420 ESR Tool Steel - 1.2083 ESU - X40Cr14 - SAE 51420

420 ESR Tool Steel - 1.2083 ESU - X40Cr14 - SAE 51420
Back to Steel Overview
420 ESR STEEL PRICE CHART
420 ESR STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
X40Cr14
50 HRC - 55 HRC
max. 241 HB
X40Cr14
50 HRC - 55 HRC
max. 241 HB

420 ESR PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
420 ESR Steel (ESR = Electro-Slag-Refined or Remelted), a corrosion-resistant cold work steel, belonging to the plastic mold steels, with a high chromium content it has very good corrosion resistance (in its hardened condition) and good wear resistance.
It can easily be machined and is, due to the purity of the ESR material, highly polishable. With high compression strength and high wear resistance, the low-distortion through-hardener is suitable for injection molds of all types where good resistance to chemical aggressive molding compounds are required.
The remelting process provides this tool steel with a very low inclusion content, which makes it possible to provide a mirror finish when used for instance for lens molds or photoetching.
Electro-Slag-Remelted or ESR is a process where steel is remelted and passes through slag which removes debris and impurities from the steel.
What is left is steel with a higher cleanliness and a finer, more homogeneous microstructure. Reducing the impurities from steel gives the steel an overall integrity as there are fewer weak spots.
ESR steel can exhibit better mechanical properties like higher tensile strength, yield strength, toughness, wear resistance, better surface finishes, longer tool life.
Specifically for the 420 ESR as an already corrosion resistant steel, the ESR process improves the corrosion resistance due to the reduction of inclusions and other impurities.
To be classed as stainless steel the material has to have at least 10.5% chromium, the 420 ESR has 12.5 - 14.5% of chromium.
It is part of the 400 Series Stainless Steel.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the corrosion resistance for 420 ESR stands at 4.
Careful management is required to cold work the 420 ESR to prevent cracking and dimensional accuracy. Cold working this material can enhance its hardness and strength.
420 ESR TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
Due to its purity, toughness, corrosion resistance and edge retention the 420 ESR lends itself to knife making. Though the 420 ESR has good corrosion resistance, regular maintenance, cleaning and drying will prolong tool life and performance.
Typically the density of 420 ESR tool steel is 0.282 lb/in3 (7.8 g/cm3) at room temperature.
The yield strength shows how much stress can be applied to a material before it plastically deforms. Beyond this point it does not return to its original form when stresses are removed. The material deforms permanently or breaks past that point.
The thermal conductivity for tool steel 420 ESR is at 22.6 W/(m*K) (157 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
22.5 | 73.4°F |
24.0 | 302°F |
24.6 | 572°F |
24.9 | 662°F |
24.4 | 752°F |
23.7 | 932°F |
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
11.1 | 68 - 212°F |
11.6 | 68 - 392°F |
12.0 | 68 - 572°F |
12.3 | 68 - 662°F |
12.4 | 68 - 752°F |
12.5 | 68 - 842°F |
12.6 | 68 - 932°F |
The specific heat capacity of tool steel 420 ESR is at room temperature at 0.46 J/g-°C (0.109 BTU/lb-°F).
This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.6 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |

PASSION!


