Cold Work Steel - No Minimum Order Value or Quantity
The hardness and ductility of cold work steel can be increased by plastic deformation under the crystallization temperature and can be enhanced by choosing ESR material.
The crystallization temperature is unique to different steel grades. Most steel grades can be cold worked at room temperature and some at more elevated temperatures as their crystallization temperature is a bit higher.

Your success is our success!
HOW IS COLD WORK STEEL PRODUCED?
The production of cold work steel involves various stages, from the choice of raw material to the final heat treatment to improve its mechanical properties for applications involving cold forming processes such as cutting, forming and shaping.
The process involves:
• Melting and adding alloys
• Casting
• Hot rolling
• Cold rolling
• Heat treatment
DISTINCT FROM HOT WORKING
The main difference to hot work steel is the working temperature. Hot work steel is used above the recrystallization temperature and cold work steel is used at and around room temperature.
COLD WORK STEEL VS. HOT WORK STEEL | |
Cold working steel | Hot working steel |
Working temperature is below recrystallization temperature. | Working temperature is above recrystallization temperature. |
Maintains its hardness when used at or around room temperature. | Maintains its hardness at high temperatures. |
The wear resistance is maintained at low temperatures. | The wear resistance is maintained at high temperatures. |
Although cold work steel is harder and more brittle, it still has sufficient toughness for cold forming. | Hot work tool steel retains its toughness at high temperatures to prevent thermal fatigue or cracking under heavy loads. |
Less resistant to thermal fatigue. | Resistant to thermal fatigue. |
Resistance to oxidation is not needed due to the working temperatures. | Resistant to oxidation. |
Smoother surface, no scaling or oxidation | Rougher surface due to scaling and oxidation |
Better dimensional accuracy | Good dimensional accuracy |
VARIOUS COLD WORKING TECHNIQUES
Following are examples how metal can be cold worked:
Here metal is passed through two rollers which exert high pressure reducing its thickness.
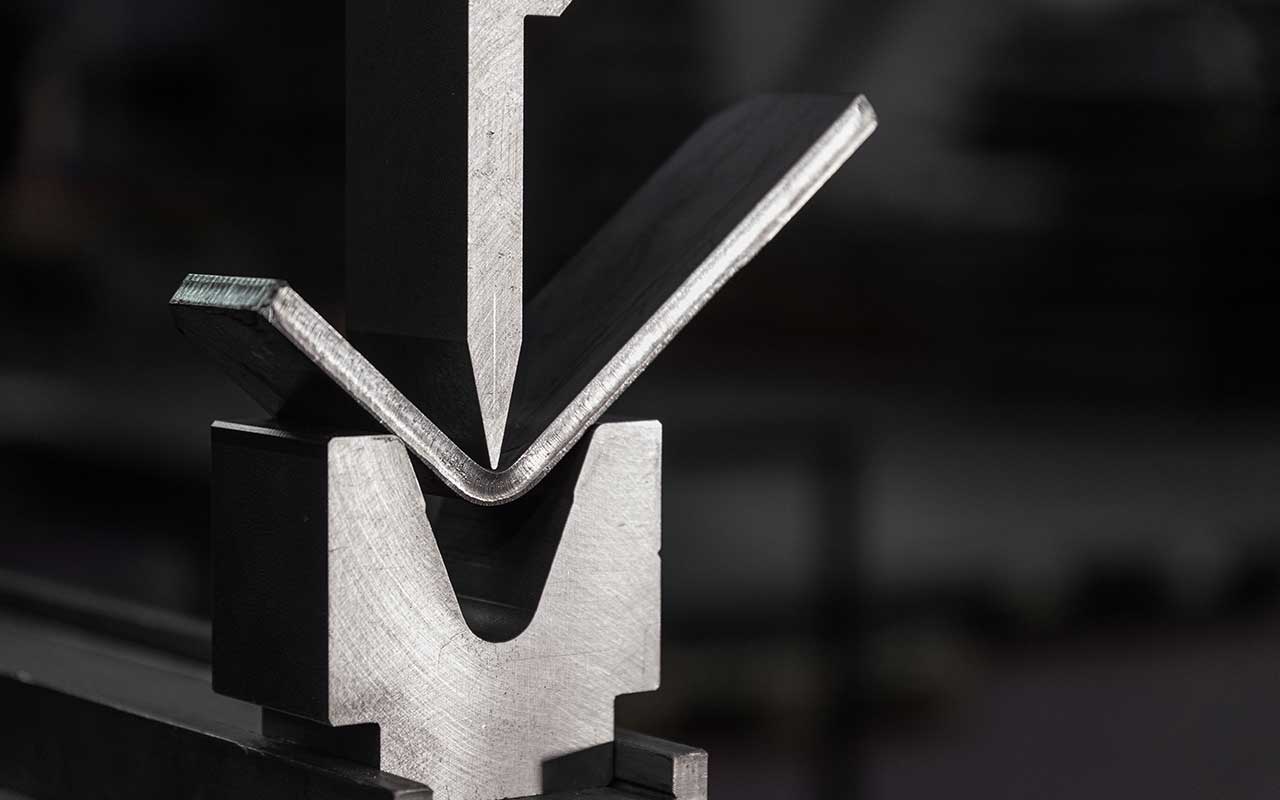


