H10 Tool Steel - 1.2365 - 32CrMoV12-28 - JIS ~SKD 7

H10 Tool Steel - 1.2365 - 32CrMoV12-28 - JIS ~SKD 7
Back to Steel Overview
H10 STEEL PRICE CHART
H10 STEEL STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
32CrMoV12-28
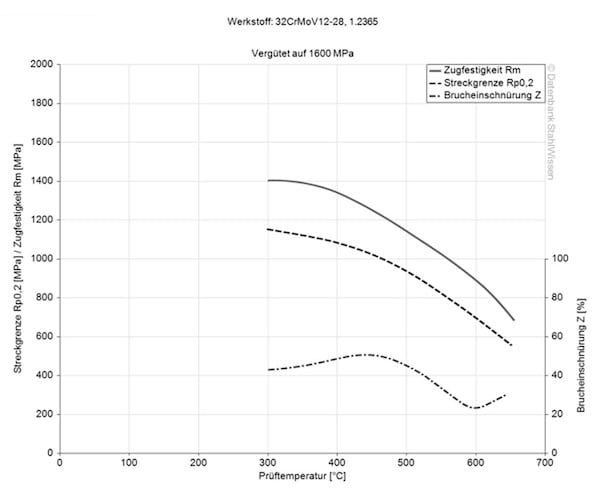
50 HRC - 52 HRC
max. 229 HB
32CrMoV12-28
50 HRC - 52 HRC
max. 229 HB

H10 STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
The thermal conductivity, which makes the H10 steel grade unresponsive to temperature changes and the ability to be water cooled, make H10 an excellent choice for high-speed forging dies or for tools which are exposed to high thermal strains.
H10 offers high toughness and can be used very well for cold forming. The former mentioned characteristics make this tool steel the best choice for a lot of applications in a good variety of industries.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the corrosion resistance for H10 Steel stands at 3.
H10 tool steel has good thermal toughness, high hot hardness and is resistant to thermal cracking. This makes the H10 a good choice for forging, hot punches or hot shear blades for example.
H10 STEEL TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Typically the density of H10 tool steel is 0.281 lb/in3 (7.78g/cm3) at room temperature.
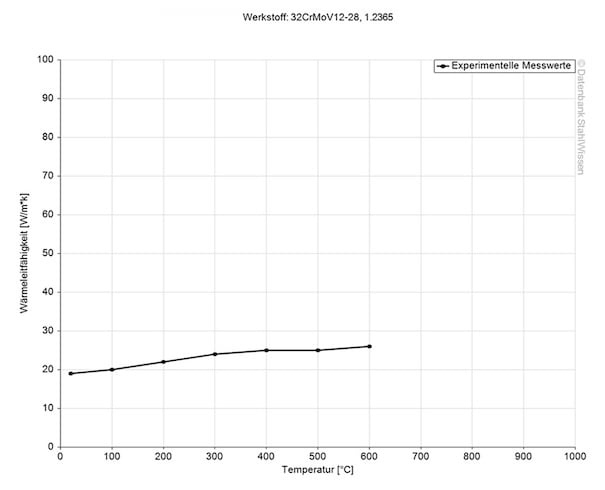
The thermal conductivity for tool steel H10 is at 32.8 W/(m*K) (227 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) in its annealed condition at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | ||
Value (annealed) | Value (tempered) | By temperature |
32.8 | 31.4 | 68°F |
34.5 | 32.0 | 662°F |
32.2 | 29.3 | 1292°F |
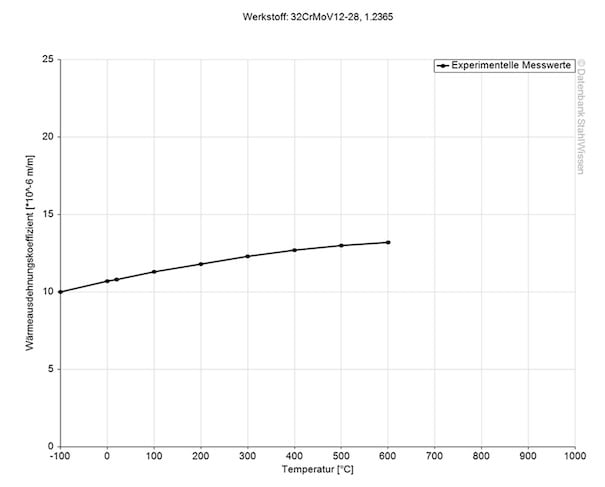
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
11.8 | 68 - 212°F |
12.5 | 68 - 392°F |
12.7 | 68 - 572°F |
13.1 | 68 - 752°F |
13.5 | 68 - 932°F |
13.6 | 68 - 1112°F |
13.8 | 68 - 1292°F |
The specific heat capacity of the H10 tool steel at room temperature is 0.46 J/(g*K).
