431 Stainless Steel - 1.4057 - X17CrNi16-2 - ~SUS 431

431 Stainless Steel - 1.4057 - X17CrNi16-2 - ~SUS 431
Back to Steel Overview
431 STEEL PRICE CHART
431 STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Ni
X17CrNi16-2
32 HRC - 47 HRC
max. 331 HB
X17CrNi16-2
32 HRC - 47 HRC
max. 331 HB

431 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
431 with added chromium and nickel alloys, giving it its better toughness as well as better corrosion resistance compared to straight up chromium stainless steels. This makes this steel grade ideal for operations like deep drawing, compressor parts and construction. This steel grade is also often used in processing chemically aggressive plastics, like PVC for instance.
Due to its tensile strength and corrosion resistance 431 can be used for fasteners like bolts and screws or mechanical components like shafts and axles. Furthermore it can be used for pumps and valve components, aircraft components like landing gear or pivot pins. Automotive parts like engine components and exhaust system parts or in the food processing industry as it can withstand harsher cleaning processes. With its sharpness and corrosion resistance the 431 lends itself for cutlery and surgical instruments.
Yes, the 431 is a stainless steel as it contains a mass fraction of 15 - 17% of chromium. It is part of the 400 Series Stainless Steel.
A corrosion resistant steel has a minimum of 10.5% chromium, with 15 - 17% chromium content the 431 is a classic stainless steel and is therefore corrosion resistant.
As a martensitic stainless steel the 431 can be magnetized and can be used for applications where this is desired or needed like magnetic clamping.
On a scale of 1 to 6 where 1 is low and 6 is high the 431 scores a 3.
431 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Stainless steel 431 can be used as a knife steel it offers good corrosion resistance though there are other stainless steels better suitable as they have a higher toughness and are easier to sharpen and hold an edge for longer.
The working hardness for the 431 stainless steel is approx. 300 - 447 BHN (32 - 47 HRC).
VTypically the density of stainless steel 431 is 0.278 lb/in3 (7.7g/cm3) at room temperature.
Stainless steel 431 has a tensile strength of approx. 152.2 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The yield strength shows how much stress can be applied before a material plastically deforms. Beyond that point the material will not return to its original form if the stresses are taken away but will stay deformed or even break.
The yield strength for the 431 stainless steel is 7469 KSI (515 MPa).
The heat conductivity for stainless steel 431 is at ~25 W/(m*K) (~173 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature
The following table shows expansion or contraction at various temperatures, which may be very important for high temperature works or when working with high temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10 | 68 - 212°F |
10.5 | 68 - 392°F |
10.5 | 68 - 572°F |
10.6 | 68 - 752°F |
11 | 68 - 932°F |
The specific heat capacity of the 431 stainless at room temperature is 0.46 J/g-°C (0.109 BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
|---|---|
Value | At a temperature of |
~0.7 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 68°F |

431 AS $MART FLAT STOCK, COLD FINISHED ROUNDS OR DECARB FREE ROUNDS.

431 PROCEDURE
Desired properties dictate temperatures, holding times and cooling rates during the heat treatment of the 431 stainless steel.
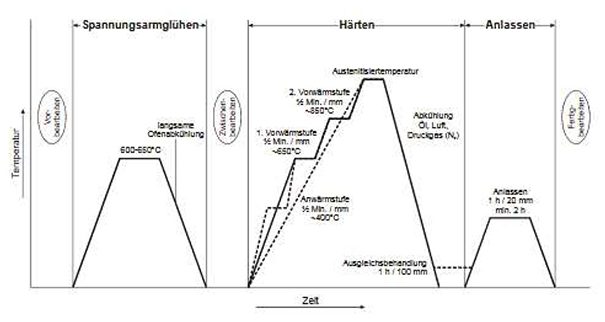
Heat parts to a temperature range of 1256-1472°F (680-800°C) and hold, then cool slowly and controlled in the furnace.
Quenching the 431 stainless in oil, air or water quickly transforms the austenite into a hard and brittle martensitic structure. Properties are depending on which quenching medium is being used.
• Oil
• Air
• Water
To reduce the brittleness and to improve toughness, tempering is a critical step in the heat treatment process for the 431 stainless steel.
