440C Stainless Steel - 1.4125 - X105CrMo17 - ~SUS 440C

440C Stainless Steel - 1.4125 - X105CrMo17 - ~SUS 440C
Back to Steel Overview
440C STEEL PRICE CHART
440C STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
X105CrMo17
57 HRC - 60 HRC
max. 285HB
X105CrMo17
57 HRC - 60 HRC
max. 285 HB

440C PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
440C is a high carbon steel. As a martensitic, medium corrosion resistant cold work and plastic mold steel, it has good machinability, excellent polishing properties, low distortion, good hardness, and good wear resistance.
When correctly heat treated the 440C has the capability to reach the highest strength, hardness and wear resistance among the corrosion and heat resistant stainless steels.
The corrosion resistance for 440C is lower than for the usual austenitic grades, and the useful operating temperature range is limited due to loss of ductility at temperatures below zero and loss of strength due to over-tempering at higher temperatures as well as the reduction in corrosion resistance.
With a 16 - 18% of chromium content 440C is a martensitic stainless steel. It is part of the 400 Series Stainless Steel.
440C stainless steel has good resistance to atmosphere, fresh water, fruit, and vegetable juices, alkalis, and mild acids and its corrosion resistance is similar in many environments to 304 stainless steel.
Achieve maximum corrosion resistance by hardening from 2000°F (1093°C), to provide a better carbide solution, meaning the better the finish of the hardened and tempered part, the better its corrosion resistance.
A smooth, polished surface will support the general corrosion resistance of this AISI 440C stainless steel as well.
Care should be taken, however, to minimize the time at 2000°F (1093°C) to avoid excessive coarsening of the grain. For optimum corrosion resistance, the tempering temperature should be below 800°F (427°C).
440C stainless steel corrosion resistance includes resistance to gas corrosion like oxidizing or reducing gasses but also chlorine or sulfur gasses. As for all, certain factors like temperature, moisture or pressure may influence or reduce the corrosion resistance of this steel grade.
Pitting can be avoided by avoiding or minimizing contact with high chlorine concentrations, elevated temperatures and acidic conditions.
Intergranular corrosion can happen by sensitization, chromium depletion and the attack on the grain boundaries. To prevent intergranular corrosion for 440C stainless steel it should not be heated to 797 - 1499°F (425 - 815°C) when carbon precipitation at the grain boundaries starts happening.
The 440C stainless steel composition, with 16 - 18% of chromium, is responsible for this steel grade having a good atmospheric corrosion resistance. Chrome builds a thin oxide layer when it comes in contact with oxygen. This layer gives the 440C an extra layer of protection against corrosion.
Due to the preventive oxide layer 440C has a thin protective layer against oxidation and sensitization. Though regular inspections and cleaning may prevent unwanted oxidation and corrosion. Cleaning may remove possible other aggressive contaminants and monitoring will make for a longer life for parts made from 440C.
440C stainless steel in the hardened condition is more susceptible to stress corrosion cracking than in the annealed condition.
Stress corrosion cracking is the localized corrosion due to tensile stresses, higher temperatures or corrosive environments e.g., when 440C is exposed to a temperature above 140°F (60°C) in a chloride containing environment.
Using a protective coating and stress relieving can help to reduce residual stresses but also cleaning and inspecting the parts regularly will help to detect possible cracking.
440C is a martensitic stainless steel. Magnetic stainless steel as all other magnetic steel grades has to contain iron and has to have a martensitic or ferritic crystal structure.
The wear resistance for the 440C is 6 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high.
The high wear resistance does not only make 440C a good blade steel, it can also be found in moving parts like ball bearings.
440C stainless steel ball bearings have a high wear resistance and corrosion resistance which makes them useful in household appliances as well as the food industry where they may come in contact with chemicals or corrosive substances.
440C TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
440C is a very popular and widely used knife steel with a high hardness and a good edge retention. With its high content of chromium it has a high corrosion resistance. 440C is used to make kitchen knives as well as pocket knives. With a high wear resistance and moderate toughness they can be used for many different tasks and in various conditions.
