M4 High Speed Steel - HSS PM M4 HC - ~PMHS6-5-4 - ~SKH 54

M4 High Speed Steel - HSS PM M4 HC - ~PMHS6-5-4 - ~SKH 54
Back to Steel Overview
HSS PM M4 HC STEEL PRICE CHART
HSS PM M4 HC STANDARD VALUES
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
V
W
~PMHS6-5-4
62 HRC - 65 HRC
max. 270 HB
~PMHS6-5-4
62 HRC - 65 HRC
max. 270 HB

HSS PM M4 HC PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
PM M4 HC high speed steel impresses with a very clean and homogeneous microstructure with evenly spread carbides which optimize its wear resistance. The high carbon and vanadium content gives PM M4 an exceptional abrasion resistance which makes it suitable for cold work punches, machining abrasive alloys and cutting applications that involve high speed.
PM Steel (Powder Metallurgy) is produced by melting steel in an induction oven and blasting it with an inert gas that disperses the steel into very small droplets. These droplets then solidify again within seconds leaving extremely fine and virtually segregation free powder. This powder is then filled into a capsule and all air is removed from the capsule. Then the capsule is heated and pressure is applied to it for sintering. After an appropriate time the capsule is milled away from the steel and what's left is a steel block with a clean and homogeneous microstructure.
To be classified as a stainless steel it has to have a mass fraction of 10.5% of chromium. With a chromium content of 3.8 - 4.5% the PM M4 HC is not a stainless steel.
Though the PM M4 HC has some corrosion resistance but does not have enough to be suited for corrosive environments. Corrosion resistance can be enhanced with coating the material, limiting exposure and having a good maintenance routine and storage practices can help to prevent corrosion.
The PM M4 HC is a ferromagnetic material which can be magnetized and is suitable for magnetic clamping.
PM M4 HC has a wear resistance of 6 on a scale where 1 is low and 6 is high
HSS PM M4 HC TECHNICAL PROPERTIES
PM M4 has some great characteristics which lend themselves for knife making. Its excellent wear resistance, good toughness, high hardness as well as fine microstructure produce knives that hold a sharp edge for a long time and which are resistant to chipping. That said it is not corrosion resistant which means care in moist and acidic environments has to be taken. Its hardness, though a plus when it comes to edge retention, makes it harder to sharpen PM M4 HC knives as well as makes it unsuitable for applications needing extreme flexibility and impact resistance.
The working hardness for HSS PM M4 HC is 658 - 711 BHN (62 - 65 HRC).
Typically the density of High Speed Steel PM4 HC is 0.298 lb/in3 (8.26g/cm3) at room temperature.
PM M4 HC has a tensile strength of approx. 133.4 KSI on delivery (0.145 KSI = 1MPa). In order to reach this value, a tensile test is performed to show how much force is needed to stretch or elongate a sample before it breaks.
The heat conductivity for PM M4 HC is at 23.5 W/(m*K) (163 BTU/(h-ft*°F)) at room temperature.
Heat conductivity table | |
Value | By temperature |
23.5 | 68°F |
26.8 | 662°F |
36.2 | 1292°F |
The following table shows expansion or contraction at various temperatures, which may be very important for high temperature works or when working with high temperature changes.
Medium thermal expansion coefficient | |
10-6m/(m • K) | At a temperature of |
10.6 | 68 - 212°F |
11.7 | 68 - 392°F |
11.9 | 68 - 572°F |
12.4 | 68 - 752°F |
The specific heat capacity of the PM M4 HC at room temperature is 0.439 J/g-°C (0.105 BTU/lb-°F). This value shows how much heat is needed to heat 1lb of material by 1 Fahrenheit.
You can find the temperature dependent material constant (Resistivity) in the following table. The electrical conductivity is the reciprocal value of the specific resistance.
Table of the specific electrical resistivity | |
Value | At a temperature of |
0.53 (Ohm*mm²)/m | 68°F |

PIONEERING!


