440B Stainless Steel - 1.4112 - X90CrMoV18 - ~SUS 440B

440B Stainless Steel - 1.4112 - X90CrMoV18 - ~SUS 440B
Back to Steel Overview
440B STEEL PRICE CHART
440B STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
X90CrMoV18
53 HRC - 58 HRC
max. 265 HB
X90CrMoV18
53 HRC - 58 HRC
max. 265 HB

440B PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Stainless steel 440B is hardenable with a high chemical resistance, good polishability, good cutting edge retention and cutting performance. In some aspects the 440B exhibits similar behavior to tool steel. It is corrosion resistant in mild atmospheres, organic materials, mild acidic environments and fresh water steam
Yes, the 440B is a stainless steel with a mass fraction of chromium between 17 - 19%. It is part of the 400 Series Stainless Steel.
With a mass fraction of 17 - 19% of chromium the 440B is classed as corrosion resistant. Steel is classed as corrosion resistant with a minimum of 10.5% of chromium.
440B’s corrosion resistance is similar to stainless steel 410. It is resistant to a variety of petroleum products, organic materials, fresh water as well as steam. For the highest corrosion resistance all surfaces should be free of foreign particles, lubricants, other coatings, and scale. Parts should be cleaned and/or passivated after manufacturing.
Yes, the 440B belongs to the group of stainless steels that can be magnetized and is suitable for magnetic clamping
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high, the 440B scores a 6 for wear resistance.
Preheat the material to a temperature of 1400 - 1500°F (760 - 816°C), then heat slowly and uniformly to 1900 - 2150°F (1038 - 1777°C). Do not let the temperature drop below 1700°F (927°C) and reheat as and when necessary. Finish with cooling the material in the furnace, dry lime or ash and let the temperature of the workpiece drop to ambient temperature before annealing it.
440B has moderate cold formability, if annealed to maximum softness. As the material is sensitive to surface decarburization, it should be considered to use a protective atmosphere in heat treatments of finished workpieces.
440B TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
With a lower carbon content than others out of the 400 series of stainless steels the 440B can be sharpened very well as it is softer but will not hold an edge as well. However it still has a good balance of toughness, corrosion resistance and edge retention. Its corrosion resistance in wet and acidic environments makes it possible to make kitchen and dive knives out of the 440B.
The working hardness for the stainless steel 440B is at approx. 513 - 601 BHN (53 - 58 HRC).