Due to its natural hardness 440C can, even in its annealed condition, only be cold formed within limits. In the hardened condition this stainless steel is even harder to cold work as the risk of cracking is very high. It is necessary to understand that this steel will harden with cold working which might increase its strength but reduces its ductility and any heat treatments have to be considered with care.
The working hardness for 440C steel is in the range of 592 - 627 BHN (57 - 60 HRC (Rockwell hardness)).
Typically the density of 440C is 0.282 lb/in3 (7.8g/cm3) at room temperature.
As a high carbon stainless steel 440C has a tensile strength of approx. 139.9 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). This can vary due to heat treatment and processing. In order to reach this value, a test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The yield strength shows when a material starts deformation beyond the point that it might return to its original shape (plastic deformation). The yield strength is impacted by the carbon content and heat treatment of the various steel grades. The range for the 440C stainless steel is between 65 - 241 KSI (448 - 1660MPa).
The heat conductivity for 440C is at 15.5 W/(m*K) (8.956 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity is a physical property that showshow well a material conducts heat. Heat conductivity is very important for applications which transfer heat or need tight temperature controls. In the following table you can find the heat conductivity values listed for 440C.
This diagram shows how much 400C might expand or contract when the temperatures change which can be very important when working with high temperatures or strong temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.4 | 68 - 212°F |
10.8 | 68 - 392°F |
11.2 | 68 - 572°F |
11.6 | 68 - 752°F |
The specific heat capacity of 440C steel is at 0.460J/g-°C (0.110BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.6 (Ohm*mm²)/m | ~68°F |

WANT TO KNOW MORE?

440C PROCEDURE
It is not recommended to use 440C above the respective tempering temperature as the mechanical properties will deteriorate due to over-hardening.
440C is a martensitic stainless steel, thus it is hardenable by heat treatment. To achieve the creation of martensite, it is necessary to reduce the amount of austenite by heat treatment.
Fully annealing 440C stainless steel is done at 1562-1652°F (850-900°C). Slowly cool the parts in the furnace to about 1112°F (600°C) and then further cool the parts in air to room temperature.
Sub-critical anneal at 1355-1445°F (735-785°C), then slowly cool to room temperature in the furnace.
To relieve stresses from 440C in its annealed condition, heat the material uniformly to 1200 - 1250°F (650 - 677°C) and hold this temperature for two hours. Then cool in still air.
For hardened 440C heat the material to 25 - 50°F (approx. 10°C)below the tempering temperature and hold for two hours and then cool in still air.
Hardening 440C stainless steel heat to 1850 - 1950°F (1010 - 1066°C), followed by quenching in warm oil or cooling in air. Oil quenching is necessary for large sections or complex parts. Beware not to overheat, as full hardness cannot be reached and temper immediately to achieve a wide range of hardness values.
440C can be quenched in oil, water or gas from a temperature 1850 - 1950°F and should be followed up immediately by sub-zero treatment as explained below.
440C is tempered at a temperature range of 302-698°F (150-370°C) where several levels of hardness and mechanical properties can be obtained. Tempering in the range of 797-1049°F (425-565°C) reduces impact strength and corrosion resistance and should be avoided.
