D2 Tool Steel - 1.2379 - X153CrMoV12 - JIS ~SKD 11 - Data

D2 Tool Steel - 1.2379 - X153CrMoV12 - JIS ~SKD 11 - Data
Back to Steel Overview
D2 STEEL PRICE CHART
D2 STEEL STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
X153CrMoV12
57 HRC - 62 HRC
max. 255HB
X153CrMoV12
57 - 62 HRC
max. 255HB

D2 STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
D2 Steel is a high carbon- and chromium steel with added alloys like molybdenum and vanadium. It is a high alloy, secondary-hardening, ledeburitic cold work steel. This high chromium steel is known for its low distortion and wear resistance and can also be found under names like 1.2379 or X153CrMoV12.
This Tool Steel and Plastic Mold Steel is often used when high wear resistance, tempering resistance and good ductility is needed. As well as the forementioned properties this steel presents high compression strength, good through-hardenability, high stability during hardening as well as an excellent cutting-edge retention.
Yes, D2 Steel (X153CrMoV12) is classed as an alloyed stainless steel.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the corrosion resistance for D2 stands at 4. This makes this tool steel grade a corrosion resistant stainless steel. It has a high chromium content (11 – 13 %) which give D2 Tool Steel a certain corrosion resistance but not enough to classify this grade as rust free.
Yes, as a ferrous metal, D2 Steel can be magnetized. Grinding, milling and eroding for example can be done on machines using magnetic clamping.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, D2’s wear resistance is a 6, which makes it one of the most wear resistant steel grades in our portfolio.
The specific heat of the D2 steel grade is typically at ~0.105 BTU/(lb*F) at a temperature of about ~68°F.
D2 STEEL TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
D2 Steel is often used to the manufacturing of knife blades. D2 has a high wear resistance and hardness which means the blades cutting edges stay sharp for longer.
Although the steel has some disadvantages. Unlike other steel grades, D2 knife steel is quite brittle. This means that it is in certain conditions more prone to breaking or splitting. Due to the hardness of this steel, it can be more difficult to sharpen compared to other steel grades.
The working hardness for D2 Steel is between 592 – 658 BHN (Brinell Hardness Number). Compared to other steel grades D2 has a very high hardness which results in its high wear resistance. Depending on the specific heat treatment the working hardness can vary quite substantially.
The density of D2 is at a temperature of ~68°F at a value of approx. 0.277 lb/in3.
D2 has a tensile strength on delivery of approx. 125 KSI (0.145 KSI = 1 MPa). The tensile strength shows the maximal stress-bearing capacity. To gain this knowledge a tensile test is conducted and it shows how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks. The results can be viewed and taken from the stress-strain diagram.
The yield strength of D2 Tool Steel is at approx. 61 KSI. This value shows when the material starts to show plastic deformation under stress.
The specific heat capacity of D2 Tool Steel is between 0.1003 – 0.1099 BTU (lb*°F)at room temperature.
