AISI 430F - Stainless Steel - 1.4104 - X14CrMoS17 - ~SUS 430F

AISI 430F - Stainless Steel - 1.4104 - X14CrMoS17 - ~SUS 430F
Back to Steel Overview
430F STEEL PRICE CHART
430F STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
X14CrMoS17
approx. 26 HRC (delivery condition)
max. 270 HB
X14CrMoS17
approx. 26 HRC (delivery condition)
max. 270 HB

430F PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
In comparison with other martensitic stainless steels containing 17% of chromium, AISI 430F has a lower corrosion resistance due to the added Sulphur.
The added Sulphur gives 430F stainless steel an excellent machinability, with a fine ground surface finish which can be used for construction parts for applications in water and steam. Due to its corrosion resistance and appearance this steel grade is often used for decorative applications and kitchen fittings.
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the corrosion resistance for 430F stands at 4.
430F TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
It has moderate corrosion resistance and toughness which might let the 430F chip or break. This makes it a possible steel for cutlery knives but it will not make a good blade for knives with higher performance demands.
Typically the density of stainless steel 430F is 0.278 lb/in3 (7.7g/cm3) at room temperature.
This value is the result from a tensile test to show how much force is needed before the material starts to stretch or elongate before it breaks.
The heat conductivity for stainless steel is at 25.0 W/(m*K) (173 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.0 | 68 - 212°F |
10.5 | 68 - 392°F |
10.5 | 68 - 572°F |
10.5 | 68 - 752°F |
The specific heat capacity of the 420 FM tool steel at room temperature is at 0.46 J/g-°C (0.109 BTU/lb-°F).
This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.70 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |

HIGHEST PRECISION!