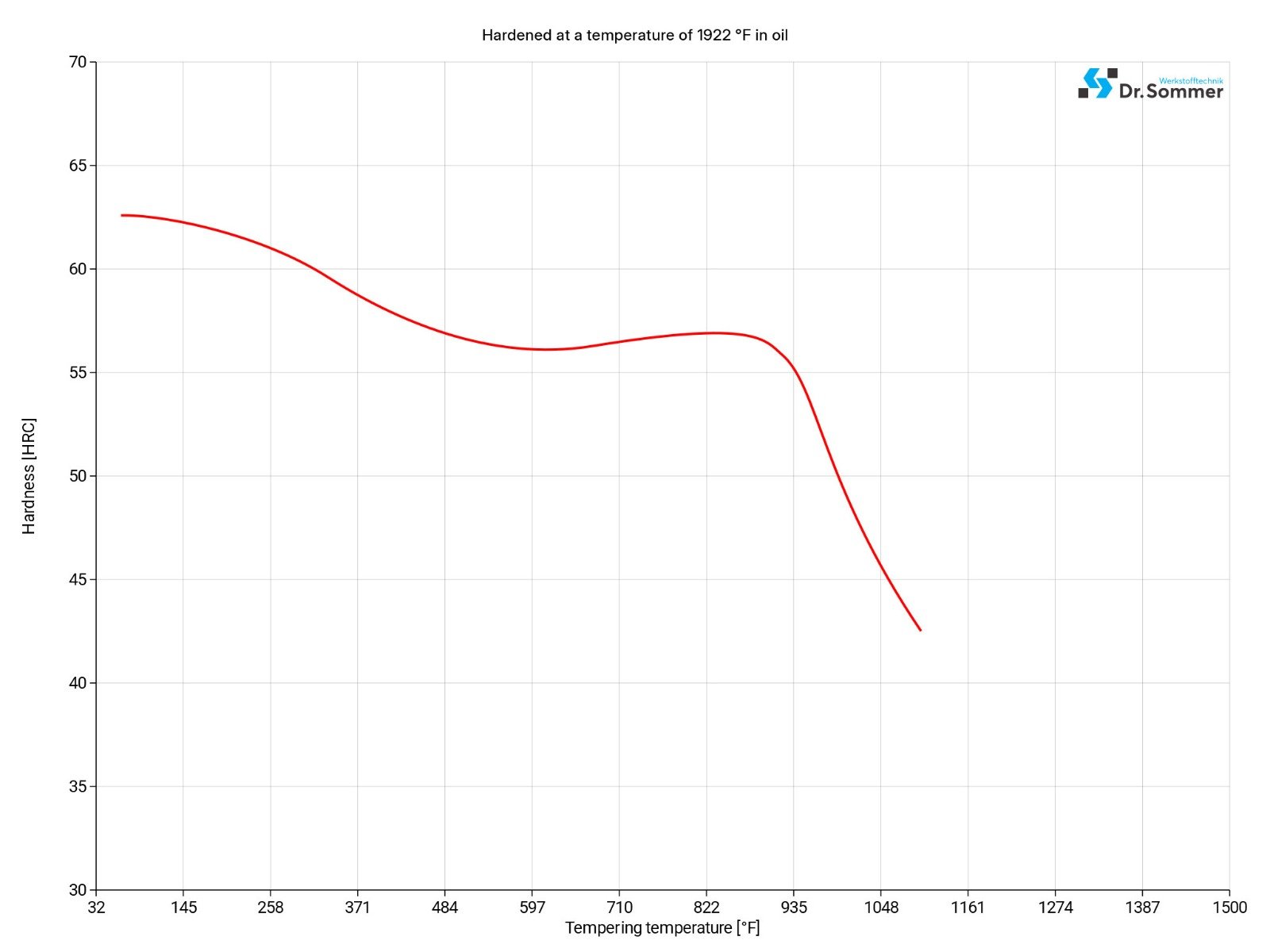
To reduce the austenite content in 440C stainless steel it can be treated in sub-zero temperatures. This procedure should be done before tempering this steel grade either by deep or shallow cryogenic treatment.
To increase the hardness up to 7% with the deep cryogenic treatment, cool the steel to -321°F (-196°C) and soak it at this temperature for 24 hours before bringing it back up to room temperature.
To increase the hardness up to 4% with the shallow cryogenic treatment, cool the steel to -112°F (-80°C) and hold it for 5 hours, then bring the temperature back up to room temperature.
After the cryogenic treatment is completed the 440C can be tempered at 392°F (200°C).