The specific heat capacity is a physical property of D2 and shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
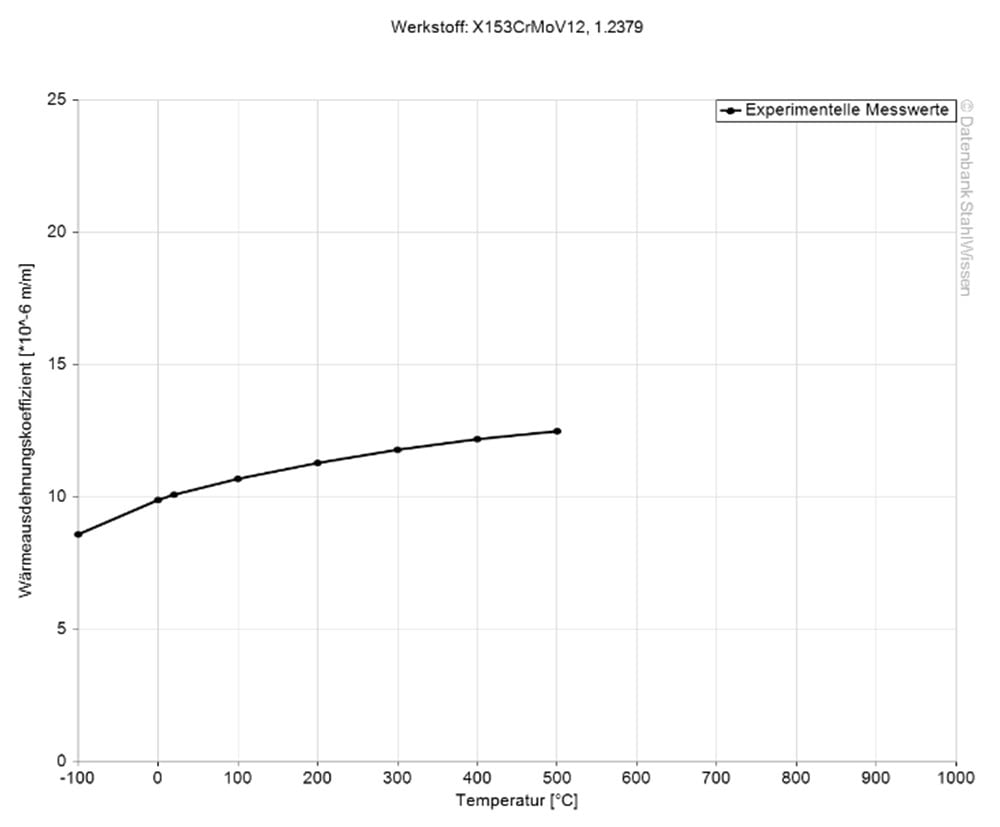
The D2 Steel thermal expansion coefficient shows how much the material might expand or contract when the temperature is changed. This is a very important information, especially when working with high temperature or where there are strong temperature changes during applications. The thermal expansion coefficient is typically in the region of approx. 5-3.3i (in*F) at room temperature.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
in 10-6 m/(m*K) | At a temperature of |
10.5 | 68 - 212 °F |
11.5 | 68 - 392 °F |
11.9 | 68 - 572 °F |
12.2 | 68 - 752 °F |
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
~ 0,453 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 68 °F |
~ 0,515 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 212 °F |
~ 0,596 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 392 °F |
~ 0,695 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 572 °F |
~ 0,798 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 752 °F |
~ 0,908 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 932 °F |
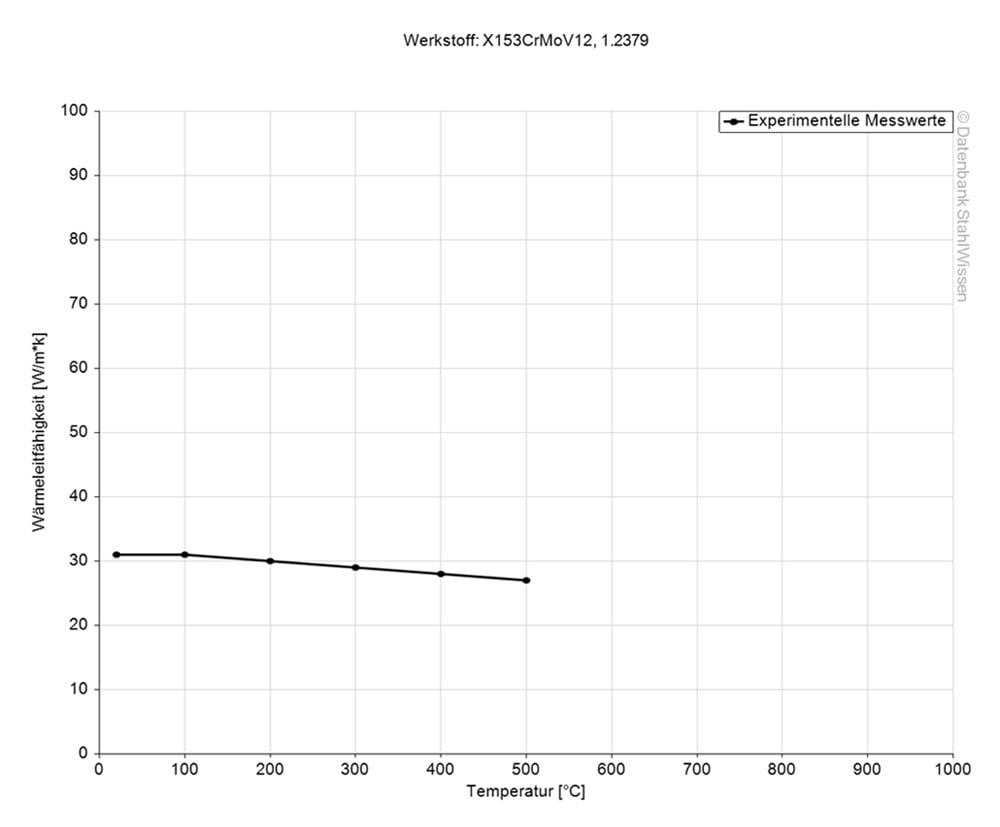
Heat conductivity is a physical property that shows how well a material conducts heat. Heat conductivity is very important for applications which transfer heat or need tight temperature controls. In the following table you can find the heat conductivity values listed for D2 Tool Steel.
