4140 / 4142 Heat-Treatable Steel - 1.7225 - 42CrMo4 - ~SCM 440

4140 / 4142 Heat-Treatable Steel - 1.7225 - 42CrMo4 - ~SCM 440
Back to Steel Overview
4140 / 4142 STEEL PRICE CHART
4140 / 4142 STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
42CrMo4
27 HRC - 48 HRC
max. 217HB
42CrMo4
27 - 48 HRC
max. 217 HB

4041 / 4142 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
As a low alloy steel, 4140 / 4142 also known as chromium-molybdenum - or chrome moly steel, it relies on the added chromium, molybdenum and manganese to increase strength and hardenability, yet it has inadequate weldability characteristics.
The chromium content in this heat-treatable steel provides hardness penetration, whereas the added molybdenum provides uniform hardness and strength. The added manganese lends itself to increase strength and hardenability. 4140 / 4142 steel may be used for both low and high temperature applications and with the relevant heat treatment can be used in sour gas environments as well. 4140 / 4142 belongs to the group of high grade structural steels.
4140 and 4142 are nearly identical but for a slightly higher carbon content for the 4142. Where the steel composition of the 4140 has a carbon content of 0.38 to 0.43%, 4142 has carbon content of 0.4 to 0.45%.
4140 / 4142 is, even with a chromium and molybdenum content, not a classic 10.5% chromium stainless steel. It belongs to the group of high grade structural steels.
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high, the corrosion resistance for 4140/4142 stands at 2. 4140 / 4142 has some corrosion resistance due to the chromium and molybdenum content but will rust when corrosion has set in.