420 ESR PROCEDURE
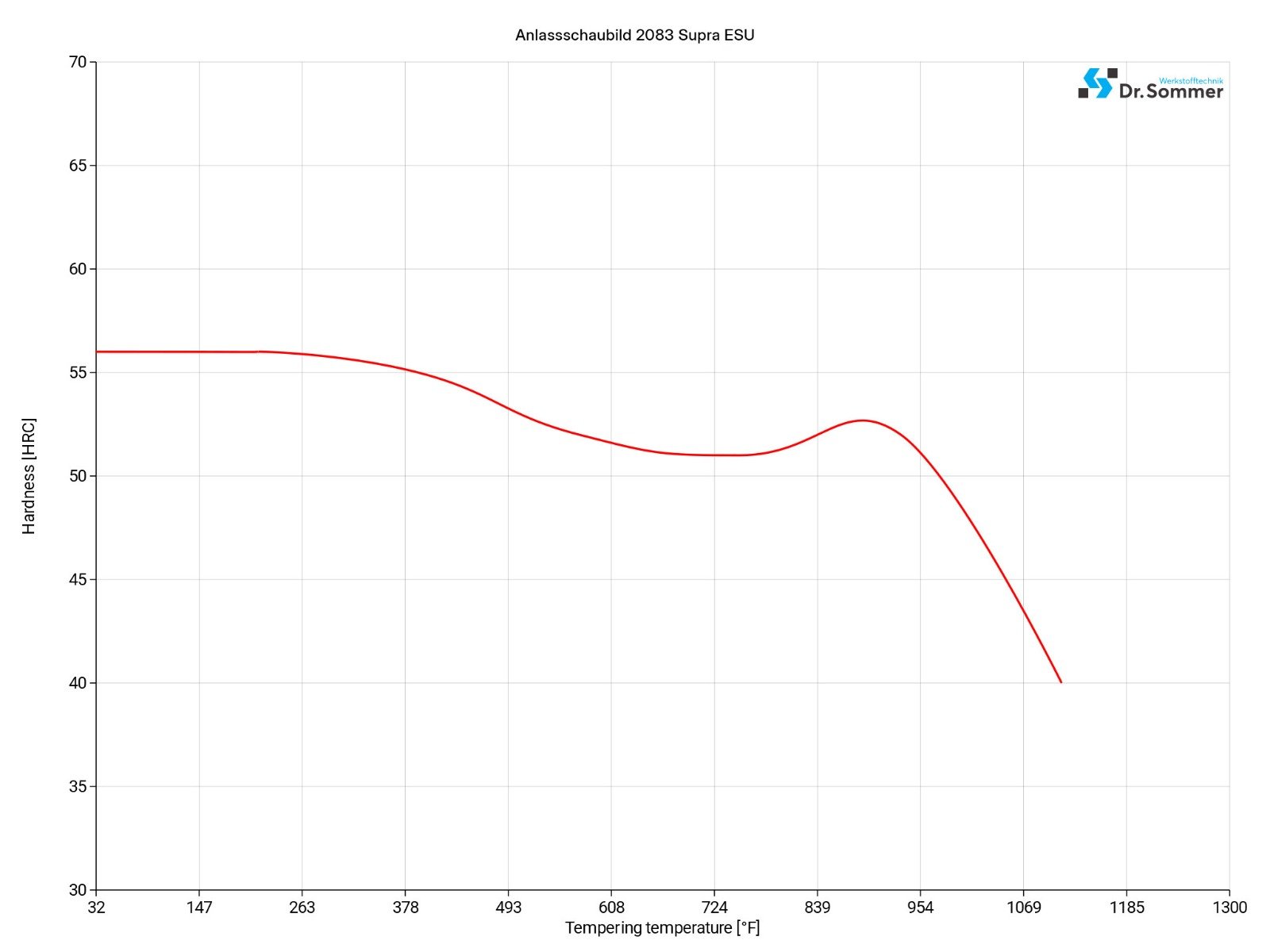
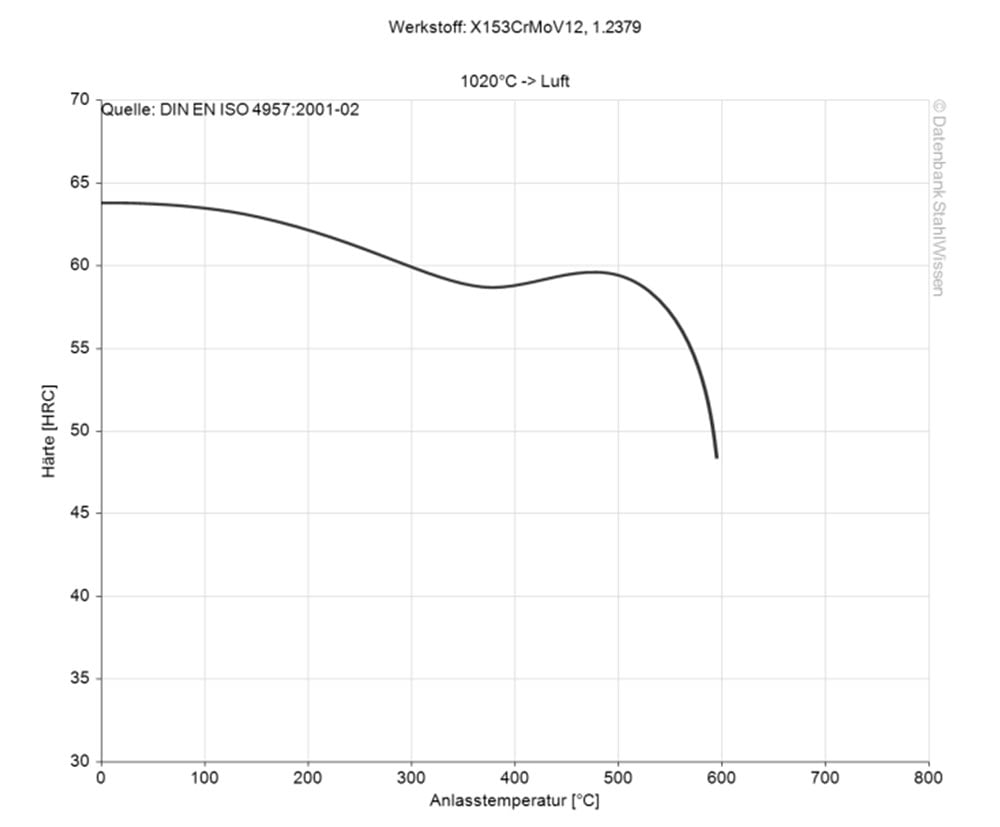
To austenitize the material heat to 1850 - 1952°F (1010 - 1067°C).
Cool quickly to obtain the best properties for the tool, but care should be taken that the rate of cooling is not as fast as to distort or crack the material.
It is recommended when heat treating in a vacuum furnace to use a minimum of 4 - 5 bars of overpressure. Then temper immediately when the parts reach the temperature of 120 - 160°F (50 - 70°C).
• Fluidized bed or salt bath at 480 - 1020°F (250 - 550°C), then cool in air blast
• Vacuum with sufficient positive pressure
• Warm oil, approx. 176°F (80°C)
Choose the tempering temperature that needs to be achieved, temper twice and cool between tempering to room temperature.
Do not let the tempering temperature drop below 480°F (250°C) and hold at the chosen temperature for a minimum of 2 hours.
The temperature of 480°F (250°F) is recommended to achieve the best blend of hardness, toughness as well as corrosion resistance.