| Heat conductivity table | |
| Value | By temperature |
| 16.7 W/(m*K) | 68 ° F |
| 20.5 W/(m*K) | 662 ° F |
| 24.2 W/(m*K ) | 1292 ° F |

D2 AS PRECISION GROUND FLAT STOCK, EDM BLOCK, HARD FLAT OR DRILL ROD.

D2 STEEL PROCEDURE
To enhance the technical properties of this steel grade D2 needs to be heat treated. Important in this process are pre-heat time, holding time, temperature, atmosphere as well as the quenching/cooling of the material
D2 Tool Steel should be protected and heated through to a temperature of 1508 – 1562°F and soaked for 2 hours at that temperature. Then it is furnace cooled at 50°F per hour to a temperature of 1202°F, after that it can freely be cooled further in air.
For stress relieving heat the D2 Tool Steel material through to 1112-1202°F after rough machining and hold for two hours. Cool slowly to 932°F, then the work piece can be cooled further in air.
Preheat the material to a temperature of 1202 – 1382°F and protect the work pieces against decarburisation and oxidation during hardening, which can be done in a special container for this process. Austenitising temperature for D2 Tool Steel is between 1814 – 1922°F. Hold the temperature for one hour per 1 inch of maximal thickness.
For instance, at a thickness of 3 inch the holding time will be 3 hours.
Then remove the work piece from the container if one has been used and cool in still air or with a mild dry air blast to a temperature of 151°F, Then, temper immediately. This steel grade is an oil hardening steel and work pieces can be cooled in oil as well. By cooling this material grade down with oil, a higher hardness and wear resistance may be achieved.
Before work pieces are immersed into the quenching medium oil, the oil should be preheated to a temperature of 151°F. Parts are then quenched at a temperature of 1800°F and held in the oil until the temperature reaches 1000 – 1200°F. At this temperature the parts can be removed from the oil and cool further in air.
Widely used quenching medias for this steel grade are:
• Oil for simple geometries
• Vacuum
• Forced Air/Air/Gas
• Martempering bath or fluidized bed at 360 – 930°F, then cool in air
D2 Steel will harden through in all standard sizes. Make sure to temper as soon as the temperature of the tool reaches 122 – 158°F.
The tempering of steel is a heat treatment process that follows hardening and is used to marginally reduce the hardness and strength of the steel and increase the toughness. D2 steel is usually hardened and then tempered to optimise its mechanical properties. The exact process can vary depending on the specific requirements of the application. Generally, it involves heating the steel to a predetermined temperature, holding the parts at that temperature for a specific time and then finish the process by cooling the material down again.
Choose the tempering temperature that needs to be achieved, hold (oven) for at least 2 hours, temper twice and cool between tempering to room temperature. Do not let the tempering temperature drop below 356°F and hold at the chosen temperature for a minimum of two hours.
For more information, please look at the D2 annealing chart below.