Heat the workpiece uniformly to a temperature of 1112-1202°F (600-650°C) and hold for a minimum of 1 hour and then cool in air.
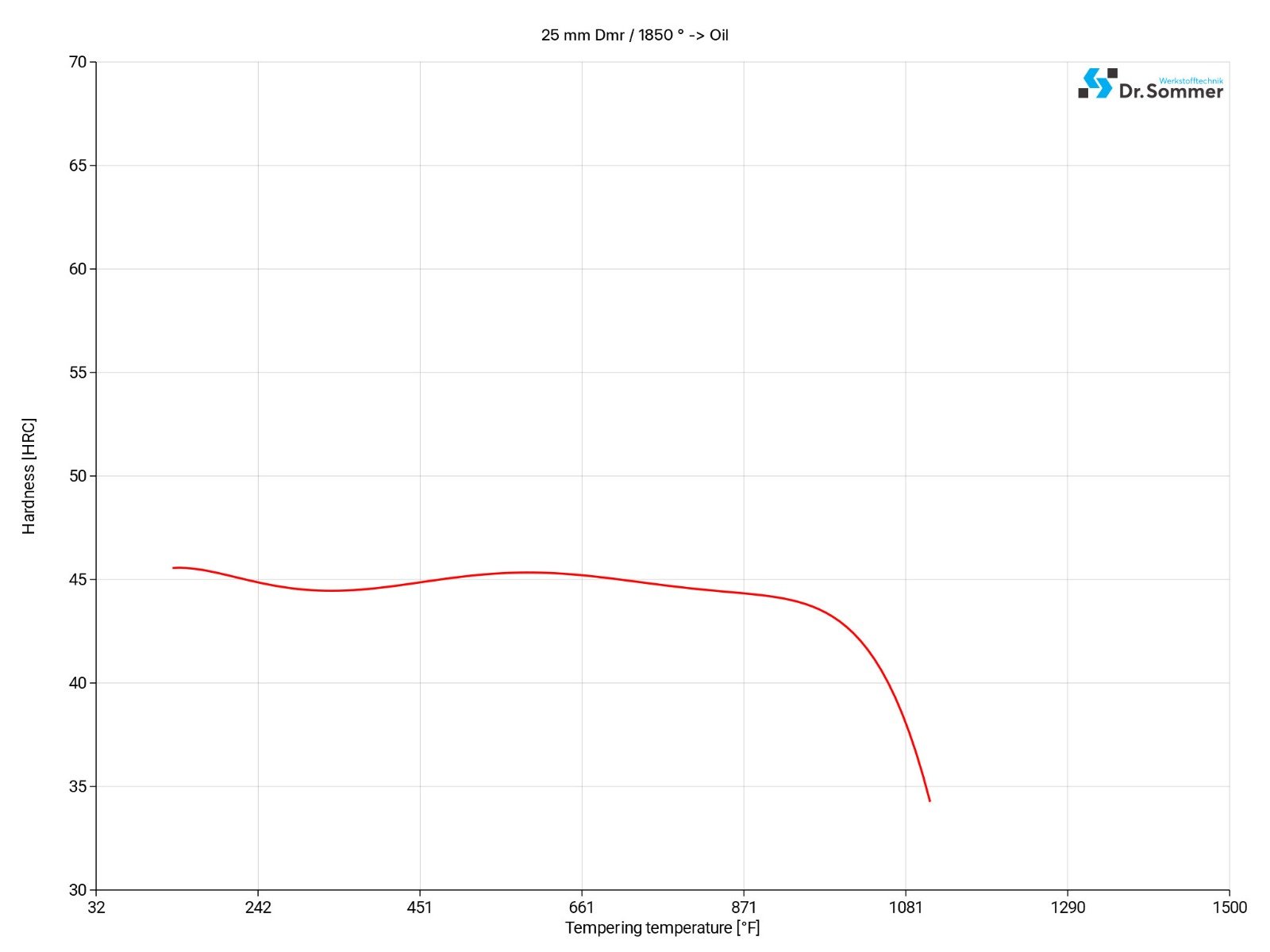
To reduce the brittleness and to improve toughness, tempering is a critical step in the heat treatment process for the 431 stainless steel.
