H13 ESR Tool Steel - 1.2344 ESU - X40CrMoV5-1 - ~SKD 61

H13 ESR Tool Steel - 1.2344 ESU - X40CrMoV5-1 - ~SKD 61
Back to Steel Overview
H13 ESR STEEL PRICE CHART
H13 ESR STEEL STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
X40CrMoV5-1
50 HRC - 56 HRC
max. 229 HB
X40CrMoV5-1
50 HRC - 56 HRC
max. 229 HB

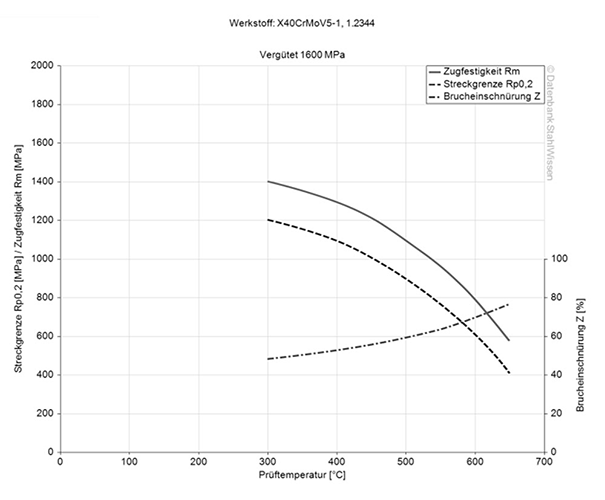
H13 ESR STEEL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
H13 ESR, a hot work tool steel, can be water cooled, oil or air hardened and has a good toughness. H13 ESR is a electro slag remelted tool steel with 5% chromium that hardens in air and is versatile enough for a broad range of hot and cold work uses. The addition of vanadium increases the resistance to abrasion and imparts superior properties at elevated temperatures.
H13 ESR Steel is often used in cold work tools because of its exceptional toughness, even though it might slightly reduce wear resistance. Apart from its high hot wear resistance and thermal cracking resistance, it also has high polishability, suitable for lens and cutlery molds.
While the H13 ESR Steel contains a mass fraction of 4.8 - 5.5% of chrome it is not a classic stainless steel. Stainless steels contain a minimum of 10.5% chrome.
Although it provides a certain level of resistance to corrosion, if corrosion resistance is a primary requirement, it would be recommended to choose a stainless steel grade or apply a protective layer.
Yes, as a ferrous metal, H13 ESR Tool Steel can be magnetized. Grinding, milling and eroding for example can be done on machines using magnetic clamping.
The H13 ESR Steel wear resistance scores a 3 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
Hot work steel like H13 ESR can be exposed to continuous high temperatures. They have a high strength, hardness and thermal stability, toughness and wear resistance for a longer service life.
Cold working H13 ESR is easier done in its annealed condition, heat treated, it is challenging due to its hardness and parts may work harden which in turn may cause breakage and wear. To relieve introduced stresses and give the parts their final properties they should be heat treated afterwards.
H13 ESR STEEL TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
H13 ESR Steel is not commonly used as a knife steel as although hard, H13 ESR Tool Steel does not hold an edge for long. However it can easily be sharpened.
The working hardness for H13 ESR steel is in the range of 469 - 572 BHN (50 - 56 HRC).
At room temperature the density of H13 ESR is 0.279 lb/in3 (7.8g/cm3).
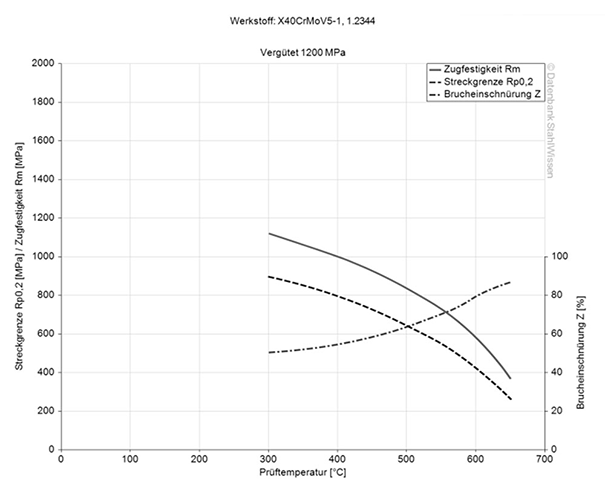
H13 ESR tool steel has a tensile strength of approx. 111.6 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The yield strength shows how much stress can be applied to a material before it plastically deforms. Before this point it will return to its original form as soon as the stresses have been taken off the H13 ESR material.
