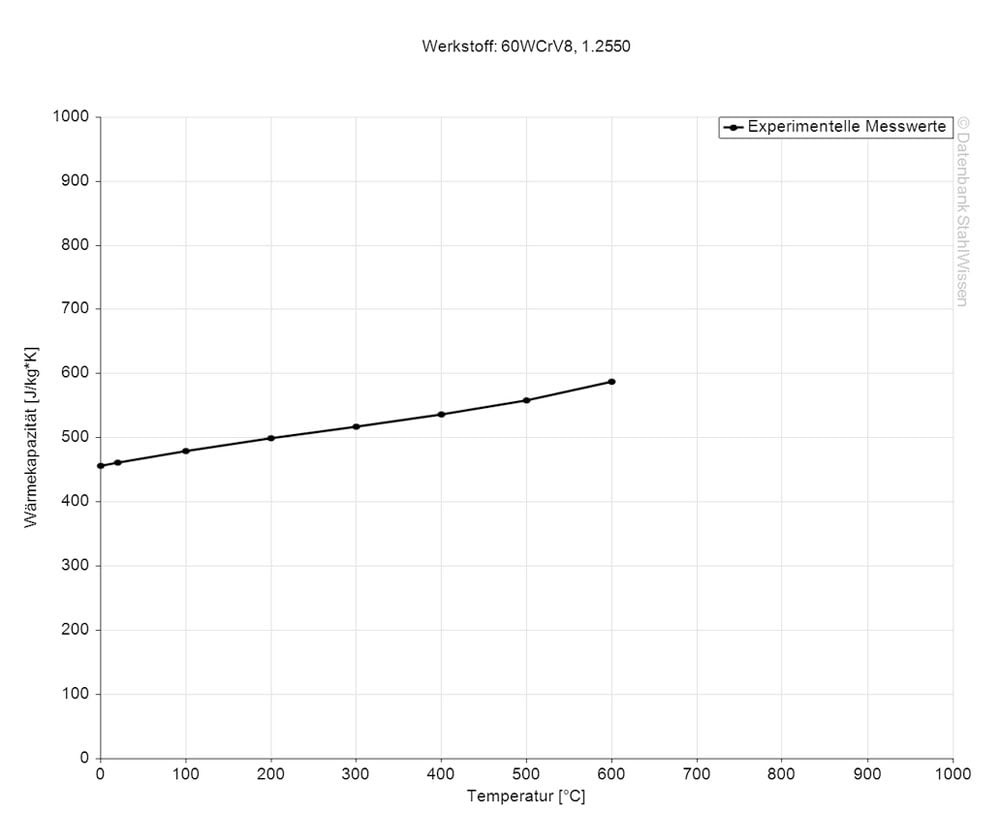
The specific heat capacity of the S7 tool steel at room temperature is 0.460J/g-°C (0.110BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.

ABRAMS STEEL – QUALITY THAT WILL IMPRESS YOU!


S7 PROCEDURE
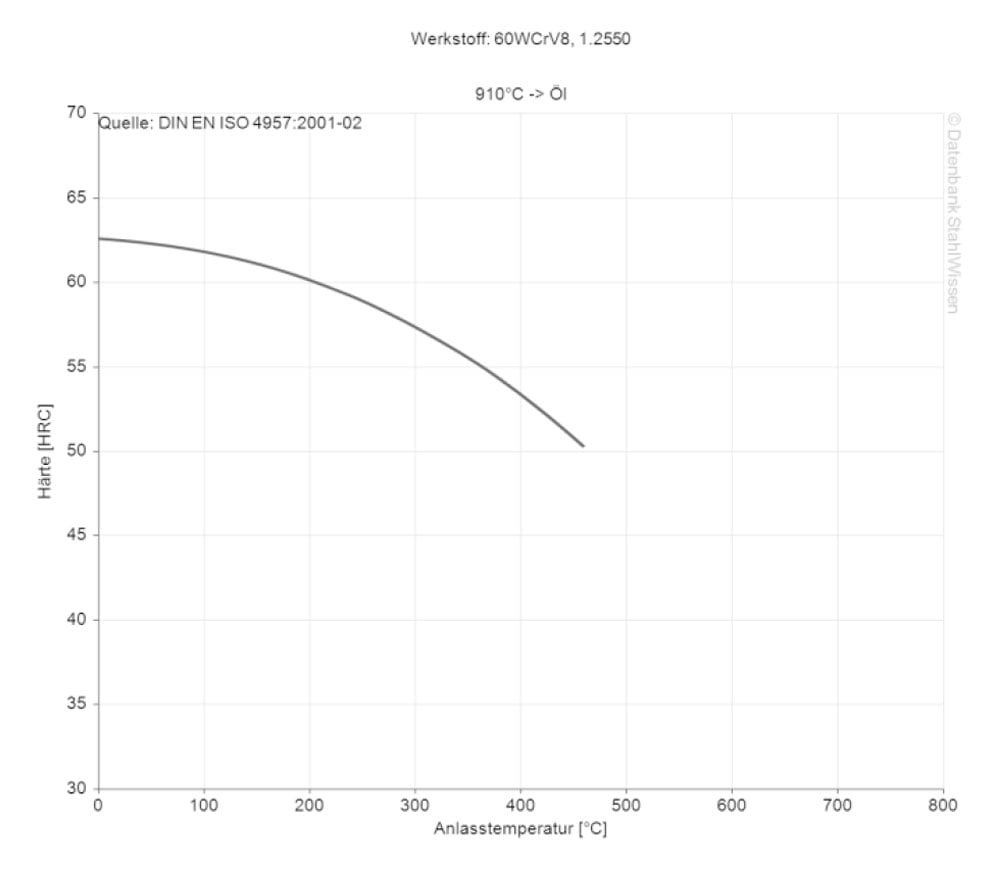
As a classic air hardening steel the S7 is for most applications quenched in air.
