A2 Tool Steel - DIN 1.2363 - X100CrMoV5 - JIS ~SKD 12

A2 Tool Steel - DIN 1.2363 - X100CrMoV5 - JIS ~SKD 12
Back to Steel Overview
A2 TOOL STEEL PRICE CHART
A2 STEEL STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
X100CrMoV5
58 HRC - 62 HRC
max. 241HB
X100CrMoV5
58 HRC - 62 HRC
max. 241 HB

A2 STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
A2 is an air hardening, cold work steel. The combination of high wear resistance and good toughness makes the A2 suitable for a wide variety of applications.
A2 tool steel with a mass fraction of 5% chromium has an excellent combination of wear and chipping resistance as well as excellent machining and grinding properties.
The AISI A2 tool steel has some corrosion resistance though not as much as a stainless steel can offer. The typical stainless steel has a minimum mass fraction of 10.5% chromium, A2 has a mass fraction of 4.8 - 5.5% of chromium. If corrosion resistance is a high priority a stainless steel should be considered.
A2 like other steels contains iron, is ferromagnetic and can be magnetizable.
The wear resistance for the A2 steel is 4 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
The A2 is an air hardening steel which can be cold worked, care should be taken when cold working it and stress relieving should be applied. Internal stresses may lead to cracking or distortion. Cold working might influence the ductility when cold working as the material gets brittle and might crack.
Cold working the X100CrMoV5 steel, which has good toughness and wear resistance, has the advantage of providing better dimensional tolerances than hot working.
A2 STEEL TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Though A2 can be used as a knife or blade steel with a combination of wear resistance, toughness, edge retention and can be easily sharpened. It is only used for tactical knives or hunting knives.
While it has some corrosion resistance, A2 knife steel is not a stainless steel and knives made of this steel grade should be maintained on a regular basis and kept out of damp environments to prevent corrosion.
The working hardness for the A2 tool steel is in a range of 601 - 658 BHN (58 - 62 HRC).
The typical density of the A2 steel is 0.284 lb/in3 (7.86g/cm3) at room temperature.
The A2 steel has a tensile strength of approx. 118.2 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The A2 yield strength is at approx. 184 - 319 KSI (1269 - 2200MPa). The yield strength value shows how much force is needed to elongate a sample of steel before it breaks. The yield strength is impacted by the carbon content and heat treatment of the various steel grades.
The heat conductivity for Tool steel A2 is at 15.8 W/(m*K) (110 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
15.8 | 68°F |
26.7 | 662°F |
29.1 | 1292°F |
This diagram shows how much A-2 steel might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
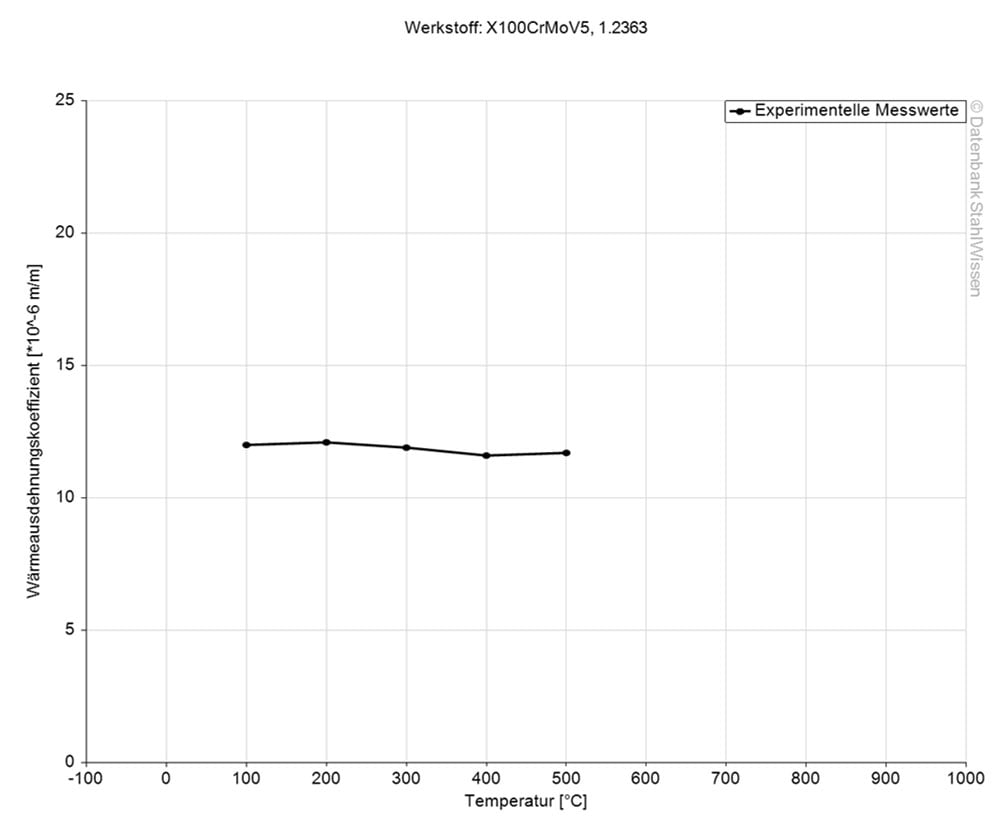
The specific heat capacity of A2 steel is at 0.460J/g-°C (0.110BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.

