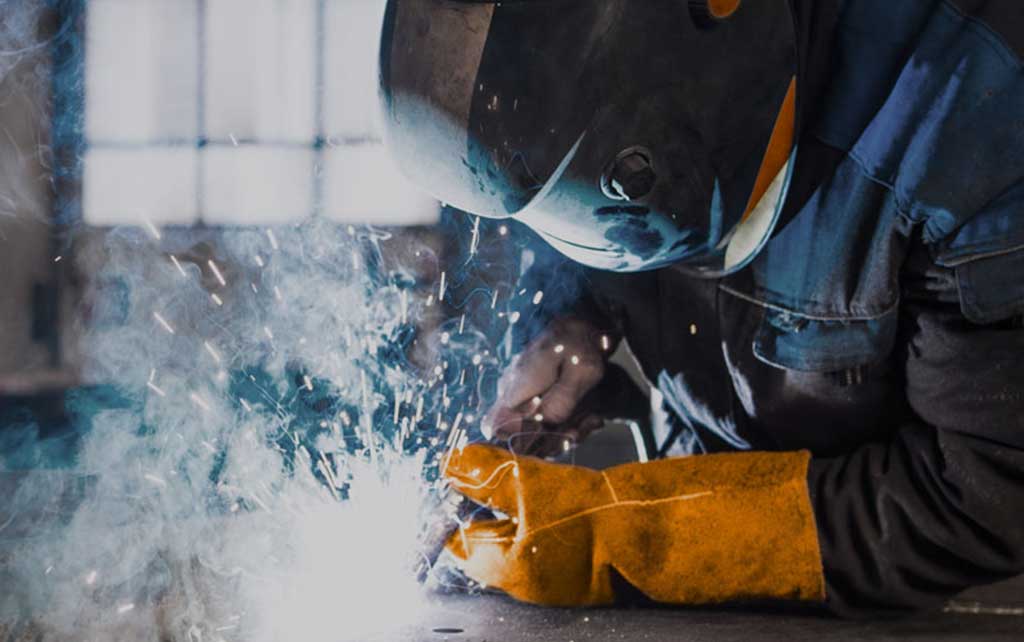
Buy Hot Work Steel without any Minimum Order Value or Quantity
During hot working metal, it is deformed above the recrystallization temperature but below the melting point. Working with this kind of heat, controlling the temperature of the workpiece is crucial to get the best results.

Your success is our success!
THE ESSENTIAL PROPERTIES OF HOT WORK STEEL
2. Termal fatigue: Thermal fatigue occurs when parts are subjected to recurring high temperatures and cooling. Hot work steel has a resistance to thermal fatigue and can endure the constant change in temperatures.
3. Thermal conductivity: Thermal conductivity is a very important property of hot work steel. Heat has to be distributed evenly as not to crack or warp the material and improve tool life as well as process stability.
4. Toughness: is important for hot work steel as it not only has to withstand high heat but also impact at the same time. Toughness is important to keep the ductility needed when great forces are used on the workpieces.
6. Fatigue resistance: is needed when parts or workpieces are exposed to repeated or cyclic stresses.Hot work steels have to resist high temperatures as well as mechanical stresses.
7. Shock resistance: The combination of toughness, formability, a refined grain structure, balanced hardness and suitable heat treatment adds to the high impact strength of hot work tool steel grades and makes them indispensable for reliable and long-lasting performance in demanding industrial environments.
8. Wear resistance: Applications like hot forging, hot extrusion or die casting expose the material to tough working conditions. High wear resistance ensures a long service life by maintaining shape, dimension and integrity.
WHAT ARE HOT WORKING PROCESSES?
Hot Forging
Forging with dies is carried out by hitting the material with a hammer or by applying high pressure from a forging press.
In addition to withstanding the temperatures of the forging, the die must have good mechanical properties such as toughness in order to withstand the pressures or blows.