• Air (this method should be used for parts under 2 inches (50.8 mm) max. thickness)
• Dry lime or ash, for larger pieces and more uniform cooling
• Oil (temper as soon as a temperature of 120 - 150°F (49 - 66°C) has been reached)
To use S7 for cold work applications, temper the parts at a temperature of 400 - 500°F (204 - 260°C), hold the temperature for 11/2 to 2 hours and then cool to ambient temperature and temper a 2nd time.
For hot work applications, heat the material to a temperature of 900 - 1000°F (482 - 538°C), then hold the temperature for 11/2 to 2 hours and cool to ambient temperature. As before it is recommended to temper the parts a second time.
Sub-zero treating the S7 tool steel will enhance its wear resistance, dimensional stability and the transformation of retained austenite to martensite.
After the first temper, cool the material to approx. -100°F (-73°C) and hold depending on size and thickness for 2 - 4 hours. Then let the parts warm up to room temperature and follow up with another tempering cycle to relieve any stresses from the sub-zero treatment and to optimize its mechanical properties.
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
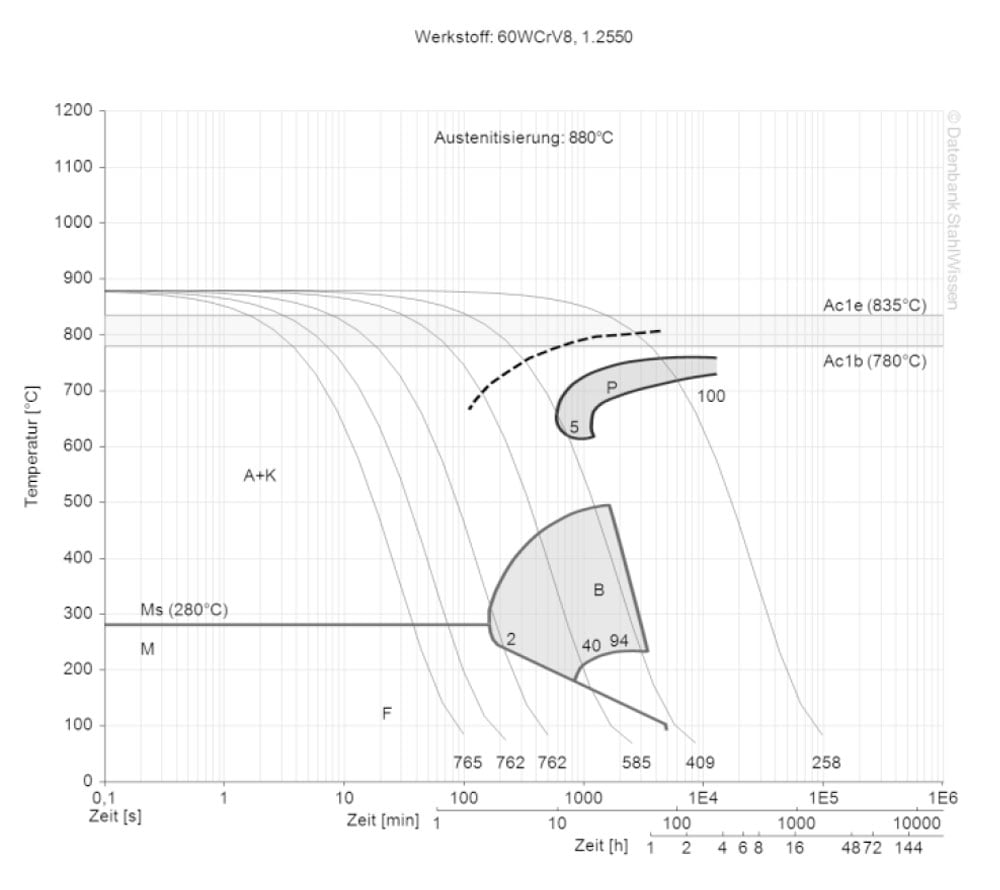
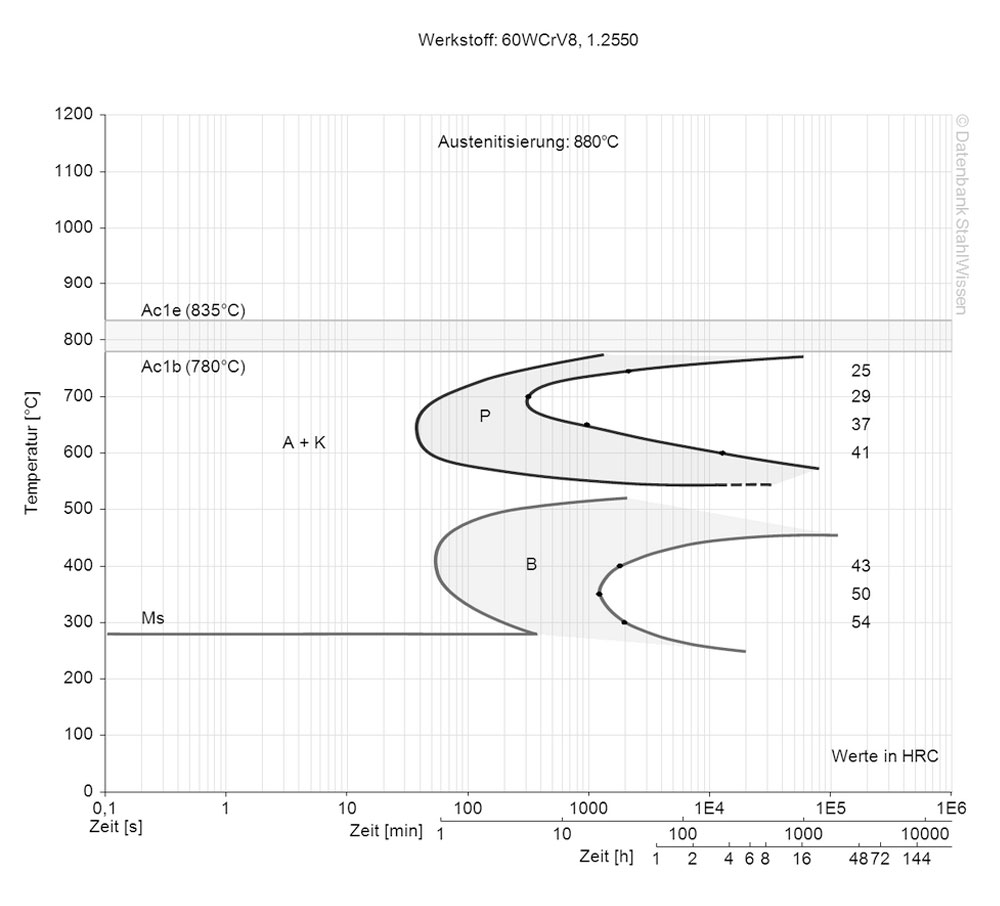
The following diagram shows the structural changes at micro levels over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperatures the different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite and bainite start to form.
S7 SURFACE TREATMENT
Following are a few examples of surface treatments that can be applied to the S7.
It solidifies the material and makes the surface more resistant which can prevent fatigue and stress corrosion failure and can also optimize the form and weight of the parts.
Note:
Protective gear like goggles, masks, helmets, gloves and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
Appropriate guards to prevent shot spillage should be in place, equipment regularly maintained and shot should be free from contaminants.
S7 PROCESSING
In the annealed condition S7 is comparatively easy to machine. It can work harden which affects sharpness and also makes machining more challenging.