WANT TO KNOW MORE?

A2 STEEL PROCEDURE
Precaution needs to be taken while heat treating A2 to prevent decarburization.
A2 steel should be protected and be heated uniformly to a temperature of 1560°F (850°C). Cool the furnace at 20°F (10°C) per hour to a temperature of 1200°F (650°C) and then cool further in air.
To relieve stress after rough machining, heat the work piece to a temperature of 1200°F (650°C) and hold it for 2 hours. Cool in the furnace to a temperature of 930°F (500°C) and then can be cooled down further in air.
A2 tool steel is heat treated by preheating the work piece to a temperature of 1200-1300°F (650-750°C), then rapidly heat to 1690-1780°F (925-970°C) and hold for 30 minutes until the part is uniformly heated through. Then cool to room temperature in dry mild air. To prevent decarburization and oxidation, parts should be protected during the A2 tool steel heat treatment.
Quenching should be done as quickly as possible. To avoid excessive distortion and/or quench cracking, cooling should be uniformly and a sufficient cooling rate should be considered.
• Oil for small and simple parts
• Vacuum furnace with overpressure of gas at cooling
• Circulating air or atmosphere
• Martempering bath or fluidized bed at 360-430°F (180-220°C) or 840-1020°F (450-550°C) followed by cooling in air.
For aging, tempering after quenching is replaced by aging at 230-285°F (110-140°C), holding time 25-100 hours.