Heat the workpiece uniformly to a temperature of 1112-1202°F (600-650°C) and hold for a minimum of 1 hour and then cool in air.
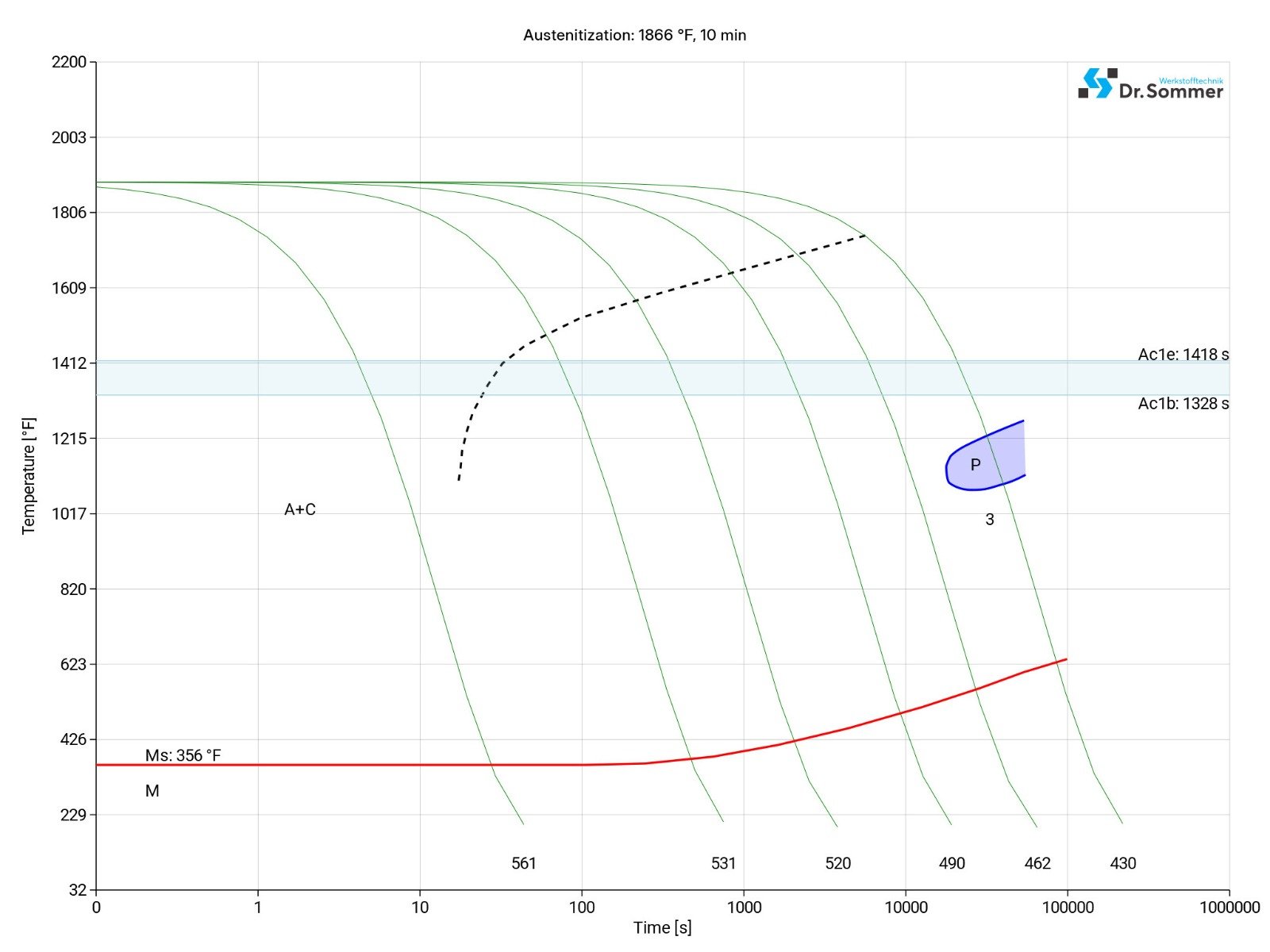
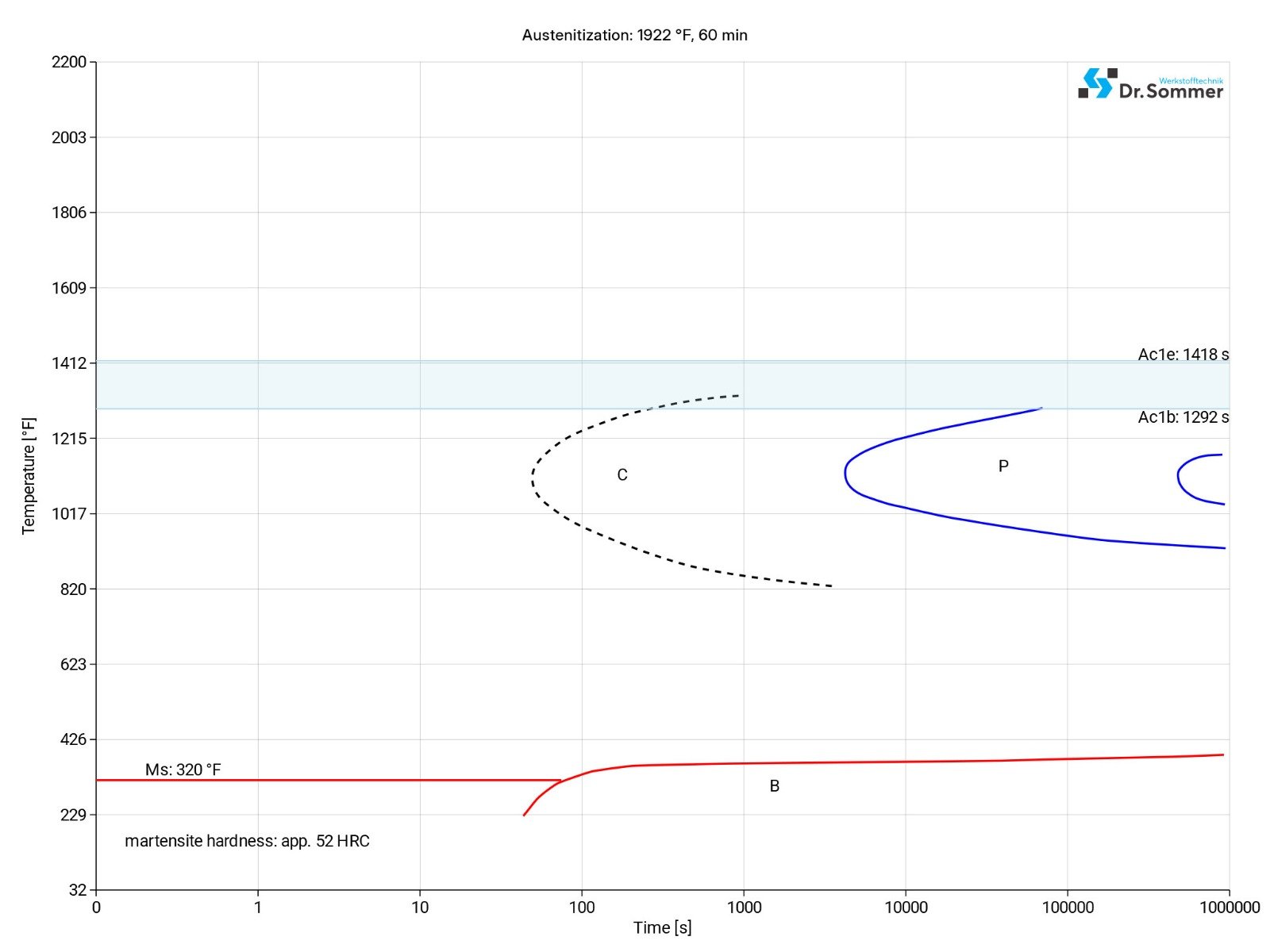
This diagram shows the micro changes at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum condition for the hardening, annealing and normalizing process.
431 SURFACE TREATMENT
Nitriding introduces nitrogen into the surface layer which gives the 431 an improved wear resistance due to the hard nitride layer.