430F PROCEDURE
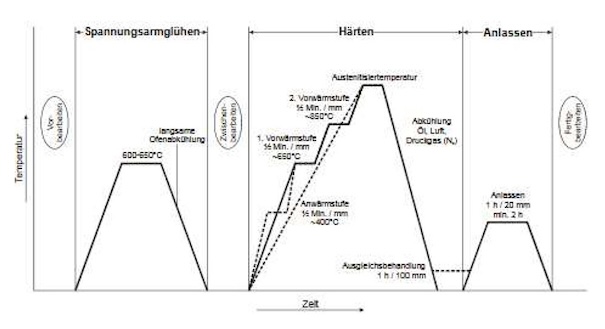
The 430F stainless tel can be quenched in the following media:
• Air
• Oil
• Compressed gas (N2)
Widely used quenching medias for this steel grade are:
- • Oil for simple geometries
- • Vacuum
- • Forced Air/Air/Gas
- Martempering bath or fluidized bed at 360 – 930°F, then cool in air
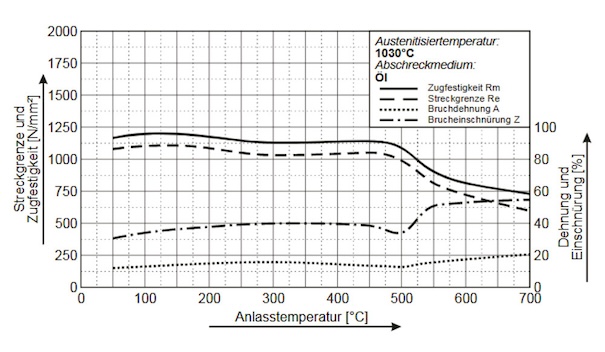
Heat the parts uniformly to temperature of 1022 - 1202°F (550 - 650°C) and cool in air. The temperature for the tempering process depends on the desired strength.
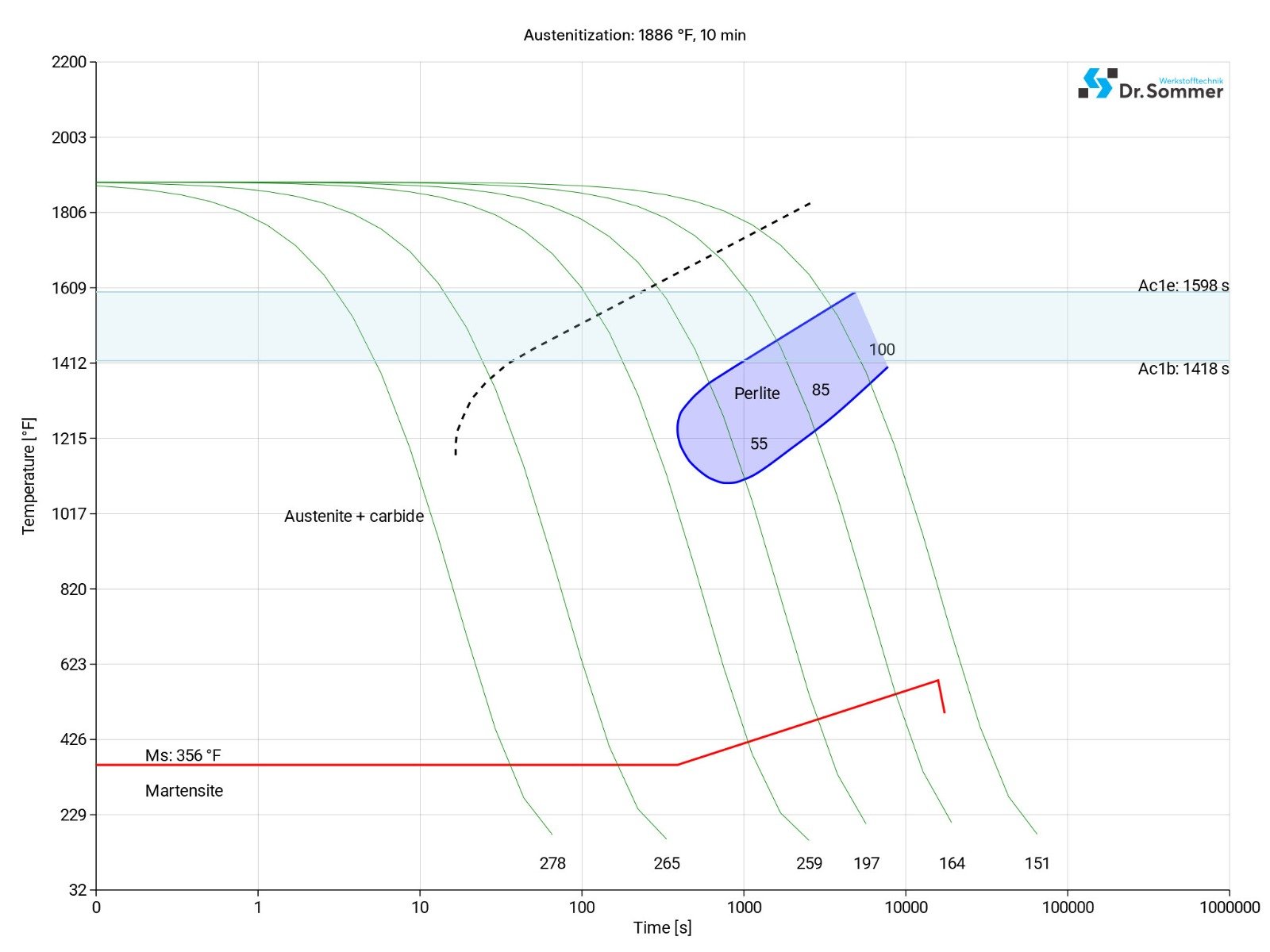
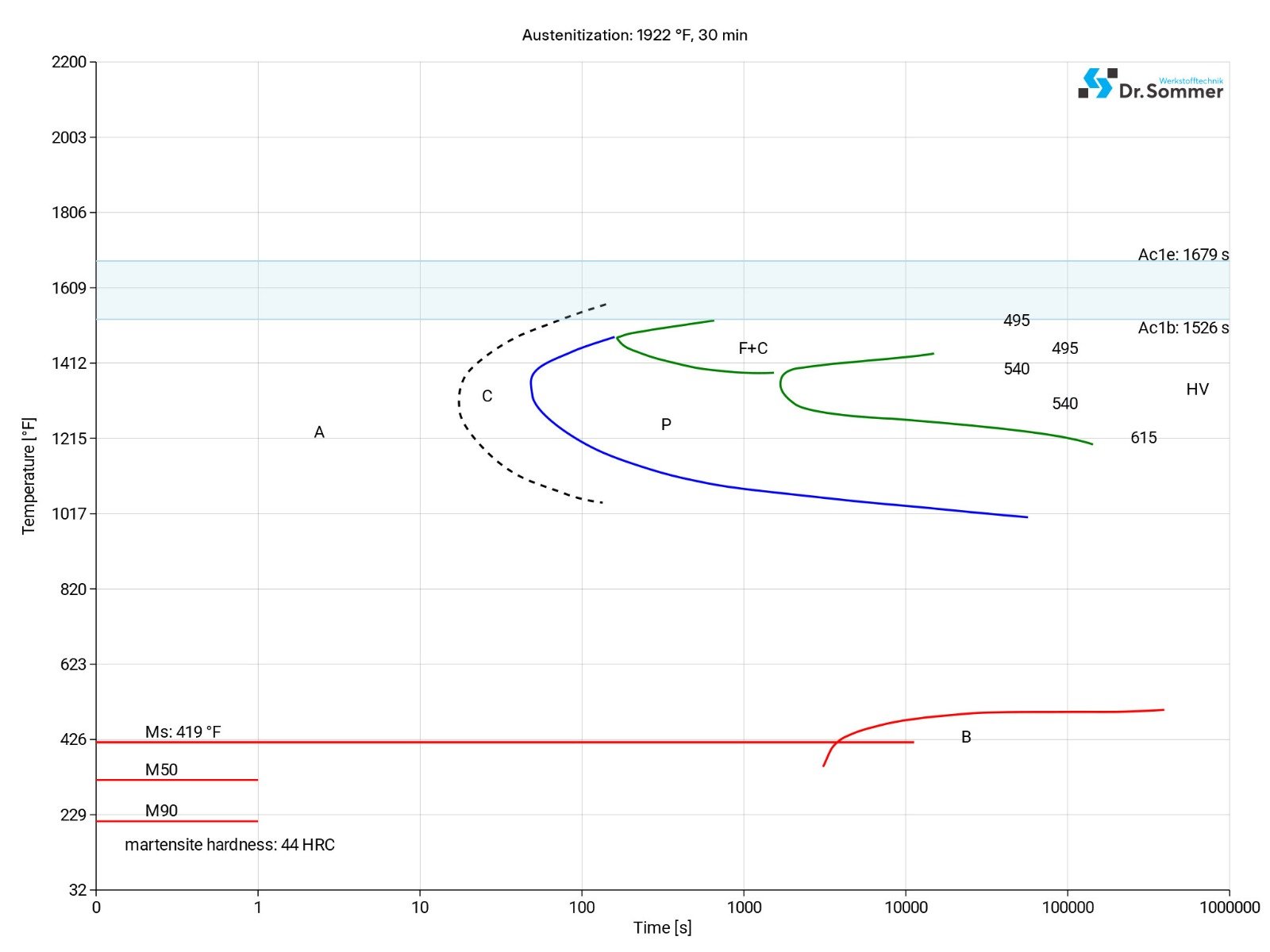
This diagram shows micro changes over time at different temperatures. Those are important during heat treatment as they show information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
430F SURFACE TREATMENT
Note: Care has to be taken during this process as the process produces dust and small parts might be propelled back. Protective gear like masks, helmets and protective clothing should be worn and adequate ventilation or dust extraction should be provided.
430F PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of 430F reaches a score of 6.
With the addition of Sulphur this stainless steel has a better machinability in comparison to other 12 and 17% chromium steels.
EDM is used for parts made from one individual piece, for cutting dies or when making intricate shapes. There are various methods to erode various materials, some of them are for example wire erosion, spark erosion or die sink erosion.
When using EDM for the 430F care should be taken to minimize heat affected zones and use the correct parameters to remove material.