This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
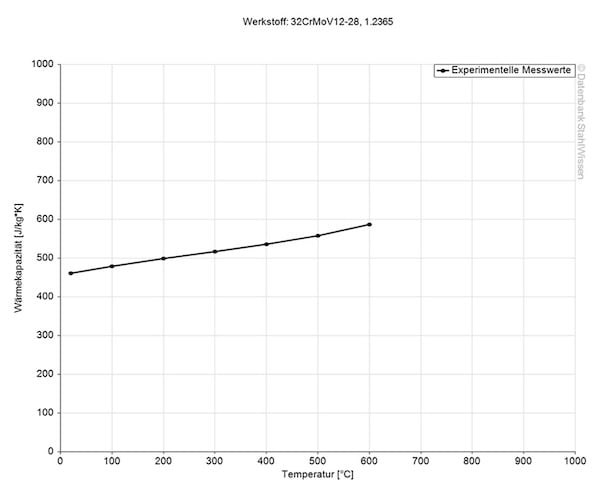
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
3.37 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |

HIGHEST PRECISION!


H10 STEEL PROCEDURE
Precaution should be taken to avoid excessive decarburization/carburization.
Hold for 2 - 6 hours, the time depends on the size of the parts, in a neutral atmosphere, then cool slowly in the furnace.
Quench for maximum hardness in oil, for most applications this material can be quenched in air. To minimize decarburization quench in salt or a controlled atmosphere furnace.
To avoid excessive distortion and/or quench cracking, cooling should be done uniformly and at a sufficient cooling rate.
• Air
• Oil
• Controlled atmosphere furnace
• Salt bath, at a temperature of 932 - 1022°F (500 - 550°C), hold the temperature for 15 - 30 minutes after equalizing.
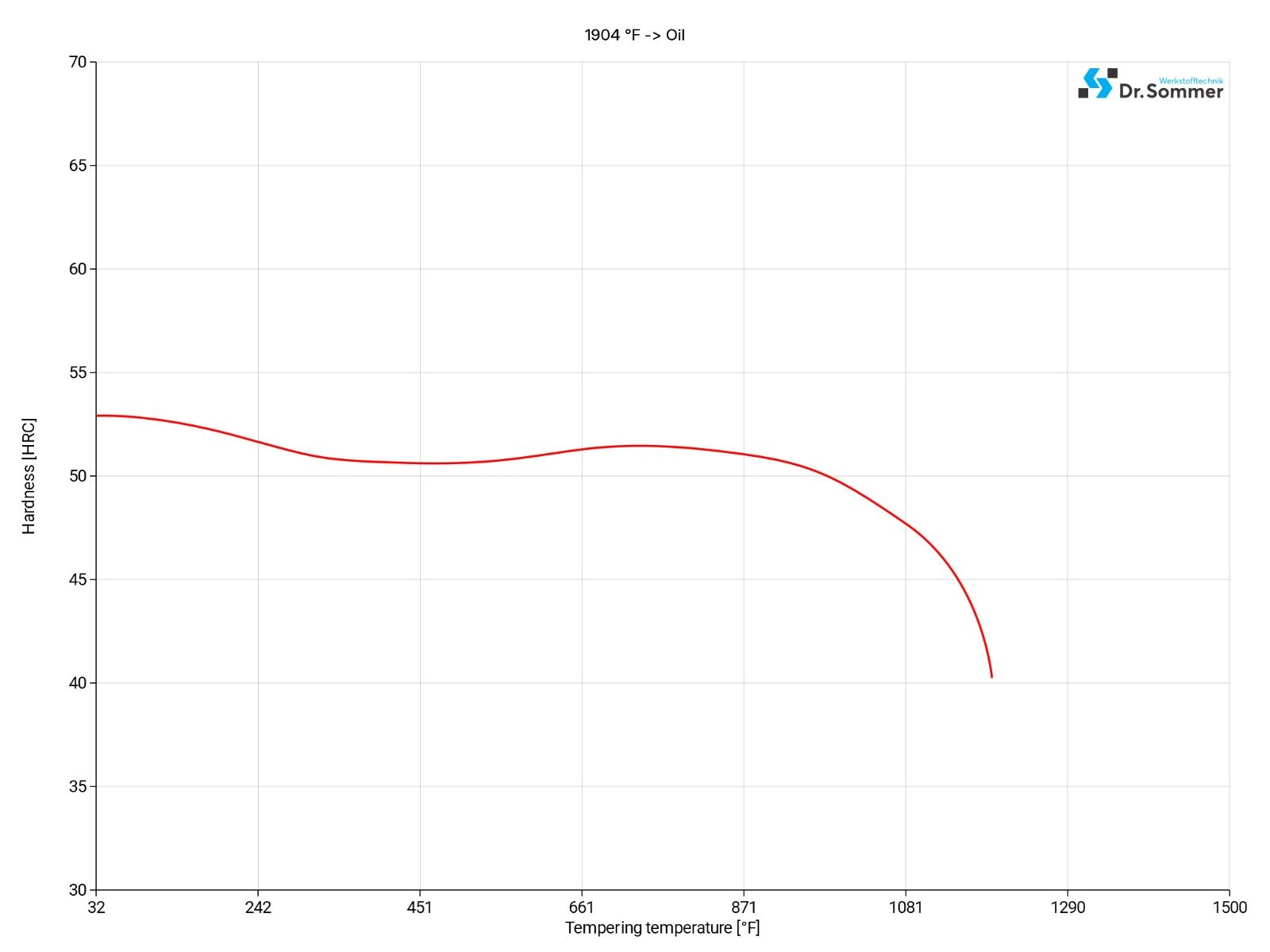