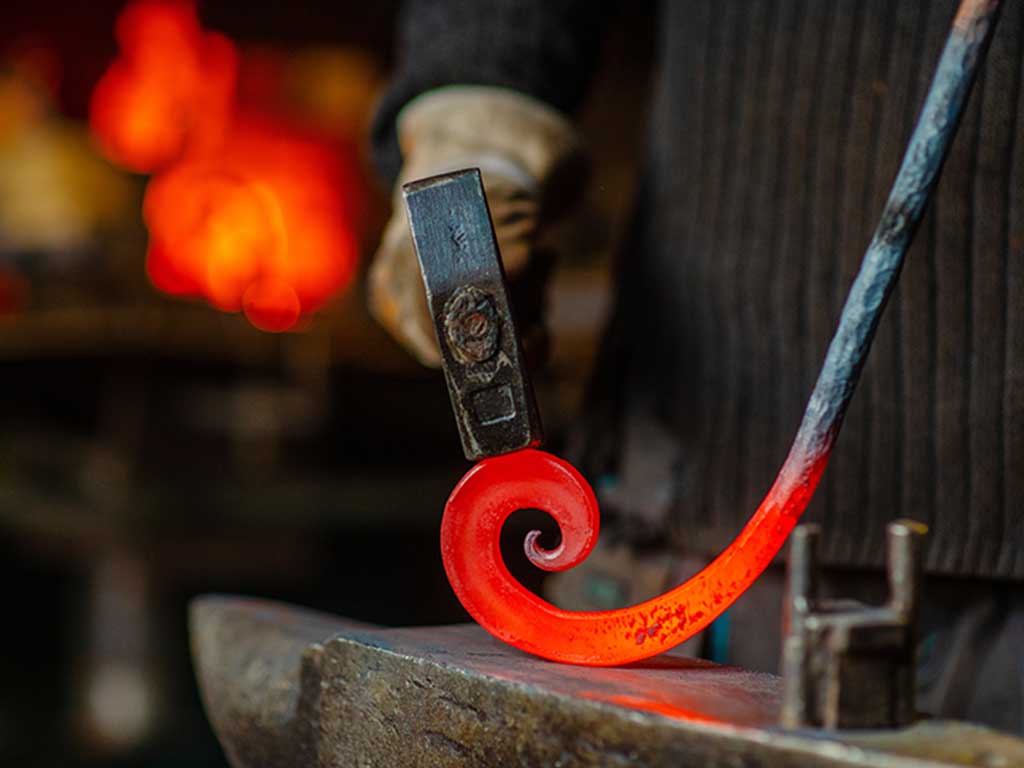
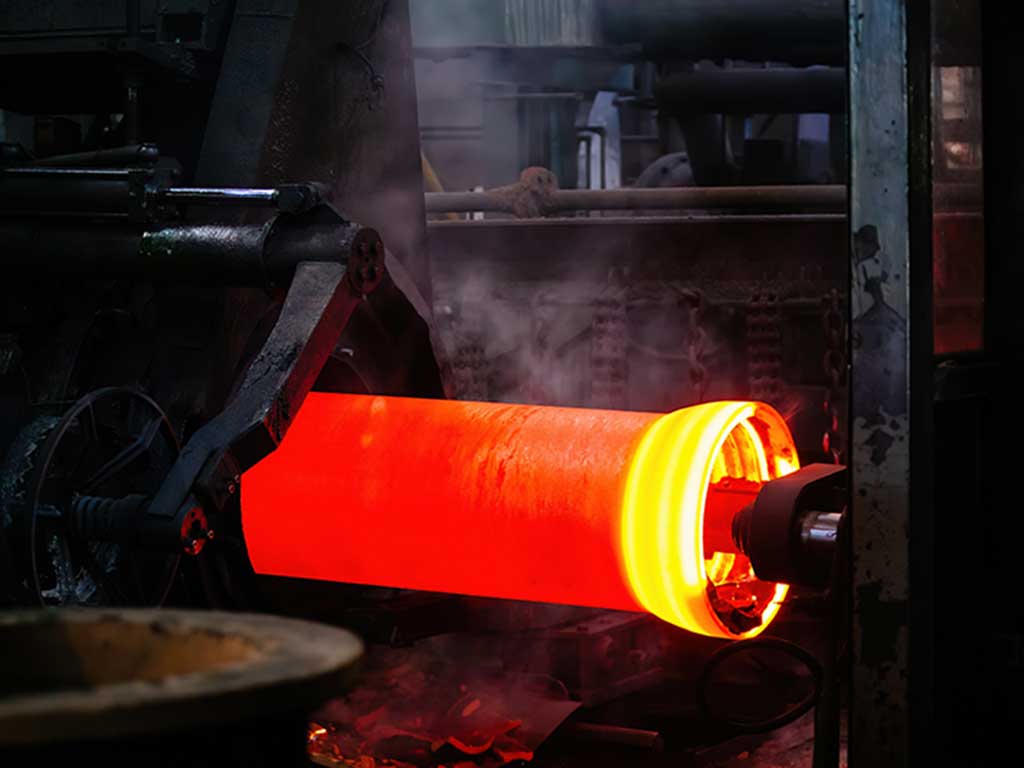


Drawing
During this process heated material is drawn through a die to increase its length.