When the point has been passed it will be deformed permanently or even break. The range for the H13 tool steel is at approx. 239 KSI (approx. 1650 MPa).
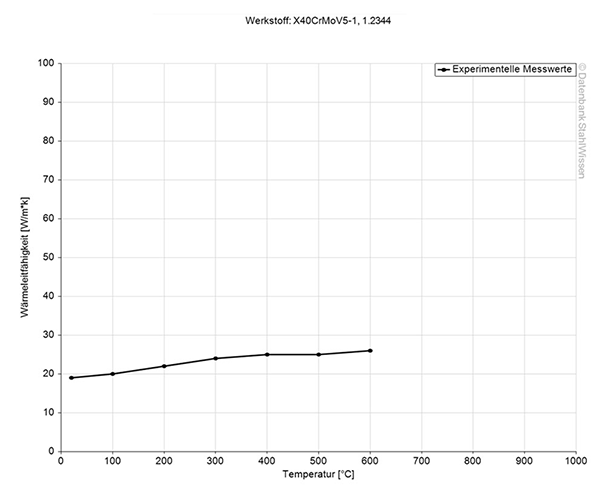
The following table shows the heat conductivity for H13 ESR steel in the annealed and hardened condition.
Heat conductivity table | ||
Value annealed | Value hardened | By temperature |
27.2 | 25.5 | 68°F |
30.5 | 27.6 | 662°F |
33.4 | 30.3 | 1292°F |
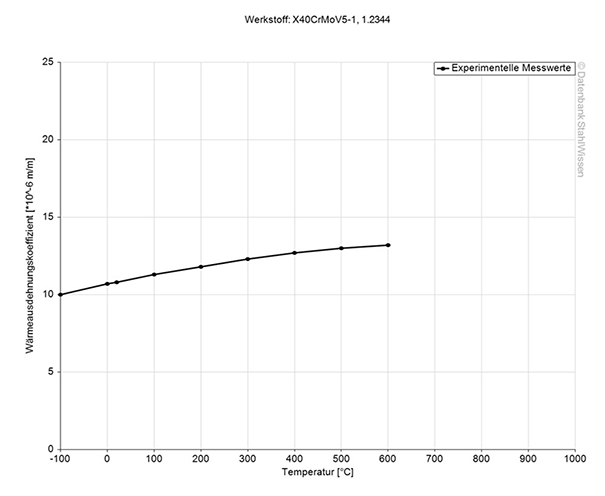
This diagram shows how much H13 ESR tool steel might expand or contract when the temperatures change, which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.9 | 68 - 212°F |
11.9 | 68 - 392°F |
12.3 | 68 - 572°F |
12.7 | 68 - 752°F |
13.0 | 68 - 932°F |
13.3 | 68 - 1112°F |
13.5 | 68 - 1292°F |
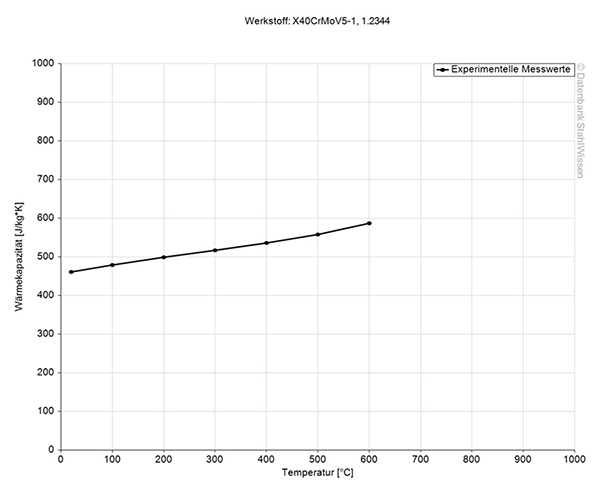
The specific heat capacity of H13 ESR at room temperature is at 0.460J/g-°C (0.110BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
~0.543 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 68°F |
~0.638 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 212°F |
~0.705 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 392°F |
~0.782 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 572°F |
~0.868 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 752°F |
~0.96 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 932°F |
~1.06 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~ 1112°F |

ON REQUEST - SAWN - MILLED - GROUND!