For tools subjected to shock for example, a double temper is recommended at a temperature of 900-1000°F (482-538°C), holding the temperature for 1 hour at least for small parts and 1 hour per inch (25.4 mm) of thickness for larger pieces.
For more information please have a look at the A2 steel tempering chart below:
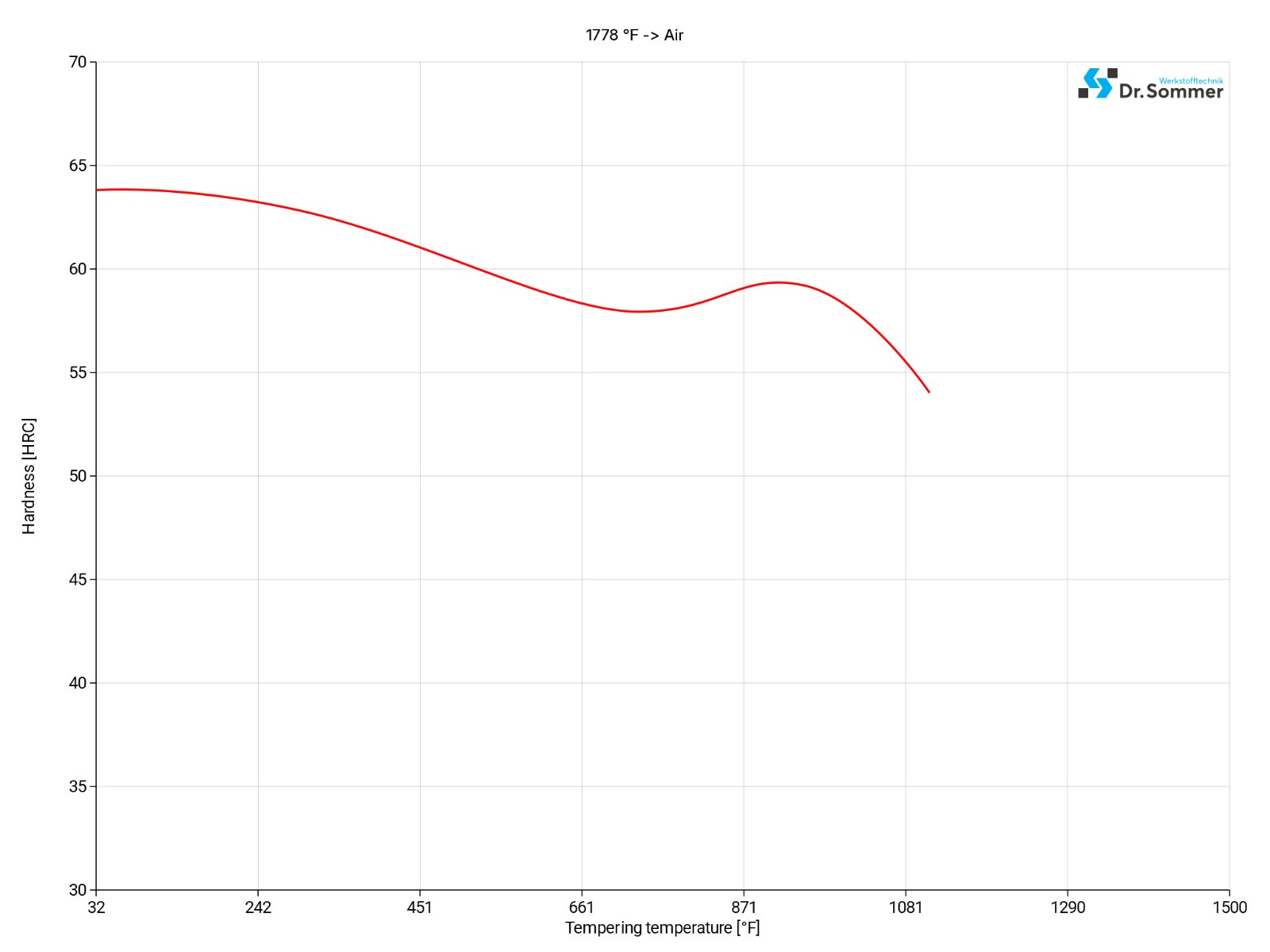
Immediately after quenching, the work piece should be sub-zero treated to between -40 to -110°F (-40 to -80°C), soaking them for 2-3 hours following tempering or aging. Sub-zero treatment will increase the hardness of 154-160 BHN (1-3 HRC). Due to cracking, it is not advised to use this treatment for intricate shapes.
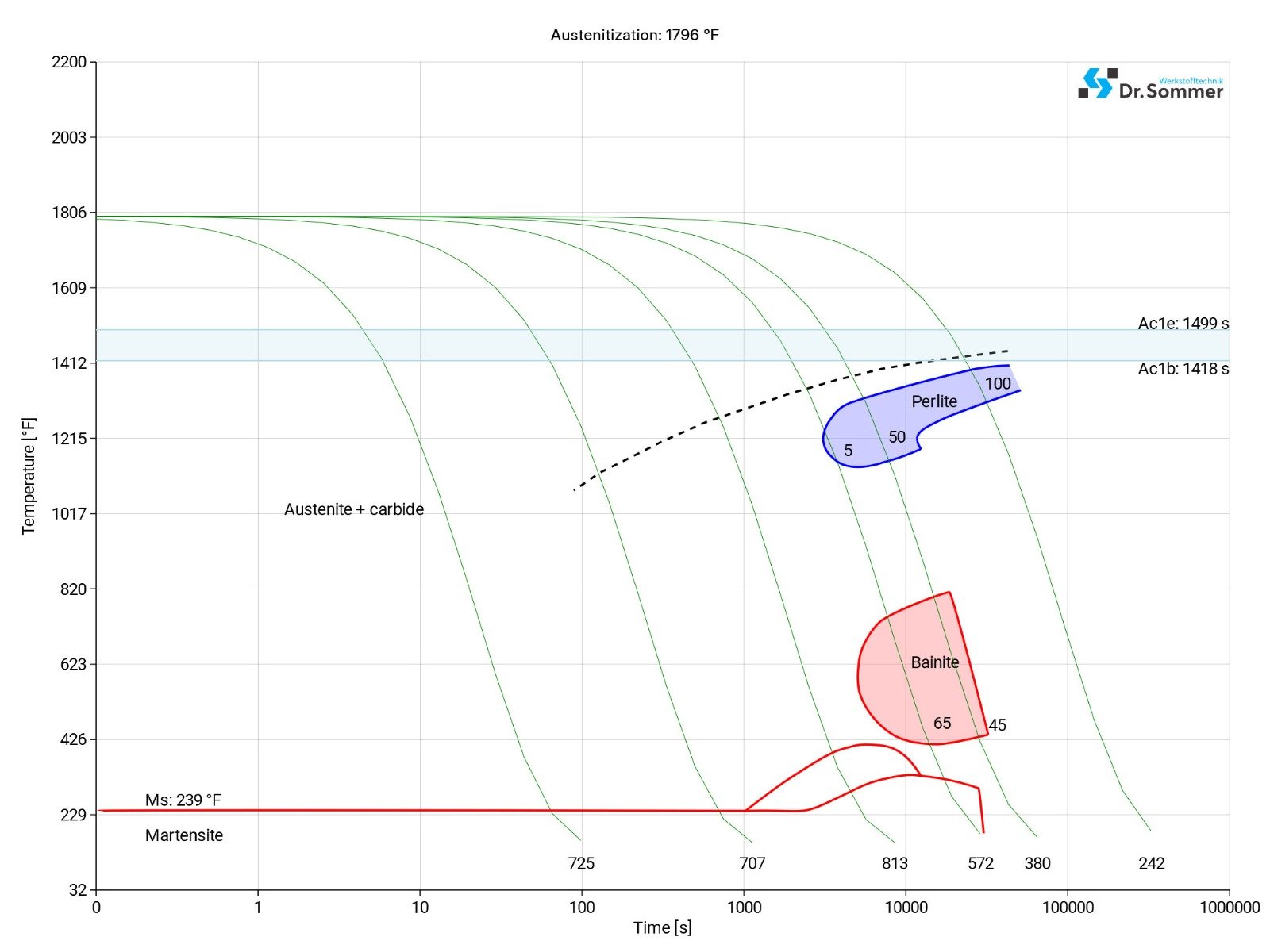
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
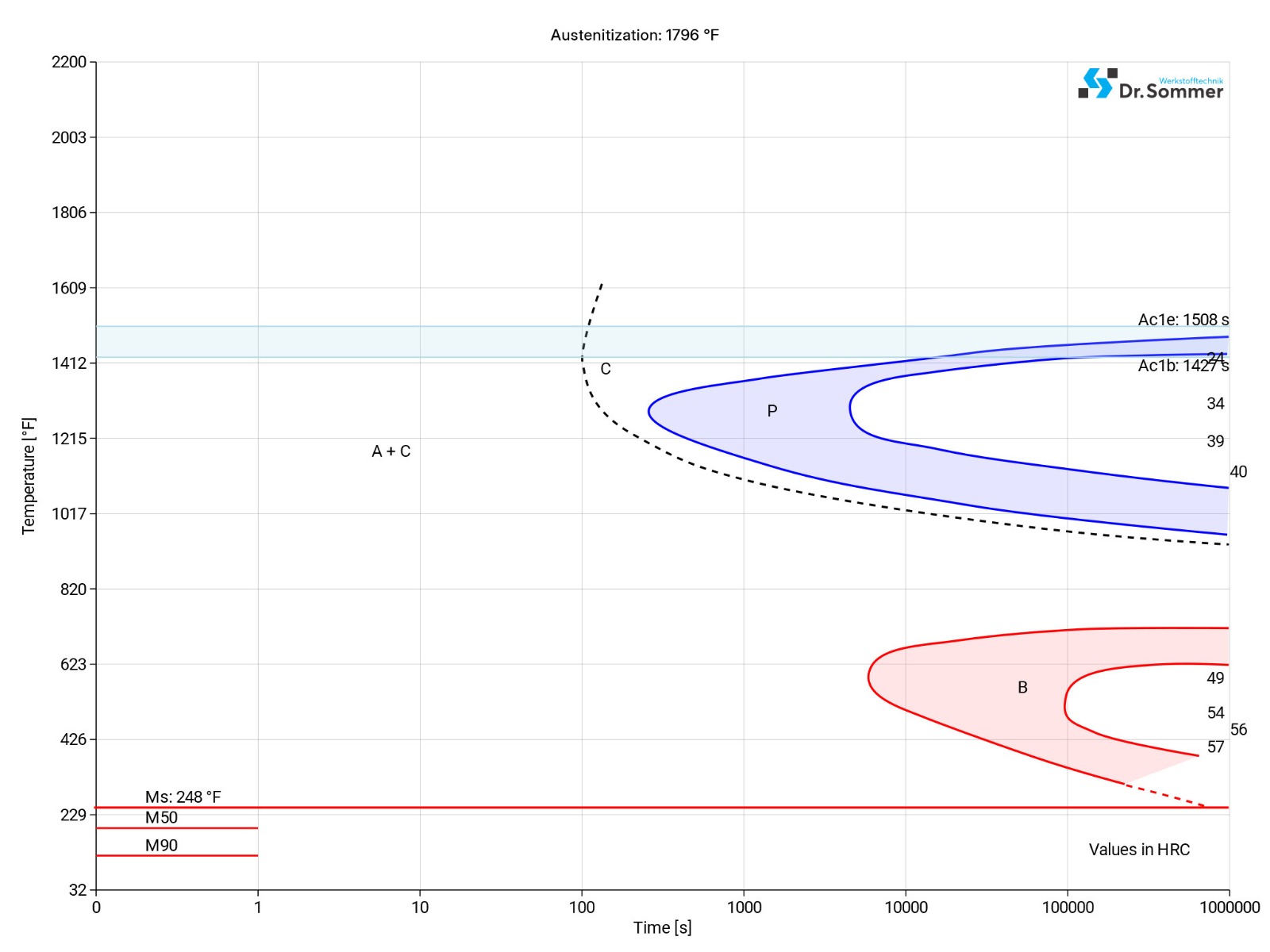
The following diagram shows the structural changes at micro levels over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperatures the different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite and bainite start to form.
A2 STEEL SURFACE TREATMENT
To reduce friction and increase wear and corrosion resistance some cold work tool steels are surface treated, using nitriding, titanium nitriding or hard chrome plating.
Nitriding gives the surface of the A2 material a hard layer with an excellent resistance to wear and galling. To suit the application, the thickness of the layer should be considered well.
A2 TOOL STEEL PROCESSING