Typically the density of 440B stainless steel is 0.278 lb/in3 (7.7g/cm3) at room temperature.
The tensile strength for stainless steel 440B is approx. 134.1 KSI (0.145KSI = 1MPa). This value is the result from a tensile test to show how much force is needed before the material starts to stretch or elongate before it breaks.
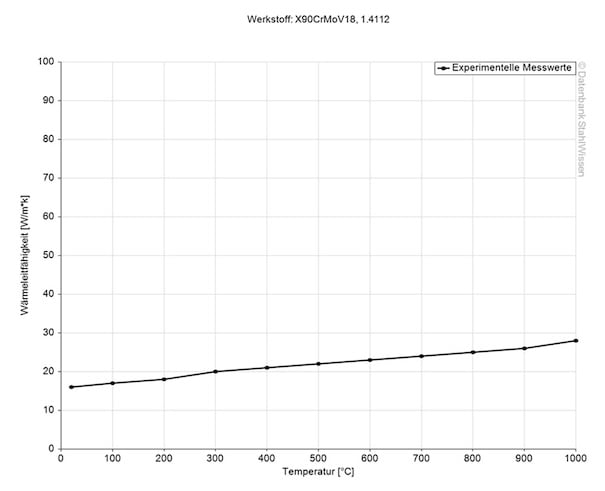
The heat conductivity for the 440B is at 15.9 W/(m*K) (110 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
15.9 | 68°F |
20.6 | 662°F |
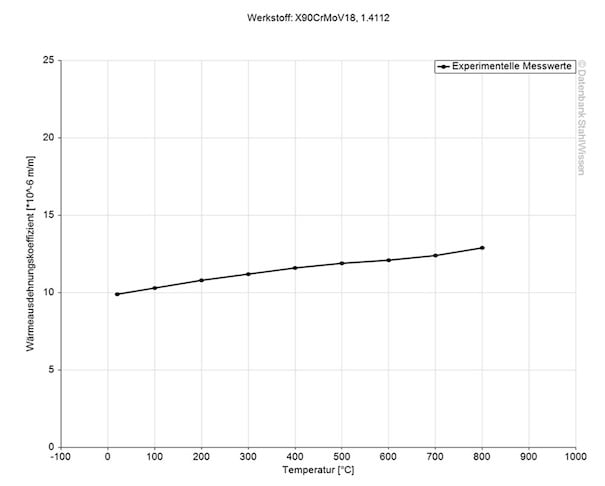
This diagram shows how much stainless steel 440B might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.3 | 68 - 212°F |
10.8 | 68 - 392°F |
11.2 | 68 - 572°F |
11.6 | 68 - 752°F |
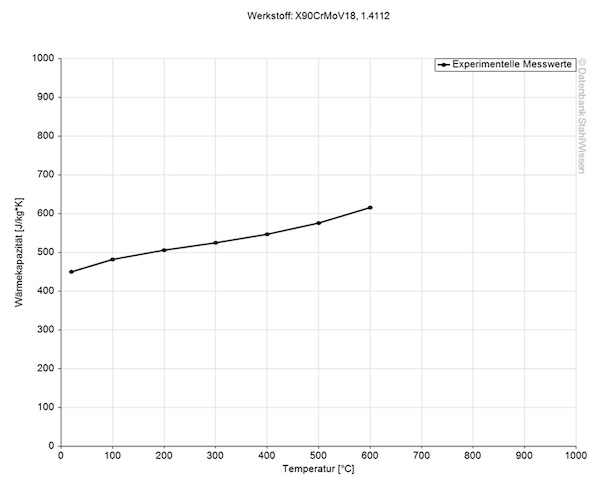
The specific heat capacity of the 440B stainless steel at room temperature is at 0.43 J/g-°C (0.103 BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
~0.8 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 68°F |

440B AS $MART FLAT STOCK, PRECISION GROUND FLAT STOCK OVERSIZE, HARD FLAT OR COLD FINISHED ROUNDS.


440B PROCEDURE
Uniformly heat stainless steel 440B to a temperature range of 1550 - 1600°F (843 - 871°C), then cool the material slowly in the furnace
Heat the workpieces uniformly to a temperature of 1202°F (650°C) and hold for 1 - 2 hours in a neutral atmosphere, then slowly cool them down in the furnace.
Heat the 440B to a temperature range of 1832 - 1976°F (1000 - 1080°C) and soak. Take care not to overheat the material, as it cannot obtain full hardness then.
The quenching medium used depends on the desired final properties that need to be achieved. Water is not usually used to quench this material grade as it can lead to cracking or warping due to thermal shock. Below are some quenching mediums usually used for the 440B.
• Oil, preheated
• Air
• Hot basin (932 - 1022°F)
• Compress 440B Tempering ed Gas (N2)
Heat the workpiece uniformly to a temperature of 300 - 350°F (149 - 177°C) and soak for at least 1 hour to remove peak stresses and yet retain maximum hardness.
After quenching the material the 440B can be treated at sub-zero temperatures to transform retained austenites back to martensite. To make sure all austenite is transformed the material should be soaked for a period of time and after the soak the material is brought back to room temperature. When the material is at room temperature it is tempered as explained above under “Tempering”.
Sub-zero treatment can increase hardness and wear resistance, improve toughness and give the material more dimensional stability.