This diagram shows micro changes over time at different temperatures. Those are important during heat treatment as they show information about the optimum conditions for processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
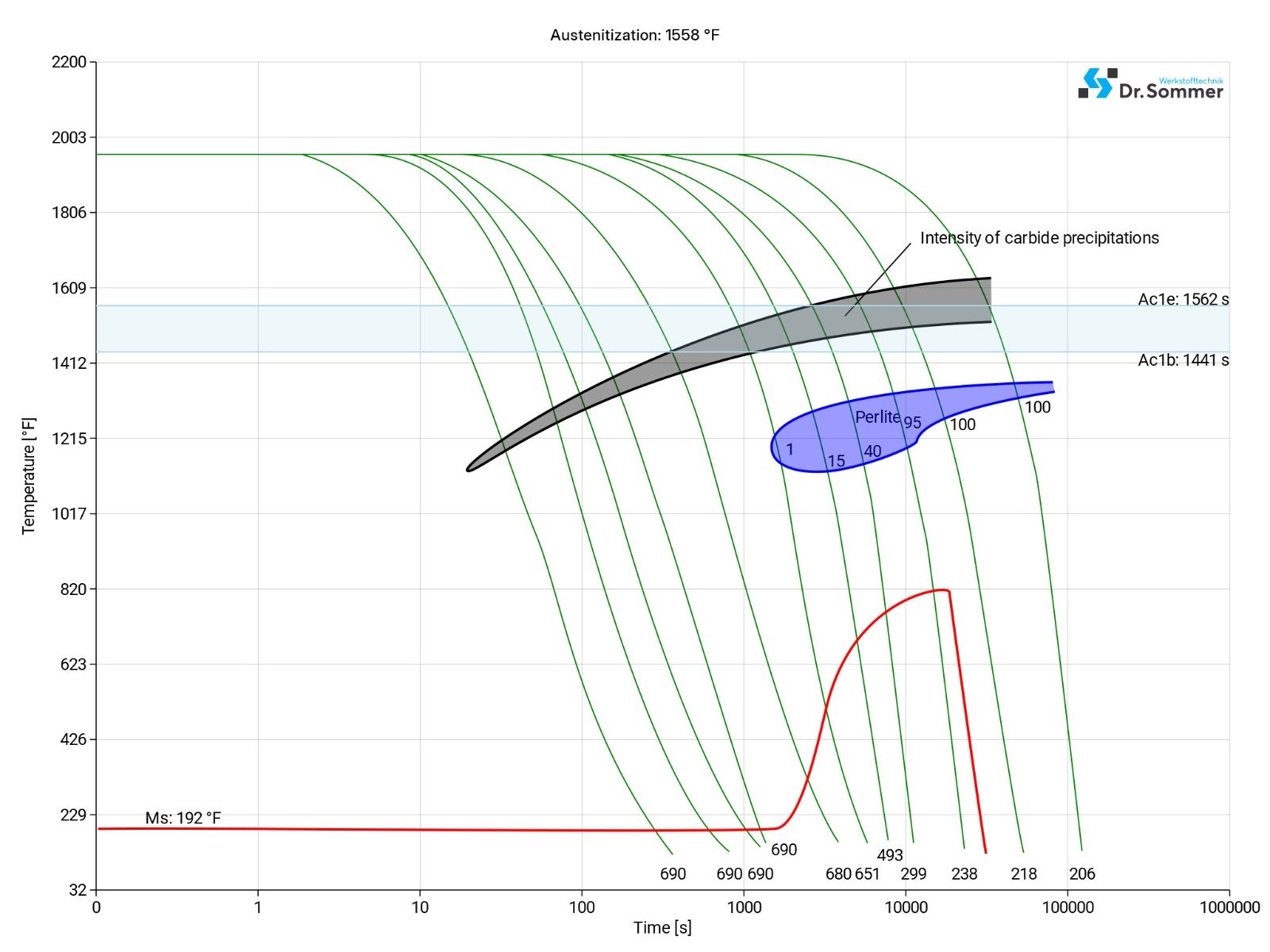
The following diagram shows the structural changes at micro levels over time at a constant temperature. It shows at what temperatures the different phases, e.g., perlite, martensite and bainite start to form.