H13 ESR STEEL PROCEDURE
To avoid damage to the surface of the H13 ESR material, anneal it in a controlled atmosphere or pack it in a suitable container, using a neutral packing compound.Heat the part slowly through to a temperature of 1382-1472°F (750-800°C).
Lower the temperature of the material gradually. Decrease it by 50-68°F (10-20°C) per hour. Continue until it reaches 1112°F (600°C). After it gets to this temperature, it can be cooled more in the air.
After rough machining or extensive processing, stress relieving H13 ESR Steel is necessary to prevent distortion caused by introduced stresses.Heat the work pieces to a temperature of 1112-1202°F (600-650°C).
Keep them at that temperature for 1-2 hours. This should be done in a neutral atmosphere. Then cool the parts at a controlled rate in air. Cooling H13 ESR down slowly is essential as not to introduce new stresses to the work pieces.a
Hardening this material improves the H13 ESR steel's mechanical properties.
To control decarburization, use a controlled atmosphere furnace or pack the work piece in an inert material. Heat uniformly to a temperature of 1868-1940°F (1020-1060°C) and hold for 15-30 minutes and quench, following this up immediately with a tempering.
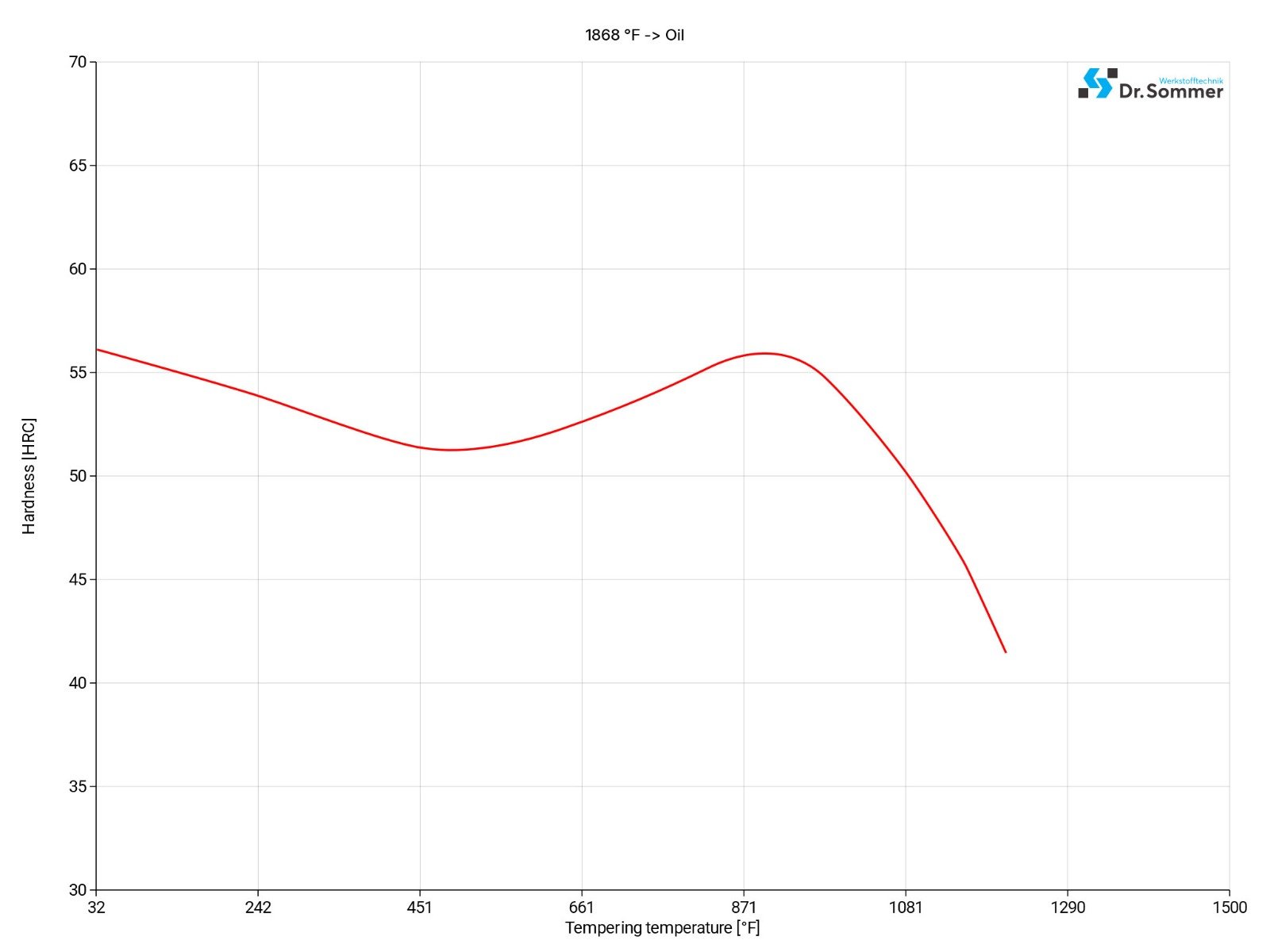
H13 ESR Tool Steel is typically cooled in air, although it can also be cooled using other substances. When determining the cooling method, factors such as the application, part shape, and size should be taken into account.