Dies and tools used to draw hot material have to be heat resistant, and wear resistant to keep the exact shape for the continuous production of precise parts.
Hot spinning
Hot spinning, the metal which needs to be formed rotates while it is heated by an external heat source and then formed by pressure.
The tools used to form the metal are usually made from hot work steel so as not to be affected by the heat the material reaches.
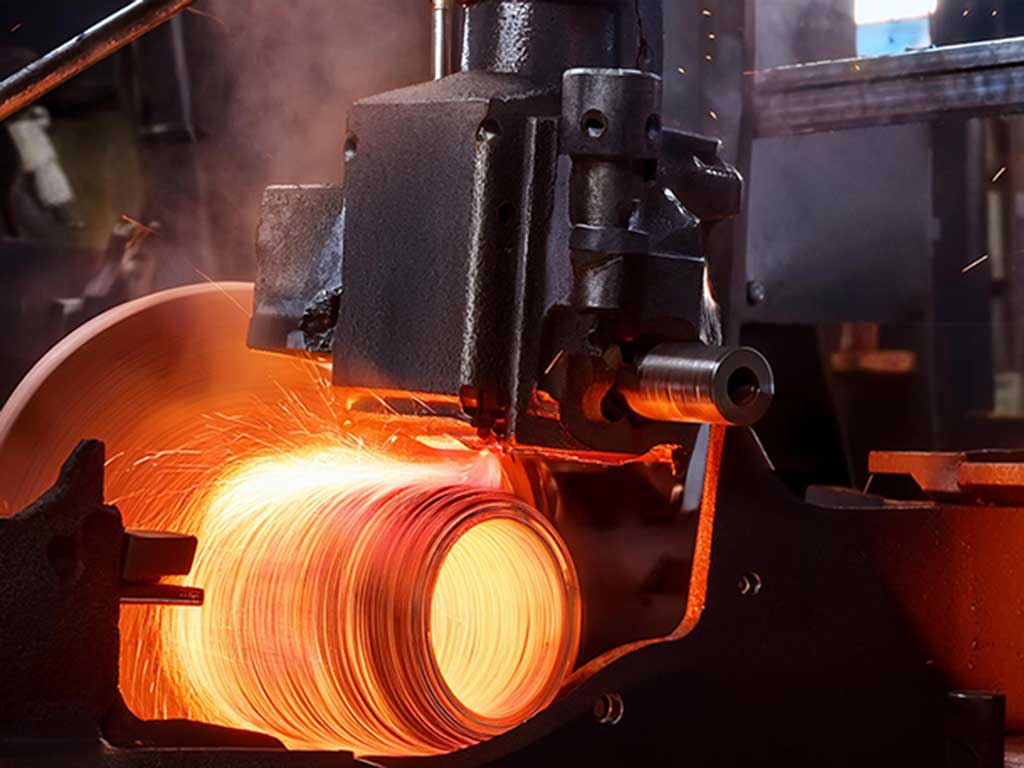
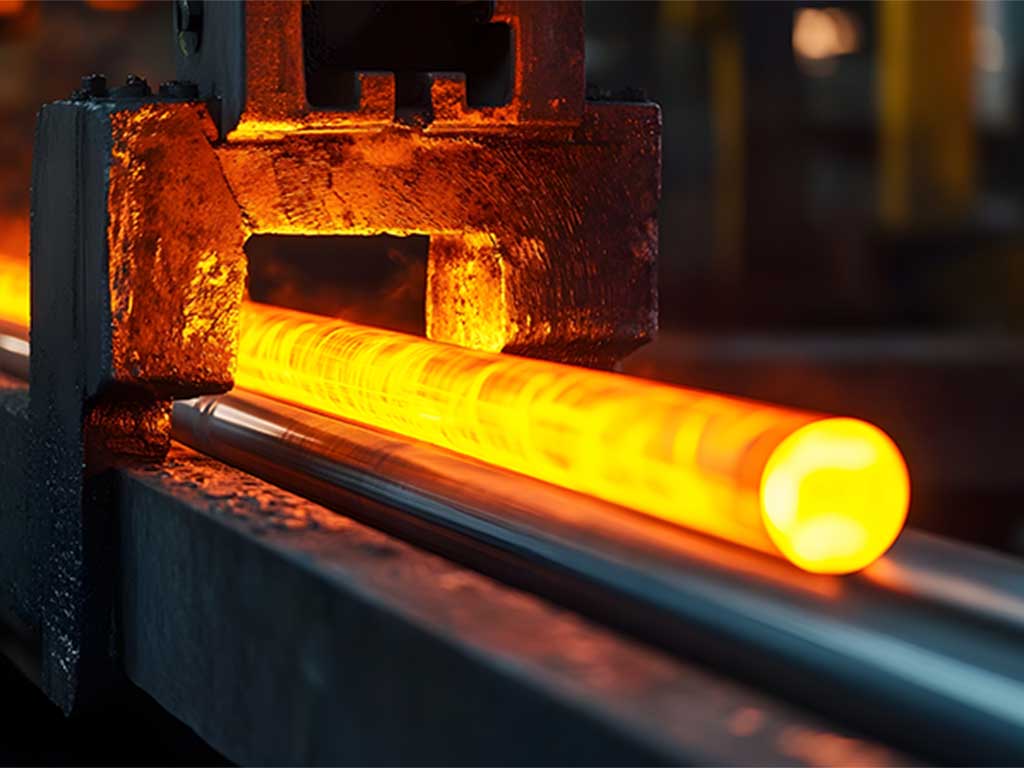


Hot Rolling
During hot rolling, heated steel is rolled between rollers to the desired shape and thickness.
Due to the contact heat and the required pressure, the rolls must not deform, break or crack.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF HOT WORK STEEL?
Like any process, hot working has some advantages but also disadvantages. Find some of them below.
Advantages | Disadvantages |
High temperature strength: Suitability of the material for high heat applications with the retention of strength and hardness | Surface oxidation and scaling: Due to the high temperatures the surface can oxidate and form scale. This does lead to an additional work step to eliminate the scaling. |
Enhanced toughness and ductility: Due to a finer grain structure hot work steel has a better toughness and ductility, preventing cracking and breaking while absorbing high impacts. | Dimensional accuracy: To achieve precise dimensional tolerances can be challenging as hot worked material might experience thermal expansion. |
Grain refinement: Hot working leads to a more uniform and finer grain structure. This improves the mechanical properties of the material. | Energy consumption: To maintain the hot working temperature a significant energy input is needed. |
Reduction of internal stresses and defects: Hot worked metal has fewer internal stresses and defects. | Potential of grain growth: Uncontrolled temperatures during the hot working process can lead to grain growth and the reduction of mechanical properties. |
Longer tool life: With its resistance to high temperatures and wear, tools made from hot worked steel have a longer tool life. | Material loss due to scaling: If the material scales during hot working it may require additional machining resulting in possible material loss. |
SUMMARY
• Temperature above the recrystallization
• Enhanced mechanical properties
• Refined grain structure
• Reduced internal stresses and defects
• Less flow stresses
• No strain hardening
• Longer tool life