4140 / 4142 steel is magnetizable.
This steel can be hot worked at 1500-1900°F (816-1038°C), it maintains its properties even after long exposure at the high working temperatures.
In its annealed condition, this steel can be cold worked with all the conventional methods
On a scale where 1 is low and 6 ist high, 4140 / 4142 comes in at a score of 3.
4140 / 4142 TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
When choosing to make a knife or blade from 4140 / 4142 the hardness and corrosion resistance as well as wear resistance should be considered. Though possible this steel grade is not commonly used to make knives with.
The working hardness for this material grade is in a range of 262 - 456 BHN (27 - 48 HRC (Rockwell hardness)).
The density of 4140 / 4142 at room temperature (~68°F) is 0.284lb/in3 (7.85g/cm3).
4140 / 4142 has a tensile strength of approx. 104.4 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The yield strength of 4140 / 4142 is at approx. 95 KSI. This shows when the material starts to show plastic deformation.
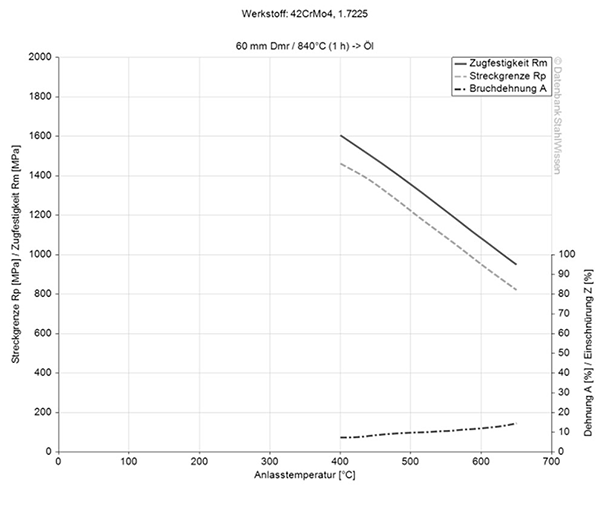
The heat conductivity for 4140 / 4142 at room temperature is at 42.6 W/(m*K) (313 BTU/(h-ft2*°F))
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
42.6 W/(m*K) | 68°F |
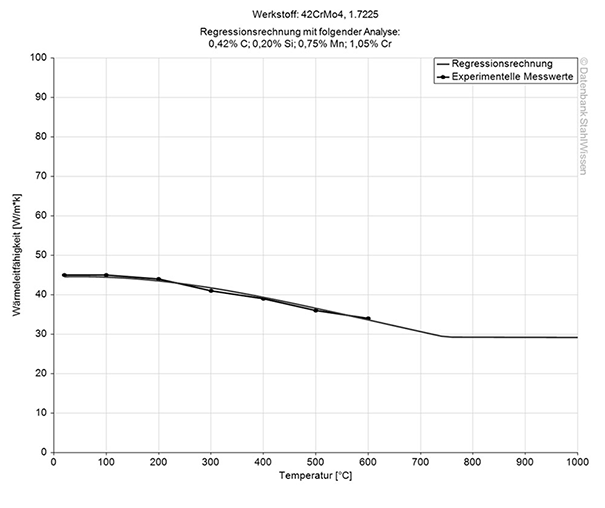
This diagram shows how much 4140 / 4142 might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
11.1 | 68 - 212°F |
12.1 | 68 - 392°F |
12.9 | 68 - 572°F |
13.5 | 68 - 752°F |
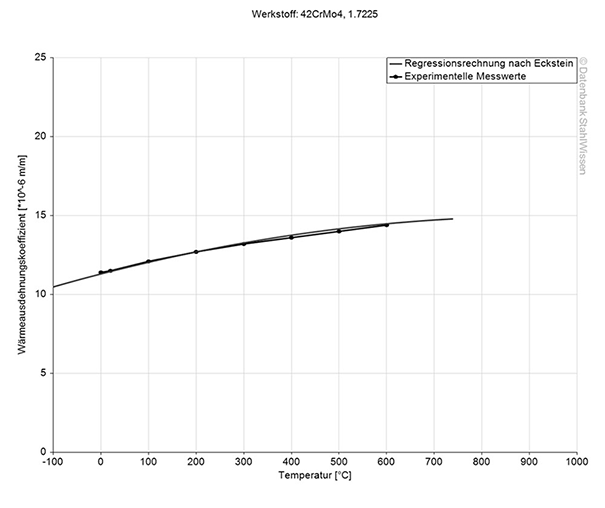
This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of 4140 / 4142 by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