• Air
• Oil
• Vacuum
• Hot bath
Immediately after hardening, heat the material slowly to a tempering temperature for a minimum of 1 hour per inch (25.4 mm) of thickness. Tempering temperature should be at least 50°F (10°C) higher than the expected maximum operating temperature of the workpiece.
Work pieces should be double tempered; a third tempering cycle can be advantageous to relieve stress.
H13 ESR Steel can be sub-zero treated. Instead of tempering the material after hardening it is cooled to sub-zero temperatures and held to transform the retained austenite to martensite.
Benefits, for H13 ESR, apart from a refined carbide structure are increased hardness and wear resistance as well as improved dimensional stability. To relieve possible newly introduced stresses, the sub-zero treatment should be followed up by tempering as explained above.
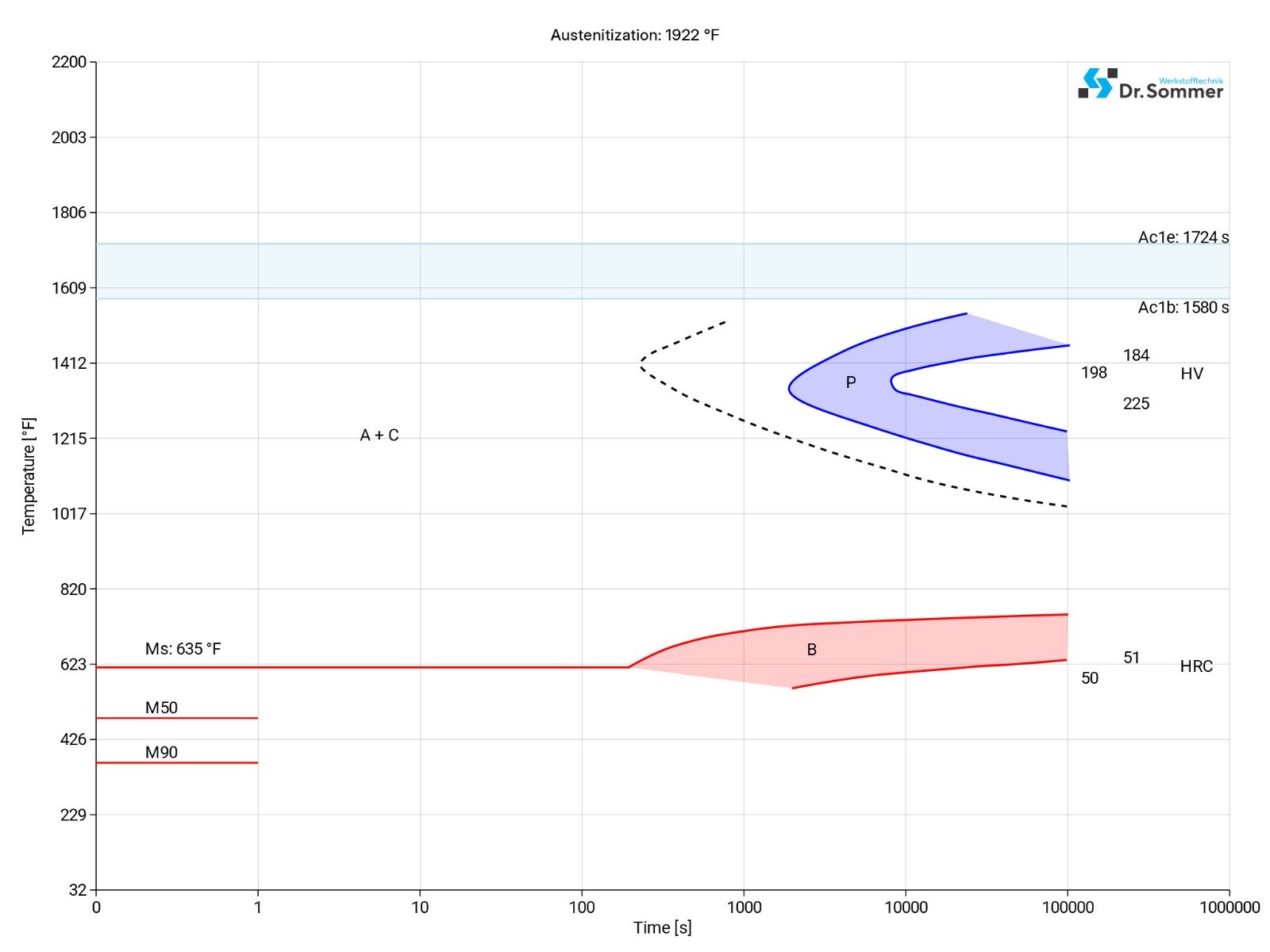
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
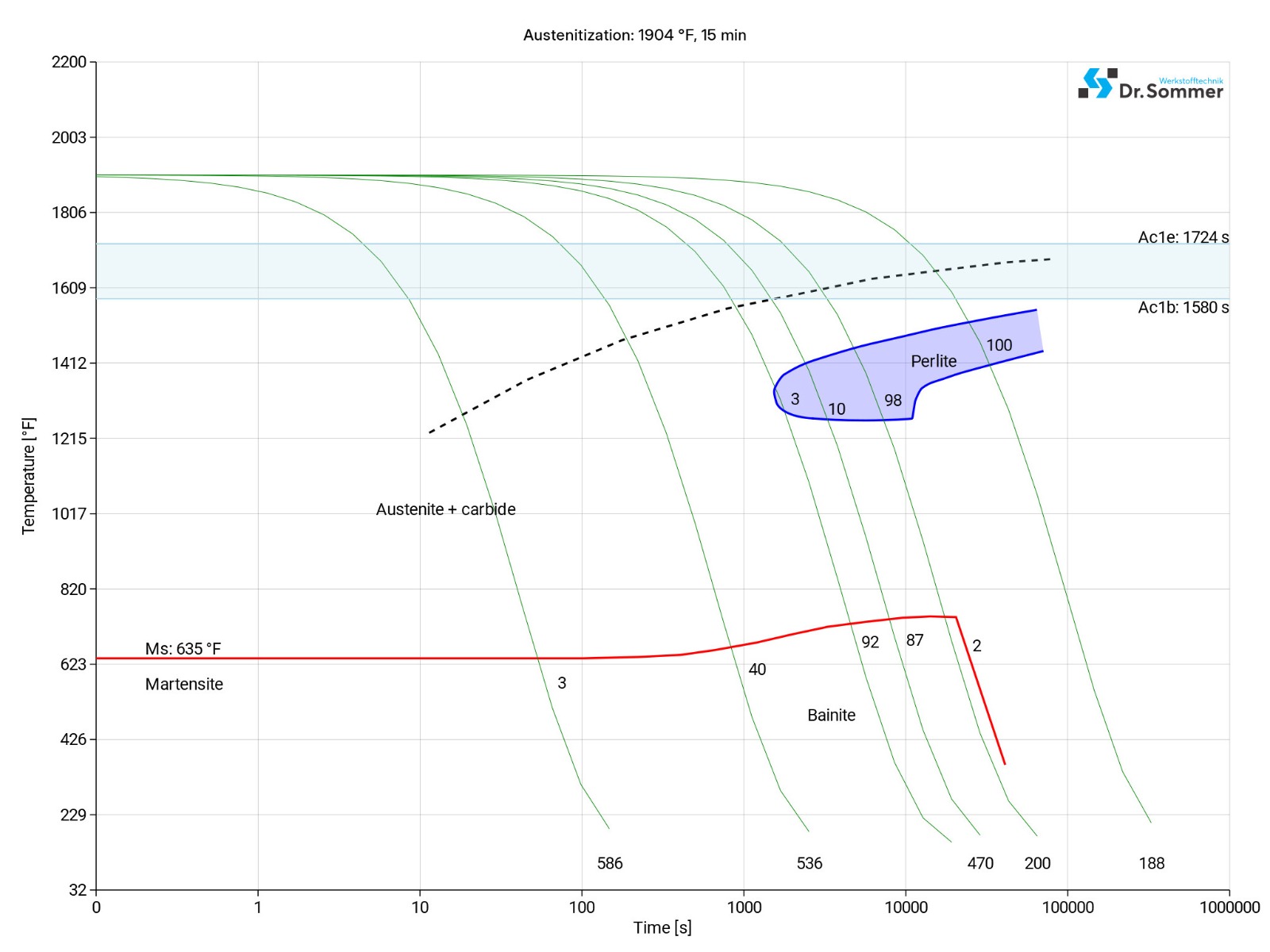
The following diagram shows the structural changes at micro levels over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperatures the different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite and bainite start to form.