Overheating, uneven heating or cooling should be avoided and controlled heating and cooling as well as proper machining with sharp tools, coolant and feed can prevent heat build up and thermal shock.
Do not let the temperature drop below 1500°F (816°C) while forging and do not soak at the forging temperature as it can result in grain build up. To finish this process let the forgings air cool and anneal them after.
Generally welding this steel grade is not done due to the added Sulphur content.
Should welding be necessary though, preheat the material to a temperature of 302 - 392°F (150 - 200°C). Embrittlement in the weld metal and in the heat-affected zone can be reduced by subsequent post annealing the parts at a temperature of 1454 - 1499°F (790 - 815°C), but no microstructural refinement will take place. Choose fillers and electrodes according to the applications of the parts.
430F APPLICATION OPTIONS
Stainless steel 430F can be used for bolts, fasteners, screws, shafts, valves, injector parts and kitchen utensils to name just a few. Due to the added Sulphur it can be easily machined, is corrosion resistant and can maintain an aesthetic finish with the correct care.
• Automotive industry
• Electronic equipment
• Power engineering
• Mechanical engineering
• Connecting elements
• Architecture and decoration
• Construction parts for automatic machining in water and steam

430F CONCLUSION
- Martensitic chromium steel (quenched and tempered version shown here)
- Addition of sulphur for improved machining
- Very good polishability
- Conditionally acid-resistant
- Magnetizable
- Welding not usual
We offer this steel as 430F Flat Stock.

430F ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
430F DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