~ 0.231 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 68°F |
~ 0.284 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 212°F |
~ 0,358 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 392 °F |
~ 0,448 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 572 °F |
~ 0,552 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 752 °F |
~ 0,671 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 932 °F |

MAXIMUM FLEXIBILITY – THAT IS OUR $MART FLAT!


4140 / 4142 PROCEDURE
4140 / 4142 can be heated to 1580°F (860°C) and quenched in oil. The material can be normalized and tempering can achieve a good range of properties.
Uniformly heat the work pieces to 1256-1328°F (680-720°C), followed by a slow cooling in the furnace to reach the annealed hardness of approx. 217 BHN.
4140 / 4142 should be heated to 1100-1300°F (593-705°C), held at that temperature for 2 hours and then the work pieces are cooled in air.
To harden 4140 / 4142 the material should be heated slowly and uniformly to 1508-1580°F (820-860°C) followed by water or oil quenching, depending on the size and complexity of the work pieces. After hardening the material can achieve a working hardness between 262 and 456 BHN (27 - 48 HRC).
4140/4142 can be quenched in oil to room temperature and then should be tempered immediately.
Alloy 4140 / 4142 can be tempered at 1004-1256°F (540-680°C) subject to hardness and according to the properties required. Cool in air after the treatment.
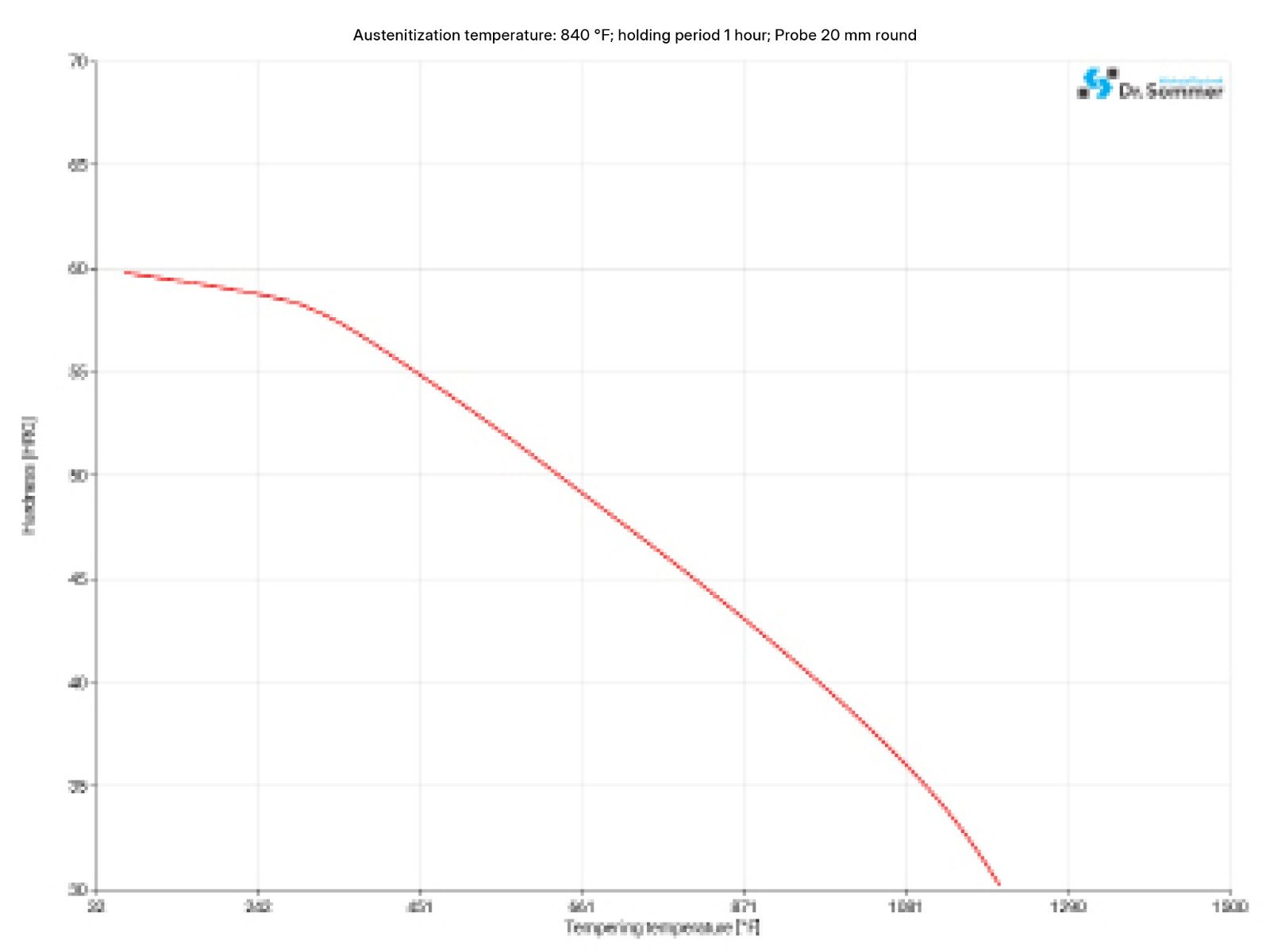