Performing EDM in the hardened and tempered condition, remove the recast layer completely by stoning and polishing. Then give the tool another temper at approx. 50°F (25°C) below the prior tempering temperature and soak at this temperature for 2 hours.
A2 like other tool steels will hold its size best when quenched from the accurate hardening temperature. A2 steel will shrink after tempering if it is overheated and should not be hardened from a temperature above 1175°F (968°C) and expands when tempered below 600°F (316°C).
Heat the parts uniformly to a temperature range of 1950-2050°F (1066-1121°C), forging should be avoided below the temperature of 1700°F (927°C). Reheat the material as often as necessary. To cool larger parts, heat the furnace to about 1550°F (843°C), place the part in the furnace and soak at this temperature until the parts are uniformly heated throughout, then turn off the furnace and let the work pieces cool slowly in the furnace. Note that this is not an annealing, the parts should be annealed as described here in the section “Annealing A2 steel” after the parts have cooled down from forging.
Good results can be achieved when welding tool steel, if the proper precautions are taken during welding (increased working temperature, joint preparation, choice of filler metals and the welding procedure). In the event that the parts are to be polished or photo-etched, it is necessary to work with a suitable electrode type of matching composition.
A2 STEEL APPLICATION OPTIONS
A2 tool steel properties like wear resistance and chipping resistance make A2 steel a good fit for applications requiring extreme accuracy of size, as well as for very large parts like large blanking dies, trimming dies, coining dies, wear inserts and precision tools.
• Blanking tools
• Stamping tools
• Dies
• Punches
• Trimming tools
• Cutting tools
• Thread rolling tools
• Thread rolling dies
• Shear knives
• Circular shear knives
• Cold pilger mandrels
• Cold stamping tools
• Plastic molds

A2 STEEL CONCLUSION
A2 tool steel is a reliable choice as it has a good balance between wear resistance and toughness. As it has good dimensional stability during heat treatment, this material is often used for tools. Care should be taken during heat treatment to maintain the best performance of the material and prevent deformation. With proper care, this material can have a long life.
Practically, this means:
- Air-hardenable cold work steel
- Good machinability
- High wear resistance
- Improved toughness
- Low dimensional change
- Repair weldable
- Nitridable
- Erodible
- Working hardness between 58 and 62 HRC
- Very good dimensional stability and A2 Round Bars Decarb Free
- High compressive strength
We offer this steel as A2 Drill Rods, A2 Precision Ground Flat Stock and A2 Round Bars Decarb Free.

A2 STEEL ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent A2 tool steel grade with just a few clicks.
A2 STEEL DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