Passivation removes free iron and contaminants from the surface of the 431. It creates a passive oxide layer which can prevent rust and other corrosion when exposed to corrosive environments.
To enhance corrosion resistance and hardness or reduce friction the 431 can be coated by PVD, CVD and Electroplating.
Shot peening an impact treatment blasts multiple high velocity shots onto a material surface leaving small indentations which replace the tensile stress on the surface with a compressive layer. It solidifies the material and makes the surface more resistant which can prevent fatigue and can optimize the form and weight of the parts.
Note: Protective gear like goggles, masks, helmets, gloves and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
Appropriate guards to prevent shot spillage should be in place, equipment regularly maintained and shot should be free from contaminants.
To improve the aesthetic, surface finish, corrosion resistance and remove embedded contaminants from the surface the 431 can be electropolished. This treatment removes a thin surface layer in an electrochemical process.
A chemical process which darkens the material surface for decorative purposes, blackening can also reduce light reflecting off the surface.
431 PROCESSING
In its annealed condition 431 is to some extent easily machined. In its hardened condition, above 277 BHN (30 HRC), it is more difficult to machine.
EDM can be used for the 431 stainless steel, though it should be considered in what condition, annealed or hardened, it is being EDM’d. Hardened it can be more challenging and machining parameters as well as specialized electrodes should be considered. So when choosing EDM for the 431 it should be carefully planned and controlled.
Dimensional changes happen when the material undergoes heat treatment or cooling due to phase changes during the treatment.
During austenitization, when the material is heated, it can expand. While tempering internal stresses are redistributed which might expand the material slightly but not as much as during austenitization. On the other hand, cooling the 431 by quenching, the phase change from austenite to martensite, can reduce dimensions by contracting. Excessive contraction of the material may result in warping, distortion or cracking when not controlled properly.
Carefully and slowly heat the work piece to a temperature of about 1562°F (850°C) and then rapidly increase heat to a temperature of 2102-2156°F (1150-1180°C). The forging temperature is 2156-1742°F (1180-950°C) followed by a slow cooling in the furnace, dry ash or other materials which support a slow cooling.
Preheat the parts to about 212-572°F (100-300°C), welding temperature under 392°F (200°C) should be avoided. After welding is finished and the workpiece has reached an ambient temperature, heat for a post-weld heat treatment to 1202°F (650°C). Without the additional post-weld heat treatment, the mechanical properties in the heat affected areas and in the weld seam may be very different to those in the base metal. To prevent contamination, welding with gas containing hydrogen or nitrogen should be avoided as it affects the mechanical properties negatively. In order to ensure the best possible corrosion resistance in the weld, tempering colors have to be removed either mechanically or chemically.
D2 APPLICATION OPTIONS
Due to its tensile strength and corrosion resistance 431 can be used for fasteners like bolts and screws or mechanical components like shafts and axles. Furthermore it can be used for pumps and valve components, aircraft components like landing gear or pivot pins.
Automotive parts like engine components and exhaust system parts or in the food processing industry as it can withstand harsher cleaning processes. With its sharpness and corrosion resistance the 431 lends itself for cutlery and surgical instruments.
• Mechanical engineering
• Automotive industry
• Oil and petrochemical industry
• Aviation
• Food industry
• Soap industry
• Acetic acid industry
• Shafts
• Pump parts
• Perforated plates
• Spindles
• Piston rods
• Valve cones
• Turbine blades

431 CONCLUSION
As with all material choices, applications and properties should be considered when choosing a steel. The 431 offers good corrosion resistance in mild to moderate corrosive environments but is susceptible to pitting when exposed to chloride rich environments. It has high tensile strength, good machinability and can achieve mechanical properties like hardness or toughness by heat treating the material.
- Martensitic chromium steel
- High strength in as-delivered condition (quenched and tempered)
- Very good corrosion resistance
- High toughness
- High tensile strength
- Good machinability
- Good weldability
- Magnetizable
- Limited acid resistance
- Forgeable
We offer this steel as 431 Flat Stock, 431 Cold Finished Round Bars and 431 Round Bars Decarb Free.

431 ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
431 DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