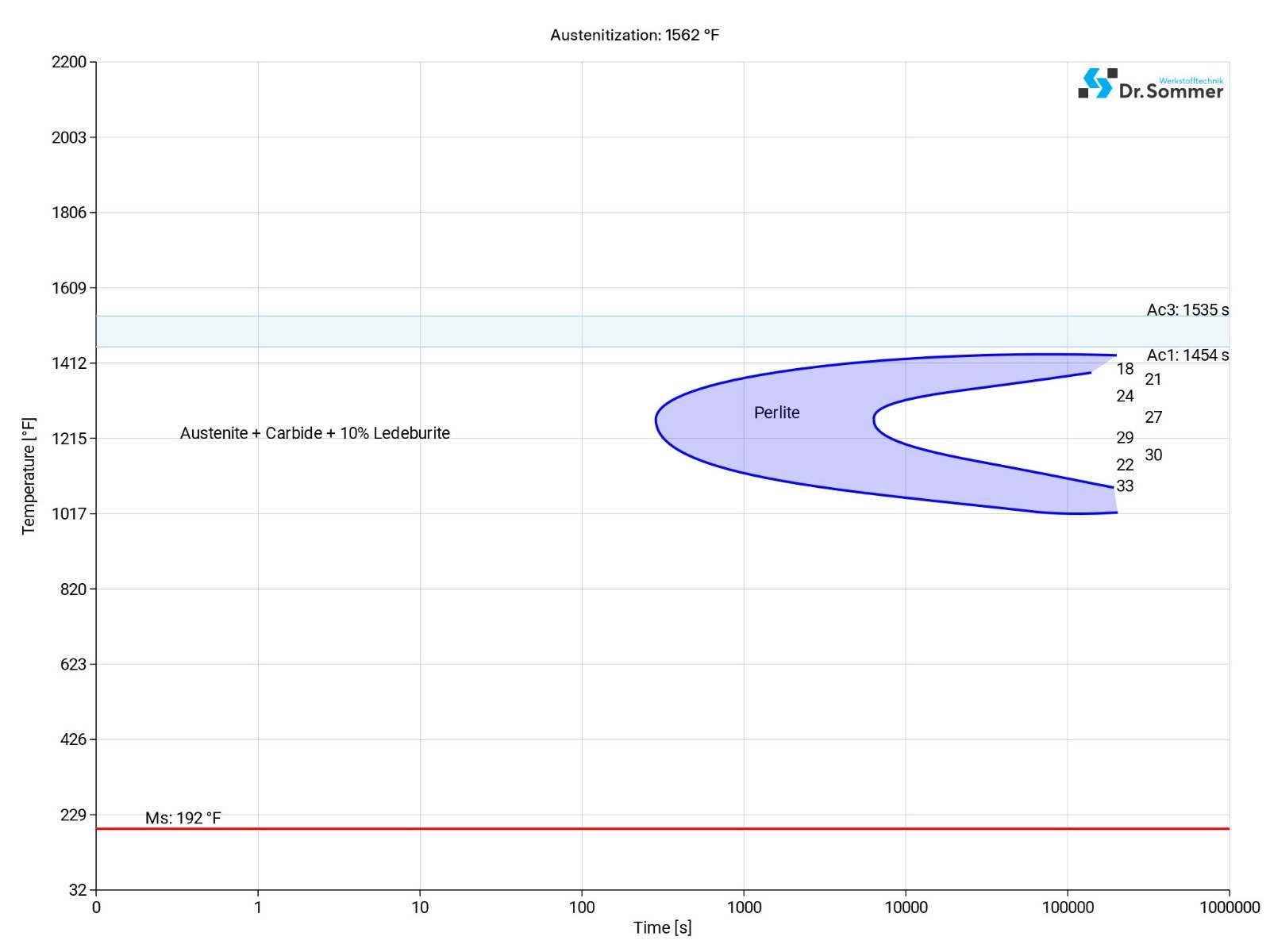
440C SURFACE TREATMENT
Polishing can be one kind of surface treatment, it can help corrosion resistance and has an appealing effect as well.