Temper the H10 steel material immediately after hardening for at least 2 hours for smaller pieces and 1 hour per 25/32 inch (20mm) of thickness for larger pieces, at a temperature of 842 - 1058°F (450 - 570°C).
To achieve a better toughness, it is recommended to temper this material twice; a third tempering cycle can be advantageous to relieve stress. The third tempering cycle should be done at a temperature of 86 - 122°F (30 - 50°C) below the highest tempering temperature.
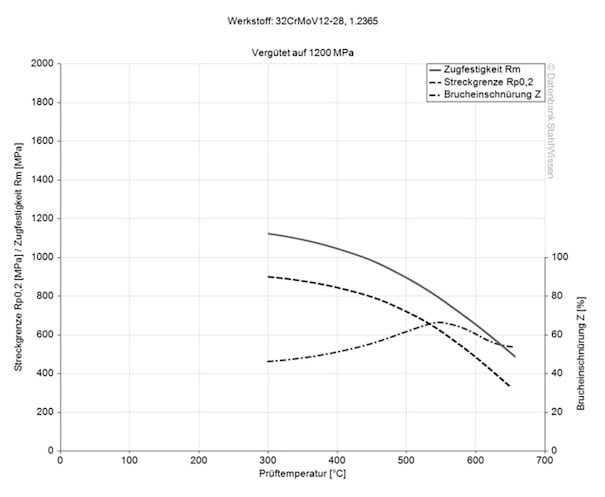
This diagram shows micro changes over time at different temperatures. Those are important during heat treatment as they show information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
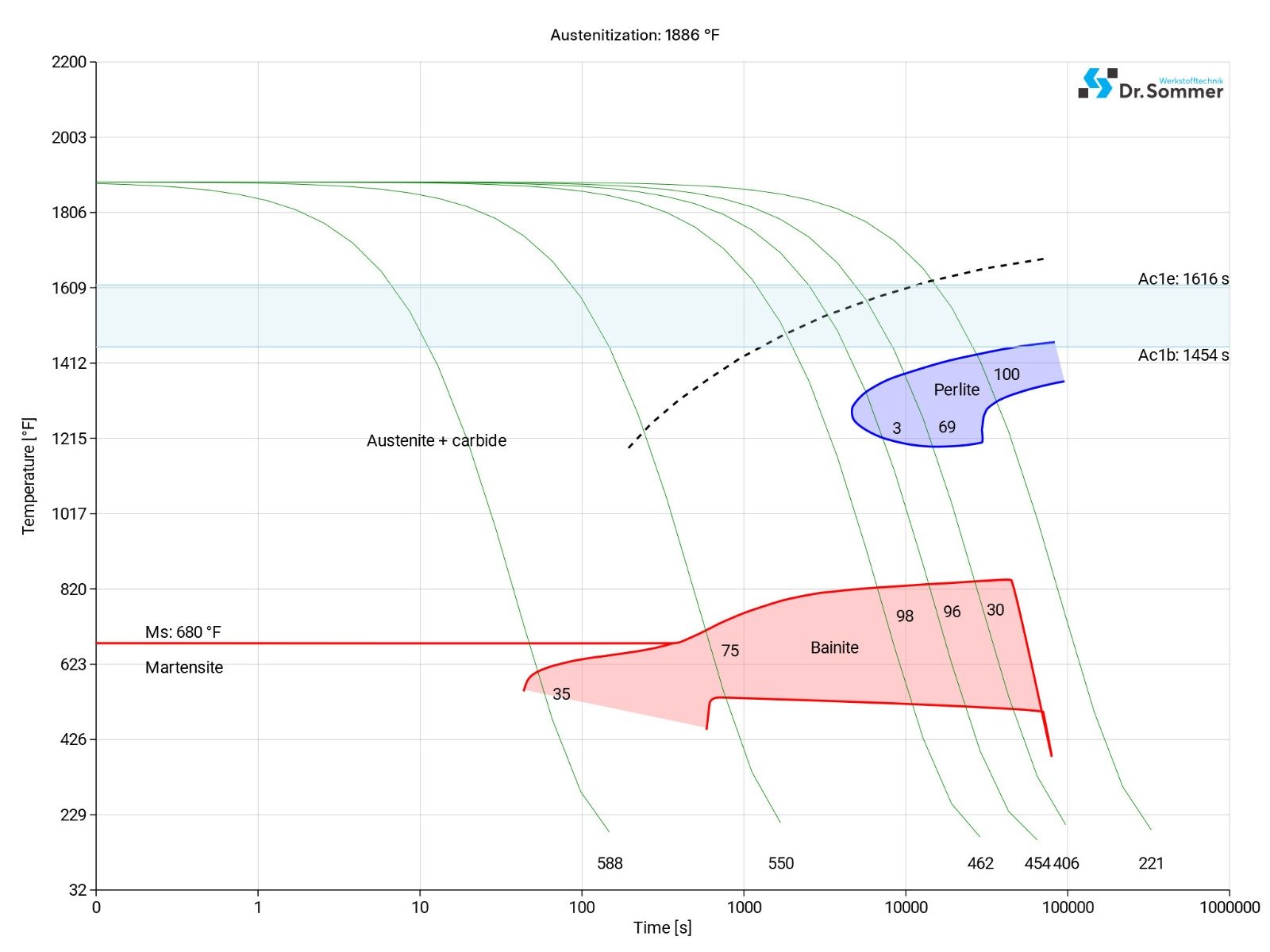
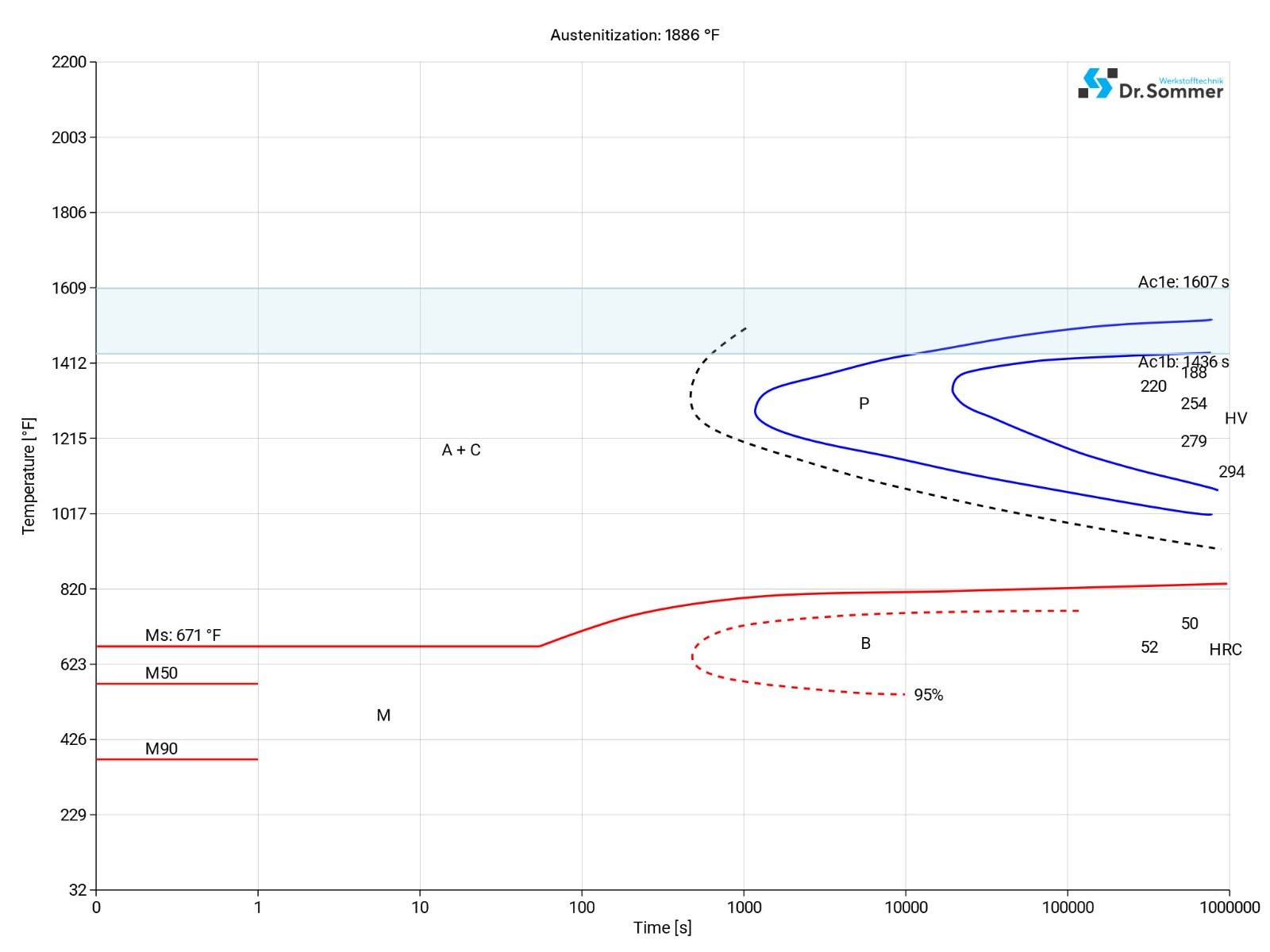
This diagram shows the structural changes at micro level over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperature and after what time different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite or bainite start to build.