EDM can be a very effective method to create intricate shapes, small details and complex geometries that may be challenging to normal machining due to its hardness and potential work hardening, especially after heat treatment of the St7 tool steel.
Using the correct electrodes and machining parameters is important to achieve the needed surface finish.
Heat affected zones might require an additional heat treatment or tempering to lessen the localized changes in hardness and microstructure.
After the EDM process the recast layer, a thin white layer, should be removed.
Cool small forgings in lime, ashes, or other insulating materials. Large forgings should be placed in the furnace which is heated to approx. 1400°F (760°C) and soaked until the parts are uniformly heated through. Finish the process by shutting the furnace off and let the forgings cool down slowly.
Note: This is not an annealing. The forgings should be annealed after forging, for that please see “Annealing” above.
To weld the S7 tool steel it is recommended to uniformly preheat the part to reduce the risk of cracking.
The filler should be similar to the base material and heat input controlled to avoid distortion and excessive grain growth in the heat affected zone.
To finish the process off it should be considered to give the parts a post weld heat treatment to restore its former/wanted properties.
S7 APPLICATION OPTIONS
This tool steel is a general purpose air hardening grade having high impact and shock resistance. It has also a good resistance to softening at moderrately high temperatures. This combination of properties makes it suitable for many hot-work and cold-work applications.
• Cutting tools
• Cold forming and bending dies
• Plastic molding dies
• Shear blades
• Chisels
• Rivet sets
• Punches
• Driver bolts

S7 CONCLUSION
The S7 has exceptional toughness and strength and is often used for punches, chisels, plastic molds, compression molds, jackhammers, forge dies, tool holders, and aircraft landing gear components.
As an air hardening steel it has, in comparison to water and oil hardening steels, less risk of distortion or warping.
We offer this steel as S7 Flat Stock, S7 Round Bars Decarb Free and S7 Drill Rods.

S7 ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
S7 DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