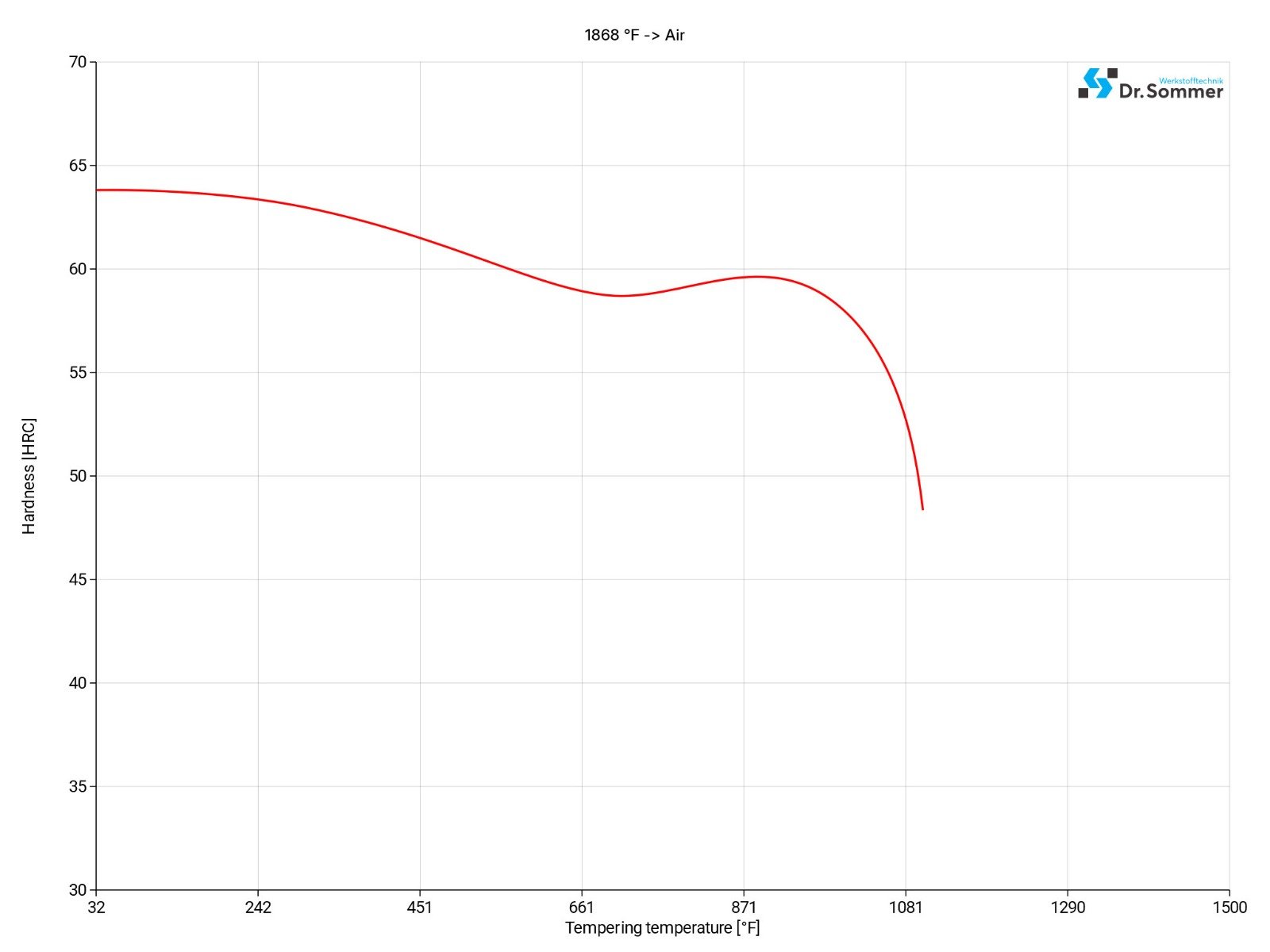
As volume changes may occur in steel over time, workpieces that require maximum dimensional stability, such as gauges or structural parts, should be treated below freezing. After quenching, the workpiece should be held at a temperature between -94 to -112°F for 3-4 hours, followed by a series of tempering procedures. Tempering once again influences the abrasion resistance and service life of the respective workpieces. This treatment increases the hardness by 1-3 HRC. Due to the risk of cracking, this procedure should not be used for intricate shapes.