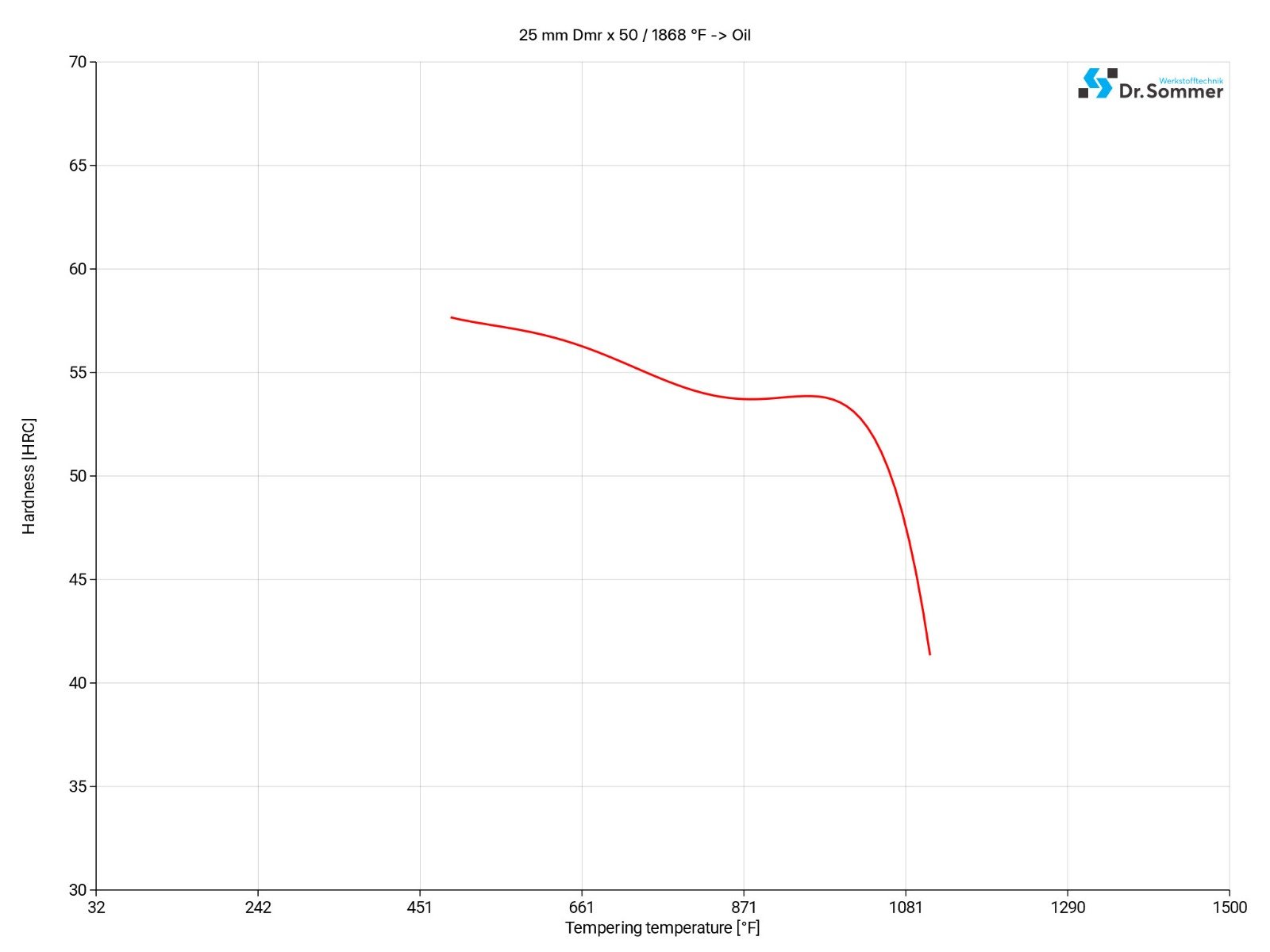
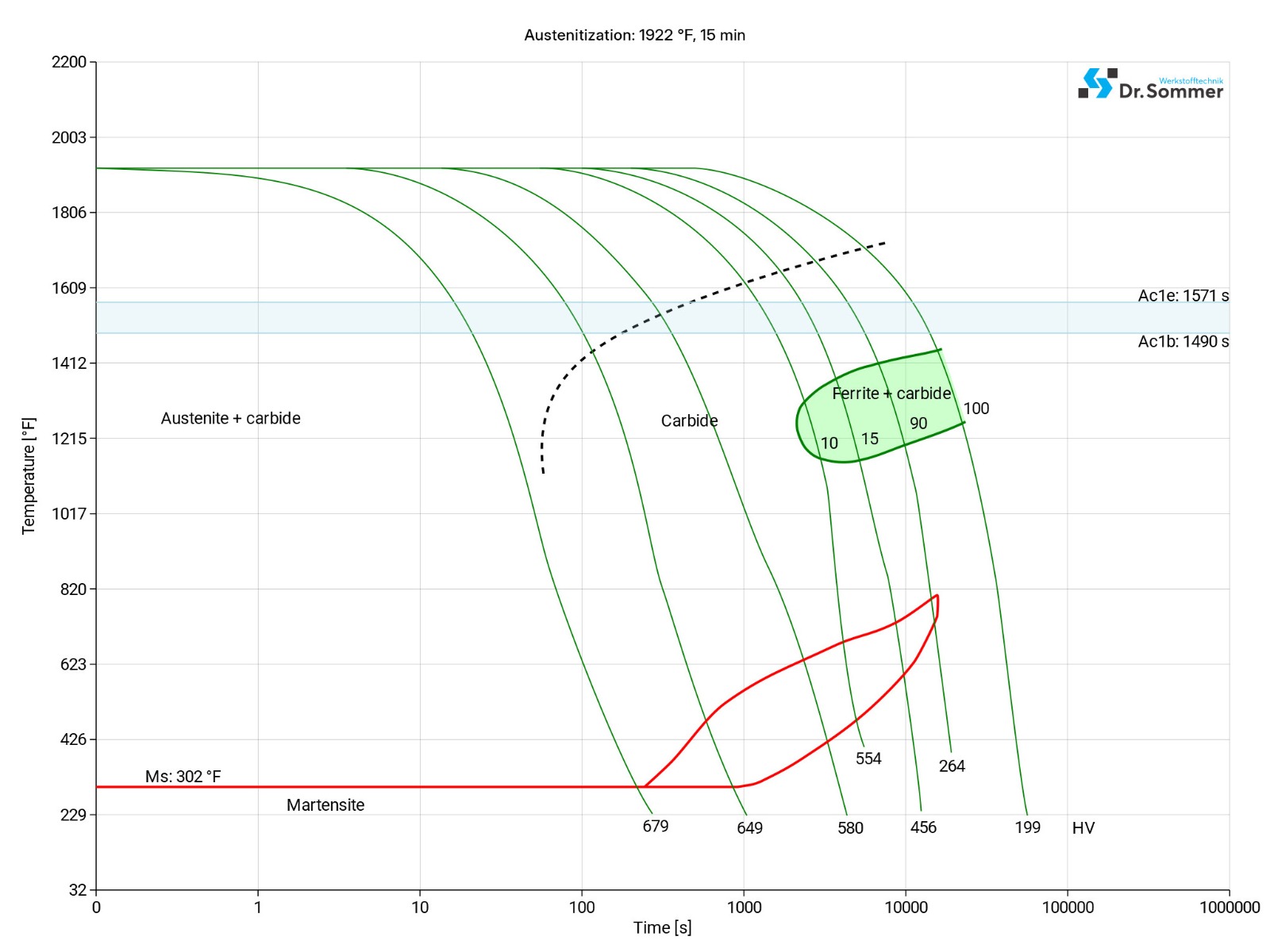
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
440B SURFACE TREATMENT
Surface treating the 440B stainless steel has benefits like extended service life, improved performance, corrosion resistance or to enhance the visual appeal of parts made from this steel grade.
Following are a few examples of surface treatments that can be given to 440B parts.