4140 / 4142 can be tempered at 1004 - 1256°F (540 - 680°C), the higher the tempering temperature the softer and more ductile it gets. In general hardness and ductility are determined by tempering the material, the higher the ductility the lower the hardness which is true for the reverse as well. Apart from the advantage to give the steel the wanted and needed properties the material can be stress relieved, is less likely to crack and has a better deformation behavior by tempering it.
This steel grade can be normalized before hardening. Heat to 1544-1616°F (840-880°C), followed by air cooling.
This diagram shows micro changes over time at different temperatures. Those are important during heat treatment as they show information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
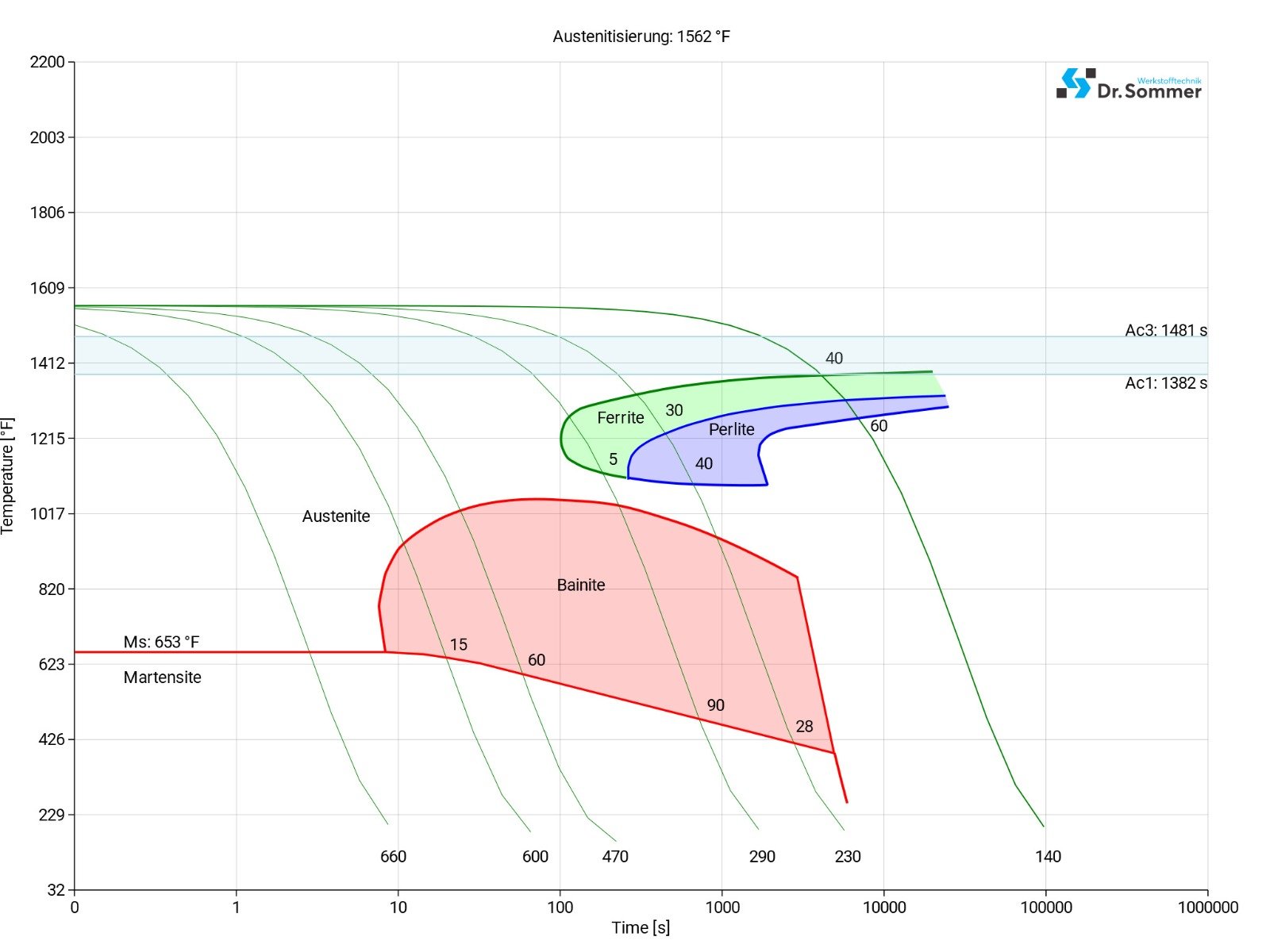
This diagram shows the structural changes at micro level over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperature and after what time different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite or bainite start to build.
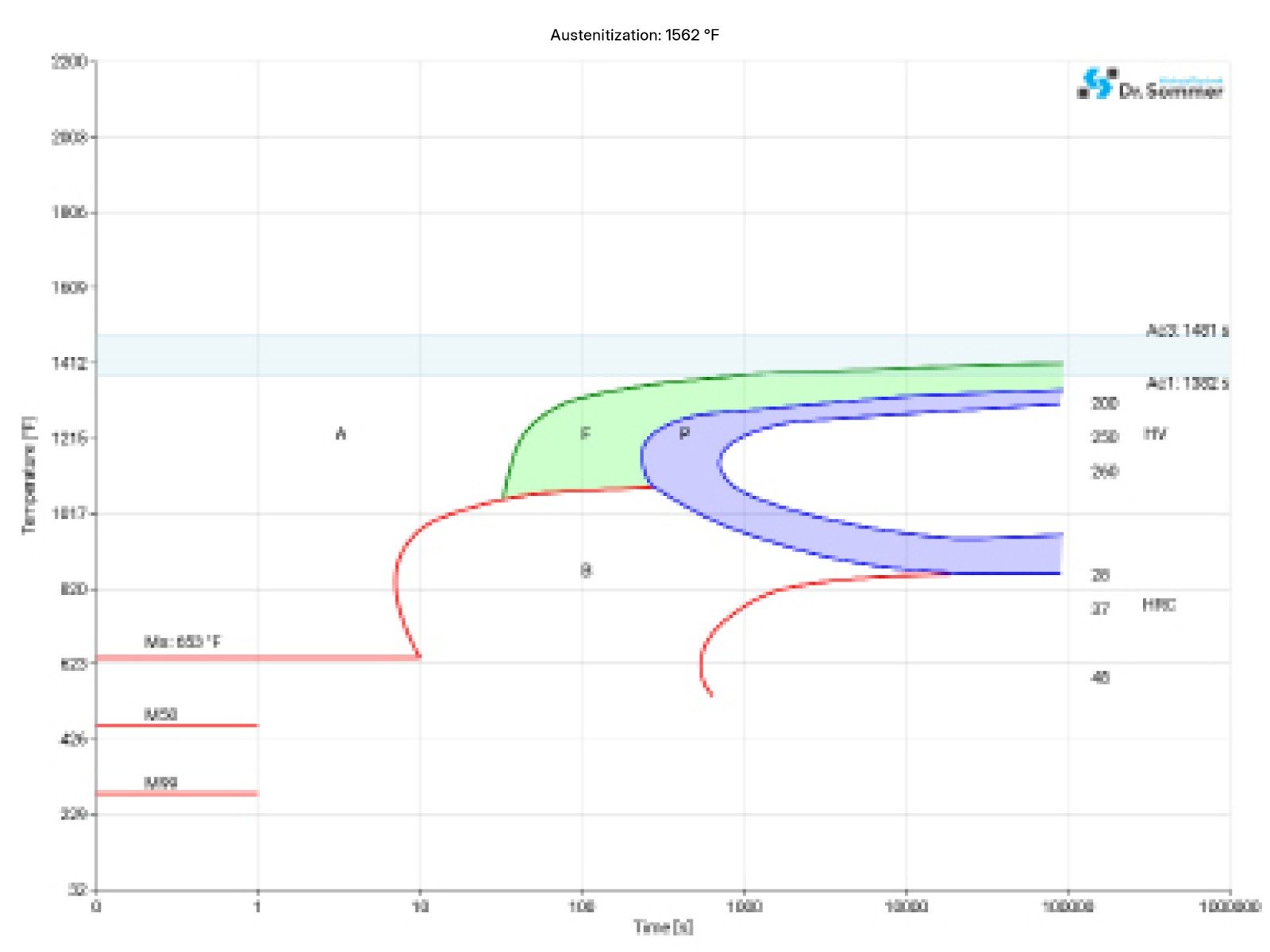
4140 / 4142 SURFACE TREATMENT
4140 / 4142 can be nitrided to give this steel grade a harder surface layer.
4140 / 4142 PROCESSING
This grade is easily machinable after it has been heat treated to produce the microstructure required for the best machinability.
It is possible to EDM this steel grade in the annealed and hardened condition. As for all EDM work the recast layer has to be removed thoroughly by stoning and polishing.
4140 / 4142 has a creep resistance up to a temperature of 1004°F (540°C) and is able to sustain its properties when exposed to relatively high working temperatures over a longer time.
4140 / 4142 can be forged in a temperature range of 1652 - 1832°F (900 - 1000°C) followed by a very slow cooling in still air or sand.