The tempering temperature for D2 Tool Steel is normally between 356 to 572°F but can vary depending on which technical properties are most important for the parts. Usually, a higher tempering temperature will give the parts better ductility but as well to a lower hardness and tensile strength.
The continuous time-temperature-transformation-diagram (short TTT) shows how the micro structure changes over time at different temperatures. This information is important during heat treatment and provides information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
A TTT-diagram typically shows the various phases and conditions of the steel and show the time and temperature when certain changes happen (e.g., perlite, bainite and martensite).
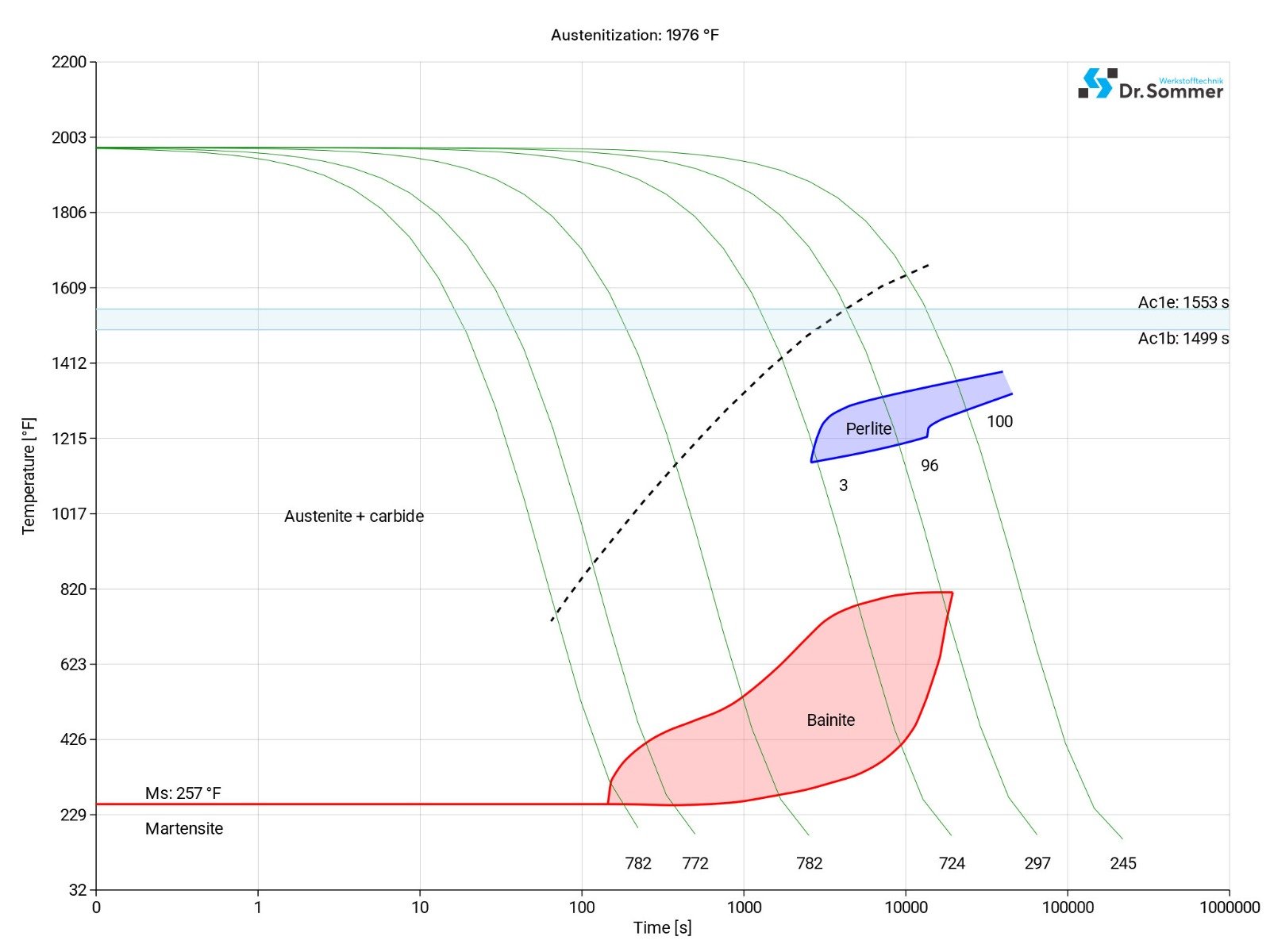
The isothermal time-temperature-transformation-diagram shows how the structure of the steel at micro level changes over time at a constant temperature.