This process deposits nitrogen into the surface of the material to increase hardness, improve wear resistance and to give tools a longer service life.
This process removes free irons from the surface of the material and enhances the natural corrosion resistance of it too.
PVD and CVD both deposit a thin layer onto the material surface to enhance corrosion resistance, improve hardness and wear resistance or to reduce friction.
This process is an impact treatment where multiple high velocity shots are blasted onto the material surface leaving small indentations removing stress risers. It makes the surface more resistant and can prevent fatigue and stress corrosion failure.
Note: Protective gear like goggles, masks, helmets, gloves and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
Appropriate guards to prevent shot spillage should be in place, equipment regularly maintained and shot should be free from contaminants.
Black oxide coating can enhance the corrosion resistance of the parts but is mostly done for esthetic purposes. It will give parts a blue-black coloring that will reduce light reflecting off the surface.
For some applications grinding and polishing is a very important step. A high-quality finish helps with the corrosion resistance in cutlery applications for example but care has to be taken not to overheat the workpieces as this can lower the corrosion resistance.
440B PROCESSING
To a degree 440B machines like high speed steel, due to its high carbon content. As chips are tough and stringy, chip curlers and breakers should be applied.
For the best results, this material should be machined in its soft annealed condition.
EDM is often used for hard to machine steels and precise dimensions or shapes that are challenging when using traditional machining methods.
Heat affected zones might need further heat treatment after EDM to align the microstructure in the workpiece and EDM may leave a rougher surface with a recast layer which can be removed by stoning and polishing
Dimensional changes can be the consequence of several circumstances. Heating , cooling, phase changes or stress relief can all be contributors to dimensional changes. These can be minimized or avoided by controlled heating and cooling or stress relieving or by using fixtures which can counteract the expansion or contraction of the material during heat treatment.
Heat the workpiece slowly and uniformly to a temperature of 2156°F (1180°C) and be mindful not to overheat the material as this might cause the loss of ductility and toughness. A temperature below 1850°F (1010°C) should be avoided, reheat the material if necessary. When finished forging, cool slowly in the furnace, and then anneal immediately after. Air cooling should be avoided as it may cause the material to crack.
440B is not typically recommended for welding, as it hardens in air and its high hardening capability. Should it be necessary to weld this material, similar fillers should be used to maintain mechanical properties. Preheat the work piece to a temperature of 500°F (260°C) and do not let the material drop below this temperature at all times. Straight after welding the parts should be annealed at 1350 - 1400°F (732 - 760°C) for 6-8 hours. Do not let the temperature between welding the part and annealing it drop below 500°F (260°C). Annealing should be followed up with a slow furnace cooling to avoid cracking.
440B APPLICATION OPTIONS
440B stainless steel is frequently used for plastic processing and for chemically aggressive molding materials. It can be used to produce surgical and dental instruments as it can be sterilized without deterioration of the steel.
• Cutting tools, knives
• Knife blades
• Cutlery
• Guide rails
• Wear parts
• Perforated discs
• Screw elements
• Pump shafts
• Scale pans
• Horizontal cutting
• Surgical instruments
• Plastic molds
• Injection nozzles
• Roller bearings
• Ball bearings
• Mechanical engineering
• Food industry
• Building industry

440B CONCLUSION
440B has a good balance of corrosion resistance, toughness, durability and aesthetic appeal. It is wide spread over various different industries. Its service life, aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance can be enhanced with a wide variety of surface treatments. All the former mentioned attributes make it possible to use this steel grade in a wide array of challenging environments
- Stainless, martensitic chromium steel
- High chemical resistance
- High hardness
- High wear resistance
- Suitable as knife steel
- Can be magnetized
- Can be polished to a mirror finish
- High corrosion resistance
We offer this steel as 440B Flat Stock, Metric 440B Precision Ground Flat Stock, Metric 440B Pre-Hardened Flat Stock and Metric 440B Cold Finished Round Bars.

440B ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
440B DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