Cryogenic treatment for the 420 ESR can transform retained austenite to martensite and can enhance properties like dimensional stability for this material.
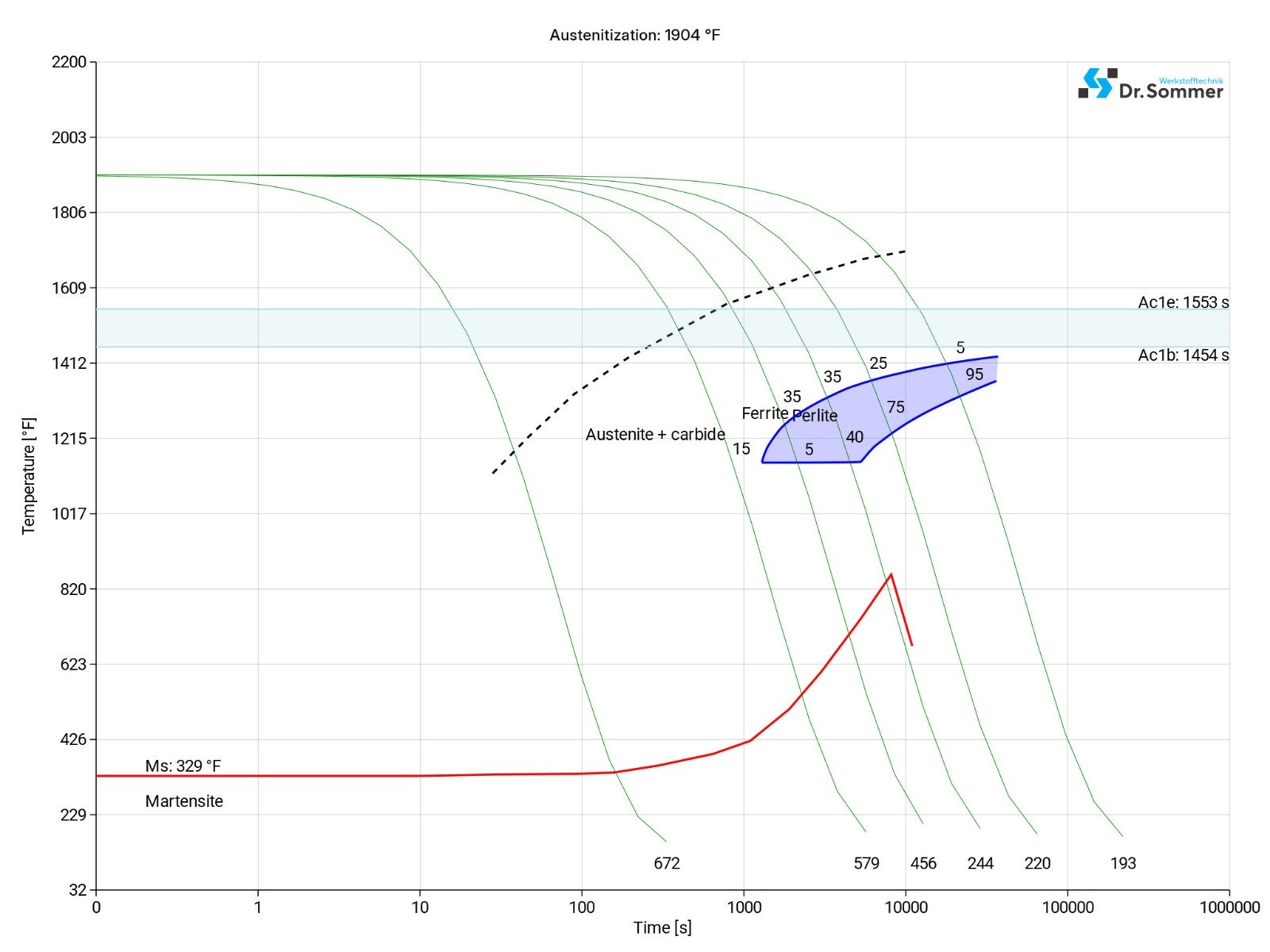
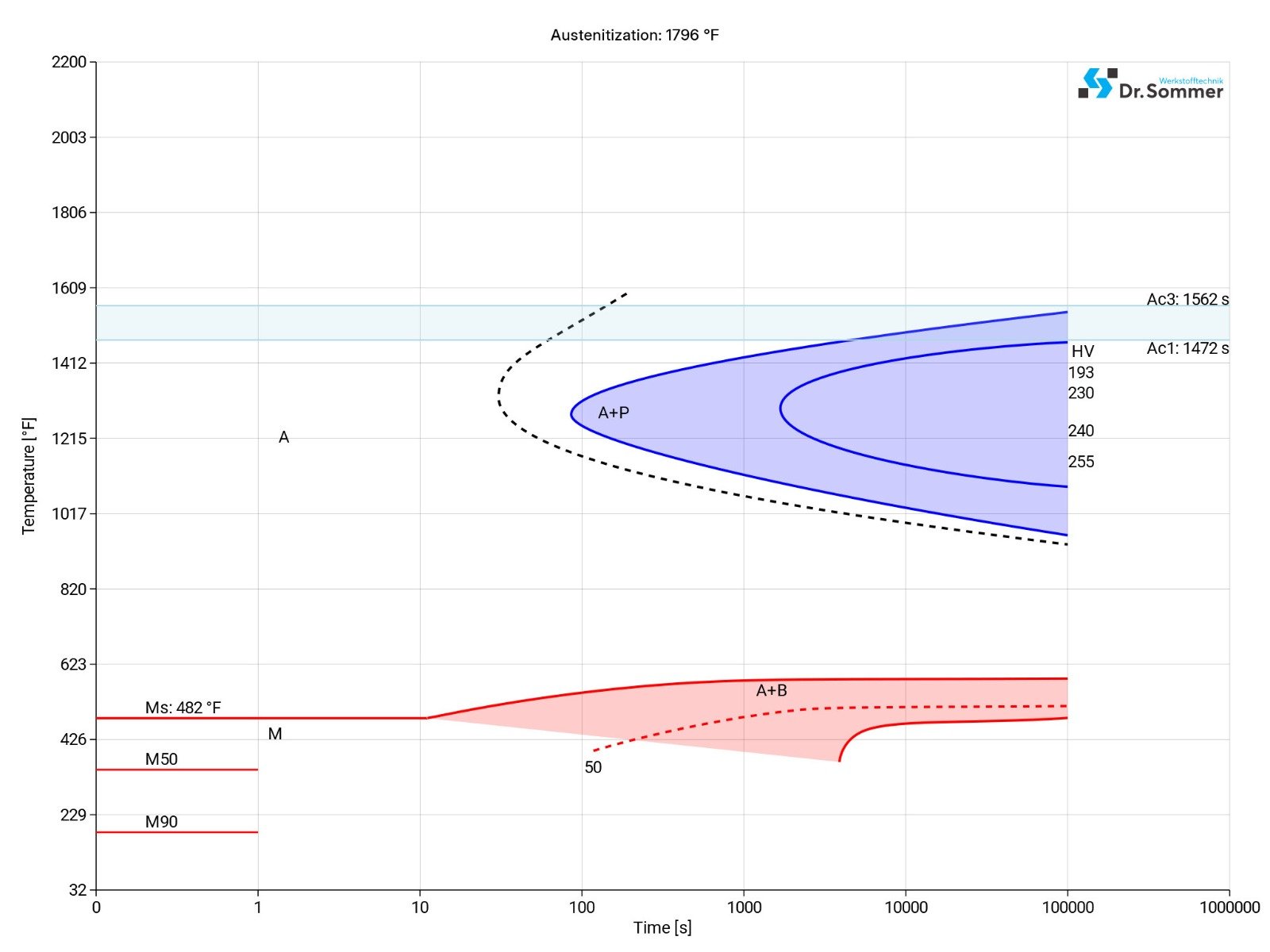
The continuous time-temperature-transformation-diagram (short TTT) shows how the micro structure changes over time at different temperatures. This information is important during heat treatment and provides information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
A TTT-diagram typically shows the various phases and conditions of the steel and show the time and temperature when certain changes happen (e.g., perlite, bainite and martensite).
420 ESR SURFACE TREATMENT
420 ESR PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of 420 ESR reaches a score of 4.
As a hard material, conventional machining methods might be challenging and can cause excessive tool wear. As there is no direct contact to the material during EDM tool wear is not an issue as such, though electrodes have to be replaced periodically.
