420 mod. Stainless Steel - 1.4021 - X20Cr13 - ~SUS 420J1

420 mod. Stainless Steel - 1.4021 - X20Cr13 - ~SUS 420J1
Back to Steel Overview
420 MOD. STEEL PRICE CHART
420 mod. STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
X20Cr13
approx. 25 HRC (delivery condition) - 47 HRC
max. 252 HB
X20Cr13
approx. 25 HRC (delivery condition) - 47 HRC
max. 252 HB

420 mod. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
420 mod. stainless steel has an average corrosion resistance that can be enhanced by fine grinding or polishing the surface to a high finish.
Finely ground or polished it lends itself for cutlery, blades, kitchen articles or decorative purposes but it can be also used in moderately aggressive media, steam or freshwater.
420 mod. does loose ductility at sub-zero temperatures and strength when over tempering this material at elevated temperatures.
It is part of the 400 Series Stainless Steel.
A stainless steel has a minimum mass fraction of 10.5% chromium.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the corrosion resistance for 420 mod. stands at 5.
420 mod. is resistant to oxidation up to a temperature of 1112°F (600°C). This grade is not suitable to be used in sea water as pitting corrosion will occur when used in this environment.
In general, the corrosion resistance of this steel grade is lower than common austenitic grades. To enhance corrosion resistance for this steel, parts should be finished with a finely ground or polished surface.
Heat the material uniformly to a temperature range of 2100 - 2250°F (1149 - 1232°C). Hot working this steel below 1700°F (927°C) should be avoided as cracking may occur.
Corrosion resistance is compromised by discoloration caused by hot forming, welding or by scaling. These should be removed by pickling (pickling solution), grinding or sandblasting. For this process only iron-free tools may be used.
It is not recommended to cold work this material in this condition, only for minor modifications can be done to the material.
Severe manipulation will result in cracking of the material. This steel grade is most often machined to shape.
420 mod. TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Typically the density of 420 mod. stainless steel is 0.278 lb/in3 (7.7g/cm3) at room temperature.
This value is the result from a tensile test to show how much force is needed before the material starts to stretch or elongate before it breaks.
The yield strength shows how much stress can be applied to a material before it plastically deforms. Beyond this point it does not return to its original form when the stresses have been removed.The material deforms permanently or breaks past that point.
The heat conductivity for the 420 mod. stainless steel is at 30 W/(m*K) (208 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.5 | 68 - 212°F |
11.0 | 68 - 392°F |
11.5 | 68 - 572°F |
12.0 | 68 - 752°F |
The specific heat capacity of the 420 mod. stainless steel at room temperature is at 0.46 J/g-°C (0.109 BTU/lb-°F).
This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.6 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |