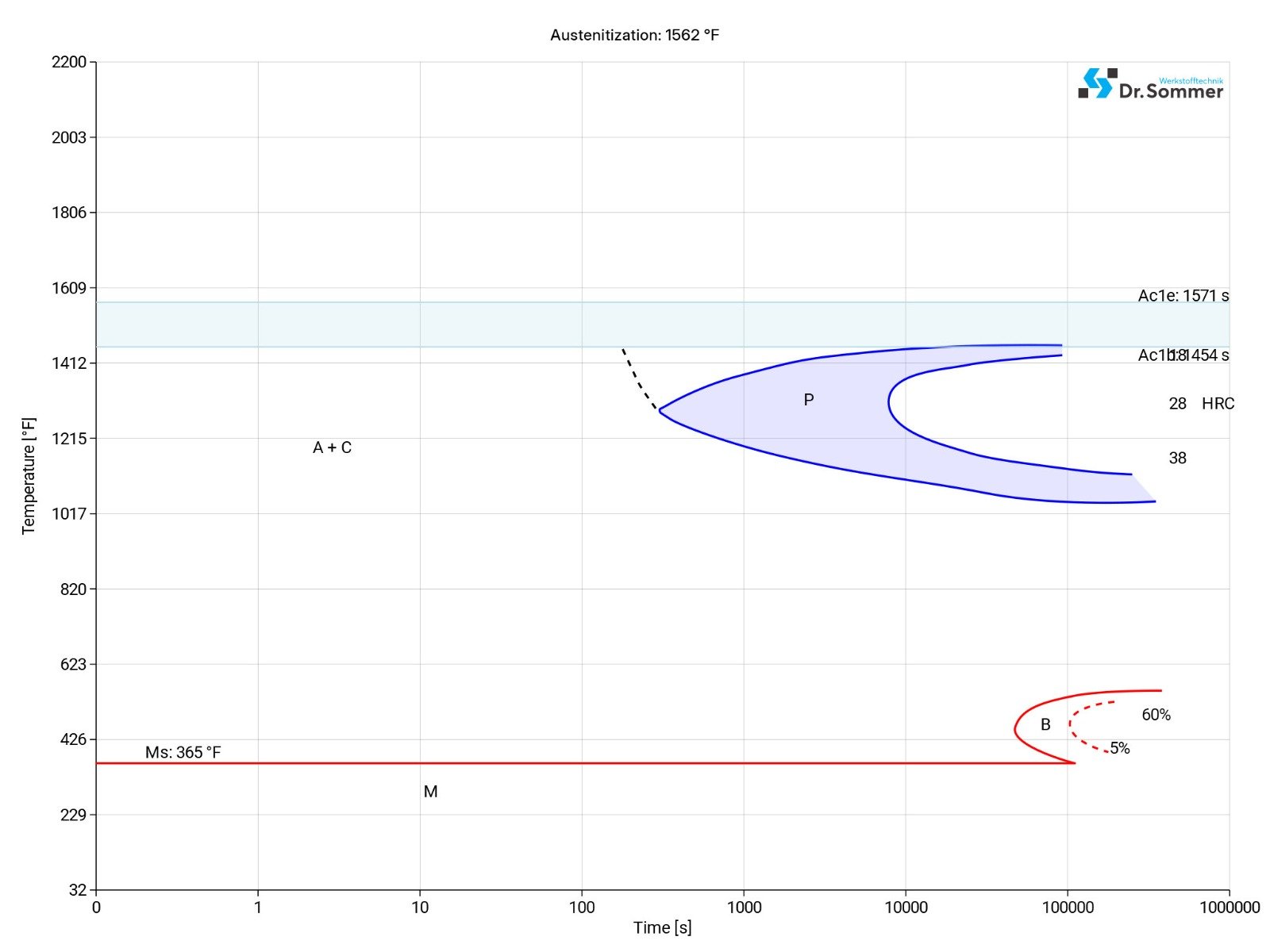
The isothermal TTT-diagram typically shows various phases and conditions as well and show at what temperature and after what time different phases (e.g., perlite, bainite or martensite) start building.