Cold bending
Cold bending is based on physical forces. To form the material the workpiece is shaped by applying mechanical force.
This is done with dies and hammers to shape the metal into a desired form without using heat.
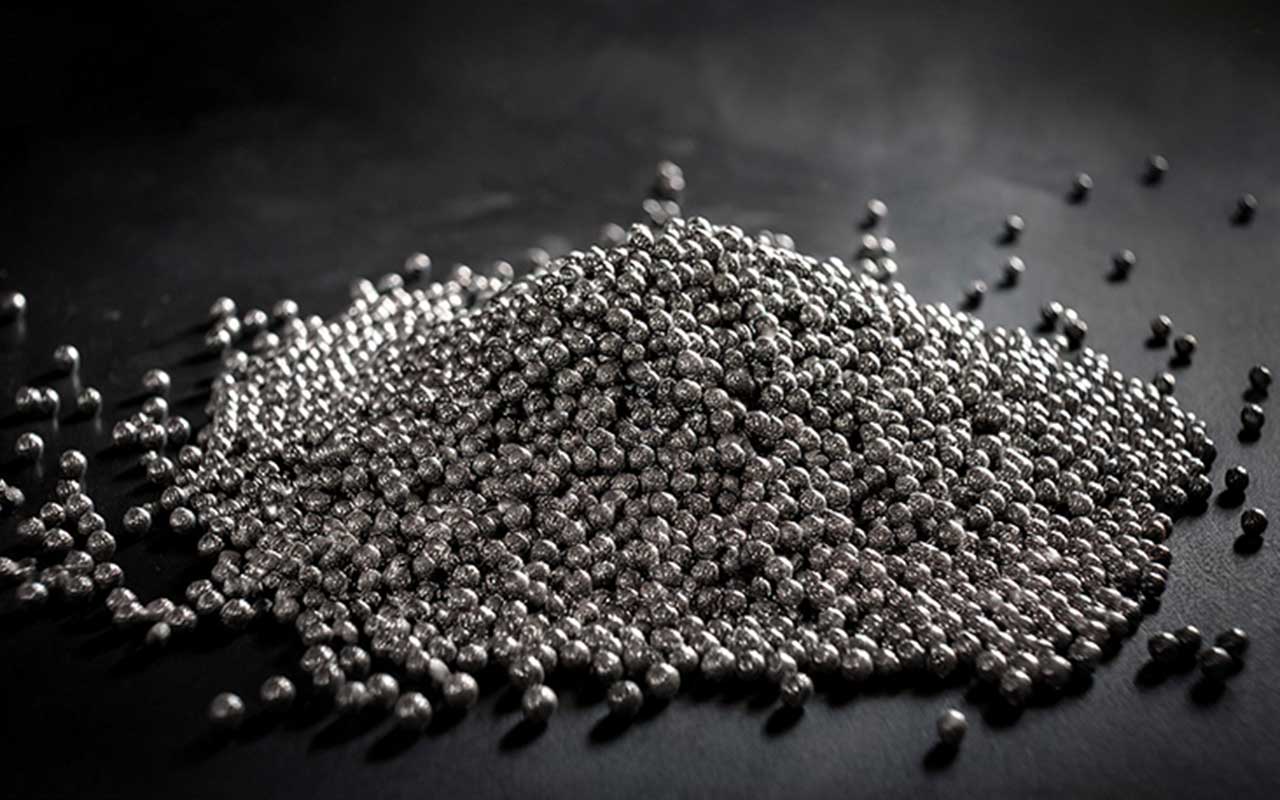


Cold peening
Shot peening will blast tiny metal balls onto the surface of the material. This leaves a series of tiny compressions on the surface solidifying the surface.
SUMMARY
• High wear resistance
• High hardness
• Good toughness
• Dimensional stability
• High resistance to fatigue
• Long service life
• Wide range of manufacturing techniques