Protecting the surface or making the surface harder is another method of surface treatment. Here the surface is nitrated, carburized, hard chrome plated, treated by CVD (chemical vapor deposition) or PVD (physical vapor deposition) to mention just a few to give the surface a higher hardness.
The surface treatment has to suit the application the parts are used for in the end. It can improve wear resistance and corrosion resistance and can give it a shiny finish by electropolishing or a matt finish by bead blasting it.
440C PROCESSING
Machining 440C stainless steel, such as turning or drilling, is mostly done in the annealed condition. As a result, to its high carbon content, it machines similar to high speed steel.
Chip curlers and breakers should be used as chips are tough and stringy.
Heat treated 440C is more difficult and probably impossible to machine due to its high hardness.
EDM is used for parts made from one individual piece, for cutting dies or when making intricate shapes. There are various methods to erode various materials, some of them are for example wire erosion, spark erosion or die sink erosion.
Due to its hardness 440C can be difficult to machine. EDM can be used to machine intricate parts and contours where mechanical stresses or deformation should be prevented. This procedure gives the work pieces a smooth finish but the electrodes will experience some wear and it might take longer than conventional machining.
If and how much machining allowance is needed depends if the material is being machined, the machining processes needed to achieve a certain finish as well as how hard the material is as harder materials can wear quicker.
440C expands while heating but will shrink back to its normal size while cooling. Care should be taken when quenching this material as uneven cooling might warp or bow it.To prevent unwanted dimensional changes care should be taken during heat treatment and welding and stresses should be relieved after machining.
When forging 440C stainless steel the material should be prepared so that no contaminants or oxidation is left on the material. The material should be heated slowly and uniformly to a temperature of 1900 - 2100°F (1037 - 1449°C).
At higher temperatures 440C’s surface can be decarburized, the loss of the carbon content on the surface can decrease its hardness. Forging should not be continued under 1700°F (327°C) as cracking can occur. Reheating can be done as often as needed. When forging is done the finished pieces should be cooled in the furnace in order to prevent thermal stresses or in still air.
To finish the forging step the parts should undergo a further heat treatment of austenitizing, quenching and tempering and any oxidation should be removed. To avoid future breaks due to inclusions or cracks within the forged parts, they can be tested with magnetic particle inspection or ultrasonic inspection.
As 440C has high-hardness capabilities, and it can air harden easily, this alloy is not welded often. Though if welding is necessary, preheat and maintain at 500°F (260°C). Immediately after the parts need a 6-8 hour anneal at 1350-1400°F (732-760°C) with a slow furnace cool.
Do not allow parts to cool below 500°F (260°C) between welding and annealing. Use high welding inputs and consider a similar filler metal to achieve complementary mechanical properties.
440C stainless steel scales at about 1400°F (760°C), the temperature may vary with the type of atmosphere, construction and cycle of operation.
For cutlery applications grinding and polishing is very important but overheating can result in loss of hardness and corrosion resistance.
440C APPLICATION OPTIONS
Material 440C stainless steel can be used for ball bearings, bushings, valve parts, cutlery, knives and blades, nozzles, pump parts as well as medical -, surgical - and dental instruments.
• Knives for the food industry
• Frozen food cutters
• Pork and beef cleaving knives
• Fish industry knives
• Accessories for meat grinders

440C CONCLUSION
Due to its higher carbon content, 440C has a higher hardness compared to most other stainless steels and can be hardened up to 60 HRC. The high hardness makes it a very good knife steel, as it has very good edge retention and wear resistance.
- Stainless steel
- Martensitic steel
- Cold work steel
- Plastic mold steel
- High hardness
- High wear resistance
- Good edge retention
- Higher carbon content
- Limited acid resistance
- Polishable
- Low distortion
We offer this steel as 440C Flat Stock, 440C Cold Finished Round Bars and 440C Round Bars Decarb Free.

440C ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
440C DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