Welding may only be done in the annealed or normalized condition, which can then be done by all the conventional techniques. In order to prevent cracking, preheat to 350-650°F (177-350°C). Due to the level of carbon in this steel, pre- and post-heat is recommended. Cool slowly to prevent/reduce embrittlement. If welded in the heat-treated condition, which is normally only done for repairs, mechanical properties are affected and a post-weld heat treatment should be performed. Welding pre-heated parts, it is recommended to stress relieve the parts before at a temperature 60°F (15°C) below the original tempering temperature in order to prevent cracking.
4140 / 4142 APPLICATION OPTIONS
• Arbors
• Flanges
• Collets
• Bending dies
• Crankshafts
• Clutch parts
• Forming rolls
• Short run stamping dies
• Mechanical engineering
• Machine parts
• Axes
• Knuckles
• Connecting rods
• Crankshafts
• Gear shafts
• Pinions
• Gears
• Bandages
• Base plates
• Assembling parts

4140 / 4142 CONCLUSION
The material 4140 / 4142, also known as 42CrMo4, is a low-alloy chromium-molybdenum steel. It is characterized by its high strength, good toughness and hardenability. It is used in mechanical engineering, toolmaking and many other industries due to its good properties.
• Excellent wear resistance
• Excellent load-bearing capacity
• Good machinability
• High strength
• High toughness
• Nitridable
• Erodible
• Difficult to weld
We offer this steel as 4140 Flat Stock / 4142.

4140 / 4142 ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
4140 / 4142 DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