EDM is often used for hard materials, for intricate and complex shapes, and when tight tolerances are needed as well as when parts need a good surface finish.
Welding should be avoided, if possible, due to the high risk of cracking.
Should welding be essential, heat material through to 392 - 482°F (200 - 250°C) and hold at that temperature to prevent cracking. After welding, temper hardened material at 50 - 70°F (10 - 20°C) below the original tempering temperature. For soft annealed material heat through to 1630°F (890°C) in a protected atmosphere.
Then furnace cool at 40°F (20°C) per hour to 1560°F (850°C) and then at 20°F (10°C) per hour to 1290°F (700°C). From there it can be cooled further in air.
Fillers with the same composition as the base metal should be used.
Due to the ESR process, 420 ESR has a very low inclusion content and makes it therefore suitable for photo-etching.
420 ESR APPLICATION OPTIONS
Applications with corrosion or staining resistance, e.g., for molding of corrosive materials like PVC, acetates, for molds subjected to humid working conditions as well as surgical and dental instruments and tools.
Wear resistance, e.g., for molding abrasive materials and high surface finish, e.g., for the production of optical parts, such as lenses, for cameras and sunglasses, and for medical containers.
• Mechanical engineering
• Medical technology
• Plastic molds
• Synthetic resin mold tools
• Die casting tools
• Light metal die casting
• Cutting tools
• Machine knives
• Kitchen knives
• Razors
• Shears
• Scraper blades
• Surgical instruments
• Measuring tools
• Roller bearings
• Ball bearings
• Ice-skates
• Pump parts
• Valves

420 ESR CONCLUSION
- Plastic mold steel
- Cold work steel
- Corrosion resistant
- Acid resistant
- Low distortion
- Good machinability
- Good hardenability
- Etchable
- Very good polishability
- Nitriding is not common
We offer this steel as 420 ESR Flat Stock.

420 ESR ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
420 ESR DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