H13 ESR STEEL SURFACE TREATMENT
The following are just an example of a variety of surface treatments for the H13 ESR tool steel. Choosing a surface treatment does depend on the application for which parts are used.a
To improve wear resistance and fatigue life, H13 ESR Steel can be nitrided. This process introduces nitrogen into the surface and can offer some corrosion resistance and does reduce the need for frequent lubrication for moving parts.
Though not as common as nitriding, this process introduces carbon into the material surface giving it extra surface hardness with a tough core.
This process forms a black oxide layer giving this material grade some corrosion resistance. Further the black layer gives pieces, exposed to light, a low reflective surface as well as an aesthetic appearance.
To reduce friction and improve the wear resistance and corrosion resistance, H13 ESR Steel is coated by PVC (Physical Vapor Deposition) or CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition). Both processes introduce a thin film of material onto the surface of the workpieces.
H13 ESR TOOL STEEL PROCESSING
Tempering after EDM might be needed as heat affected zones can have different properties to the base material. EDM can give the H13 ESR tool steel a very smooth surface with the right settings and conditions.
H13 ESR, like other tool steels, will hold its size best when quenched from the accurate hardening temperature. Overheated, the material tends to shrink after tempering and should therefore be avoided.
Slowly and uniformly heat the material to a temperature of 1900-2050°F (1038-1121°C). Do not let the temperature drop below 1650°F (899°C), if necessary, reheat to maintain the proper forging temperature.
Cool small and simple parts slowly in lime. Larger parts should be cooled down in a heated furnace at a uniform temperature of 1450°F (788°C), then turn the furnace off and let the parts cool down or use insulating material to cool it slowly.
Note, this is not an anneal, annealing should be done after the forgings are cooled down.
Good results can be achieved when welding tool steel, if the proper precautions are taken during welding (increased working temperature, joint preparation, choice of filler metals and the welding procedure). If the parts are being polished or photo-etched, it is necessary to work with a suitable electrode type of matching composition.
H13 ESR STEEL APPLICATION OPTIONS
H13 ESR steel has a multitude of good properties which makes this tool steel not only a good choice for high temperatures but in combination with its thermal fatigue and abrasion resistance can be used for casting and extrusion tools, as well as for dies, hot shear blades and stamping tools to name just a few.
With a good resistance to thermal fatigue, erosion and wear it is ideal for plastic molds.
• Forging tools and dies
• Hot shear knives
• Hot extrusion tools
• Extrusion press tools
• Press tools
• Light metal die casting
• Press mandrels
• Press dies
• Piecer Plugs

H13 ESR STEEL CONCLUSION
H13 ESR tool steel has a lot of pros and cons. Though it has some corrosion resistance it needs good maintenance to prevent rusting. The H13 ESR steel's inability to retain an edge doesn't make it an ideal option for crafting knives. However, its hardness allows for easy sharpening.
This material can be cold worked, but this grade of steel is better suited for hot work. H13 ESR has high temperature stability, good thermal fatigue resistance, toughness and wear resistance.
- Good heat resistance
- High resistance to hot wear
- High thermal shock resistance
- Very good toughness
- Erodible
- Nitridable
- Water coolable
- Fire crack resistant
We offer this steel as H13 ESR Flat Stock.

H13 ESR STEEL ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
H13 ESR STEEL DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