D2 STEEL SURFACE TREATMENT
D2 Steel is, even at higher temperatures, tempering resistant and can be nitride without reducing the hardness.
The nitriding process improves the already high hardness and wear resistant properties of D2 which may be an advantage for applications where these properties are needed for the surface of the parts.
The nitriding process should be carefully monitored to make sure that needed properties are achieved and possible problems as e.g., deformation, or cracking of the steel can be prevented.
D2 TOOL STEEL PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of D2 Steel reaches a score of 1.
This grade is known for its high hardness and wear resistance. Those properties lend themselves to a variety of tool applications but also limits the machinability for this useful grade.
To perform EDM in the hardened or tempered condition, remove the recast layer completely by stoning and polishing. Then the parts can be tempered once more (at a temperature 77°F below the prior tempering temperature) and should be soaked at this temperature for 2 hours.
Dimensional changes during hardening and tempering should be considered and a 0.15% allowance added per side added, if the parts are stress relieved between rough and semi-finishing. If stress relieving is not done the machining allowance should be increased accordingly.
This steel grade can be forged. Preheat the workpiece through to a temperature of 1299 – 1400°F, then increase the heat to a forging temperature of 1850 – 1926°F. Do not let the temperature drop below 1701°F and reheat the parts when needed. When finished equalise the parts to approx. 1400 – 1501°F and cool them slowly in ashes or lime, etc. and anneal as soon as possible.
D2 can be welded but it should be avoided if possible. Welding this material grade can be challenging and should be done with due care and knowledge. As D2 has a high hardness and contains a high carbon content this steel tends to crack quickly while welding.
Good results can be achieved, when welding tool steel like D2, if the proper precautions are taken during the welding process.
Pre-heat: To avoid stress within the steel and relieve it, the material should be pre-heated to reduce the possibility of cracking. Typically, this grade is being pre-heated to a temperature from 392 – 572°F.
Filler metals: When preparing the joint, it is very important to pay attention to choose the appropriate filler metal and welding process. Often the filler is chosen to be compatible or of similar composition to D2 to ensure the best possible results. When polishing or photo-etching D2, it is necessary to work with a suitable electrode type of matching composition.
Tempering: After welding, the parts should be cooled down slowly and then tempered to reduce the hardness and elevate its ductility again. Tempering helps to prevent possible cracking.
D2 STEEL APPLICATION OPTIONS
D2 Tool Steel is a high-performance steel, often used for its hardness and wear resistance in many different areas, e.g., in several industrial sectors.
• D2 cutting and punching tools: Due to the high wear resistance and hardness, this steel is often used to manufacture punching and cutting tools (up to 15/64 inch). These include industrial knives, shears or cutting plates as well precision cutting tools up to 15/32 inch thickness.
• D2 blanking and stamping tools: This steel grade is used for blanking and stamping tools as its properties make it a good choice for molds and dies.
• D2 Plastic molds: For applications which need a high wear resistance like for example the production of plastic parts Premium D2 is an excellent choice.
• D2 Knives and blades: This steel grade is sometimes used for high quality blades but its hardness makes sharpening them difficult.a

D2 STEEL CONCLUSION
D2 Steel is a versatile carbon chromium steel, which makes it a high-alloy, secondary hardening, ledeburitic cold work steel.
Practically, this means:
- It is low-distortion
- It is wear-resistant
- It is through-hardenable
- It is pressure-resistant
- It is temper resistant
- It can be nitrided and eroded
- It is dimensionally stable
- Black oxidizing the material is not possible
- Working hardness is a maximum of 62 HRC
We offer this steel as D2 Precision Ground Flat Stock, D2 EDM Block Hardened, D2 Round Bars Decarb Free, D2 Drill Rods and D2 Pre-Hardened Flat Stock.

D2 STEEL ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
D2 STEEL DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