H10 STEEL SURFACE TREATMENT
H10 TOOL STEEL PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of H10 reaches a score of 5.
Dimensional changes can happen during phase changes, through improper quenching, from residual stresses and decarburization. It is important to use correct temperatures, relief stresses and quench the material properly to minimize the possibility of distortion or warping.
Reheat as often as necessary and do not let the temperature drop below 1650°F (899°C). To finish the process, cool slowly in lime, dry ash or in the furnace and always anneal after forging.
H10 STEEL APPLICATION OPTIONS
H10 can be used in a wide variety of applications like hot punches, extrusion tools, die inserts as well as hot shear blades, ejector pins, tool holders, tools for extrusion for processing copper alloys like inner sleeves or the processing of light metals for bridge dies and piercing mandrels.
• Extrusion presses
• Brass casting
• Press tools
• Die inserts
• Die casting molds
• Plastic molds
• Recipient bushes
• Pressure dies
• Press mandrels
• Tube extrusion mandrels
• Piecer plugs
• Press dies
• Block receivers
• Screw production
• Nut production
• Rivet production
• Bolts production
• Hot shear knives

H10 STEEL CONCLUSION
Practically, this means:
- High toughness
- Very good for cold forming
- High hardness has a positive effect on wear resistance
- High hardness can pose a challenge during machining
- Working hardness is in the range of 50 - 52 HRC
- Hot work steel
- For the automotive industry
- For metal processing and manufacturing
- For mechanical engineering
We offer this steel as H10 Flat Stock.

H10 STEEL ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
H10 STEEL DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