PERFECT MATERIAL SELECTION WITH THE ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE®: STEEL-GUIDE.US

420 mod. PROCEDURE
Controlled heating and cooling is crucial to achieve the ideal structure and properties for this steel grade.
To finish this process, cool the material down to room temperature in still air. Finally inspect the material to see that the reduction of residual stresses has been achieved and mechanical properties and dimensions have not been altered.
Quenching is done rapidly to transform austenite back to martensite.
• Oil
• Air
• Polymer
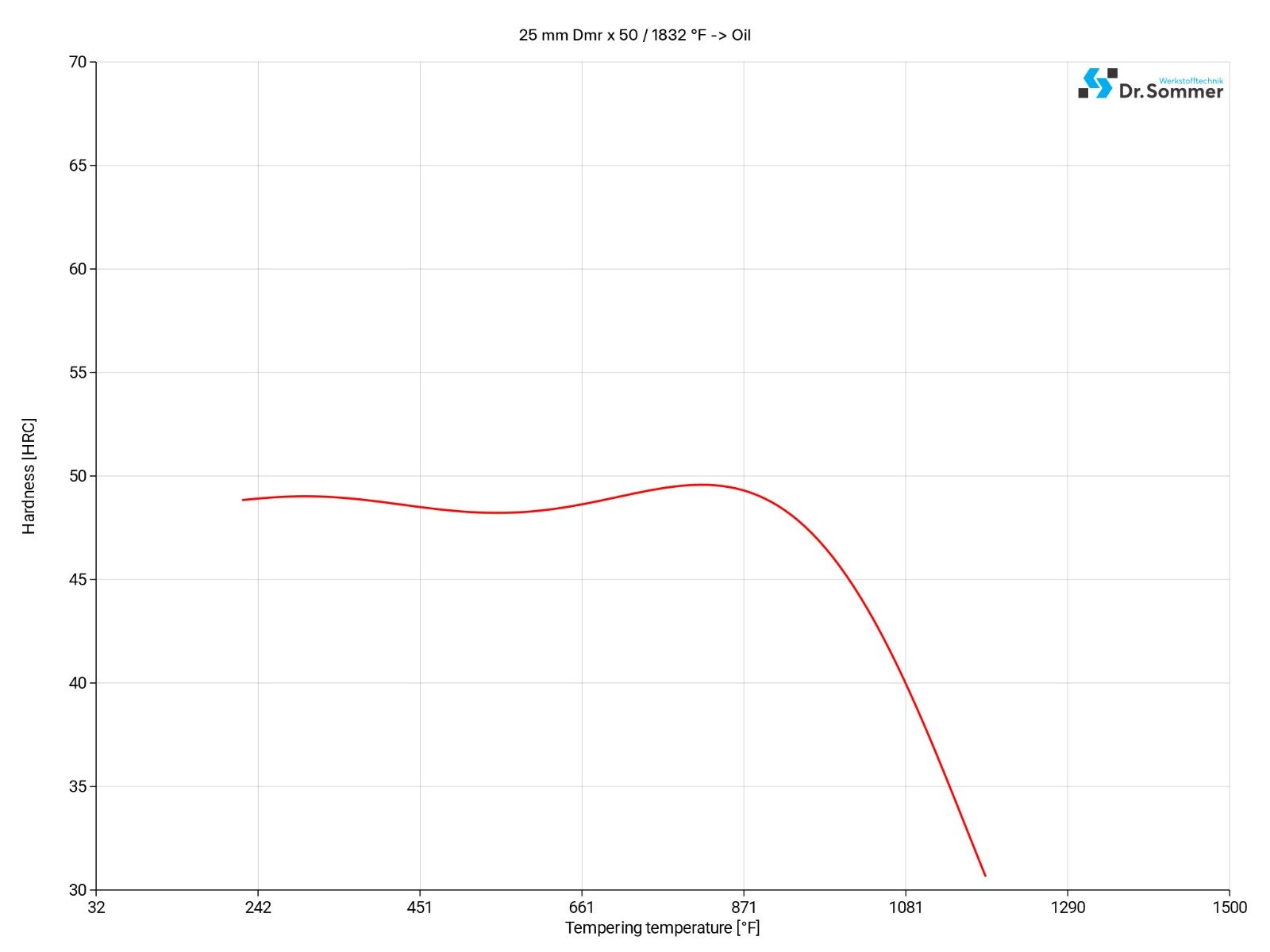
The tempering temperature is chosen for hardness requirements, to reduce brittleness after quenching or to adjust the balance between hardness and toughness.
Tempering temperatures for the 420 mod. are between 1112 - 1292°F (600 - 700°C), the temperature range of 752 - 1112°F (400 - 600°C) should be avoided due to precipitation and unwanted phases.
420 mod. SURFACE TREATMENT
Note: Protective gear like goggles, masks, helmets, gloves and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
Appropriate guards to prevent shot spillage should be in place, equipment regularly maintained and shot should be free from contaminants.
Note: Care has to be taken during this process as the process produces dust and small parts might be propelled back. Protective gear like masks, helmets and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
420 mod. PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of 420 mod. reaches a score of 4.
Machining 420 mod. is essentially no different than machining non-alloy carbon steels of similar or matching strength.Heating and cooling lets any material grade expand or contract but also can phase changes and stress relieve be a factor for dimensional changes and should be considered when tight tolerances are needed. Controlled heat treatment and good machining practices can support dimensional stability.
Forge the parts at the range of 2012 - 1652°F (1100 - 900°C) and finish the process by cooling the parts down slowly in the furnace or dry ash or similar materials that promote slow cooling.
Though 420 mod. has poor weldability it can be welded by all types of welding processes.
When gas welding care should be taken to avoid contamination, for example nitrogen or hydrogen, as this will affect the mechanical properties of the parts.
Preheat parts to 392 - 572°F (200 - 300°C) and if a filler is needed it should match the base metal. Let the parts cool down to 248°F (120°C) before tempering. To restore some of the ductility in the weld zone it should be tempered at a temperature of 1202°F (650°C).
420 mod. APPLICATION OPTIONS
The 420 mod. can be used for applications needing high hardness, strength and moderate corrosion resistance like kitchenware, cutlery, pumps, shafts, valves or machine components like gears, bolts and nuts.
• Automotive industry
• Power engineering
• Turbine and power plant construction
• Medical technology
• Mechanical engineering
• Petrochemical industry
• Cutting tool industry
• Knives
• Fasteners
• Architecture and decoration

420 mod. CONCLUSION
- Corrosion-resistant stainless steel (quenched and tempered version shown here)
- Martensitic chromium steel
- Good mechanical properties
- Can be polished to a mirror finish
- Suitable as knife steel
- Good forgeability
- Medium weldability
- Limited acid resistance
- Magnetizable
- Cold formable (low degree of deformation)
- Not resistant to seawater
We offer this steel as 420 Mod. Flat Stock and Metric 420 Mod. Cold Finished Round Bars.

420 mod. ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
420 mod. DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