HSS PM M4 HC PROCEDURE
Heat the workpiece uniformly to a temperature of 1550 - 1600°F (843 - 871°C), hold for 2 hours and then slowly cool by a rate of 20 - 40°F (11 - 22°C) per hour to a temperature of 1100°F (593°C).
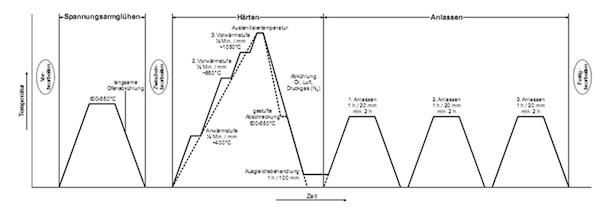
After machining the material roughly, heat it to a temperature of 1110 - 1290°F (599 - 699°C) for about 2 hours, then slowly cool down and finish machining after cooling.
It is recommended to harden PM M4 HC in a salt bath, vacuum furnace or in a controlled atmosphere.
Preheat PM M4 HC uniformly to 1450 - 1550°F (788 - 843°C), then raise the temperature to a range of 2175 - 2225°F (1191 - 1218°C) and soak slightly according to the chosen working hardness, avoid over-soaking. Finish the process with cooling the part down to a temperature of 100 - 120°F (38 - 49°C) and quench.
This steel grade is susceptible to decarburization which can be prevented with a controlled atmosphere furnace during heat treatment.
• Air
• Oil
• Vacuum
• Molten salt (temperature of 1000 - 1099°F (538 - 593°C)
Tempering should be done straight after quenching. Heat the parts uniformly to a temperature range of 1000 - 1200°F (538 - 649°C) for the first temper.
A double temper is required, with a cool down to ambient temperature in between tempers and a third temper recommended for maximum wear resistance when hardening from 2100°F (1149°C).
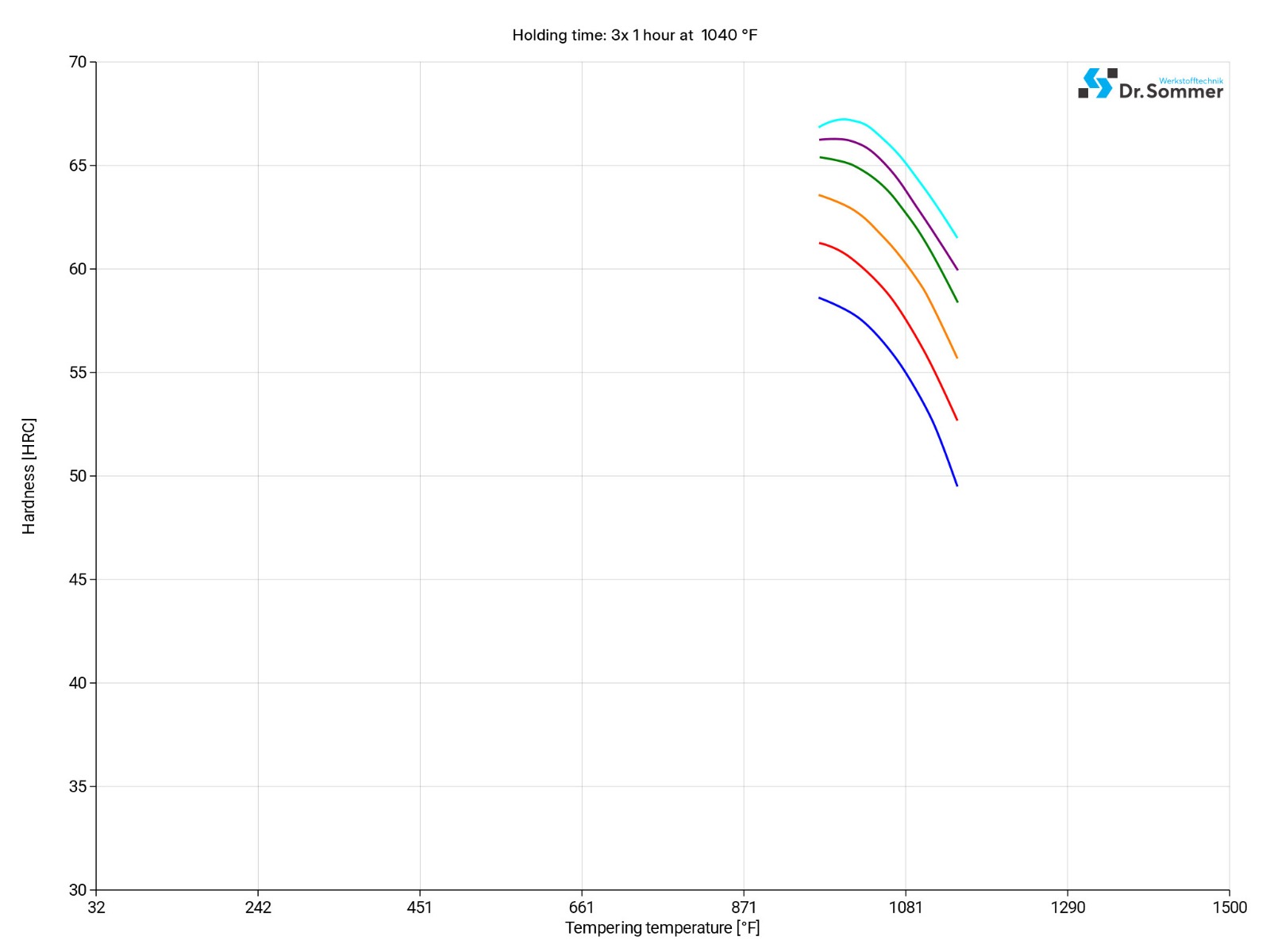
Treating HSS PM M4 HC at sub-zero temperatures can increase the wear resistance, dimensional stability, enhance toughness and relieve stress. Considering temperature, time and applications, with their needed properties, can prevent unwanted outcomes like cracking, excessive brittlement, reintroducing stresses or even risking tool life.
The following diagram shows the micro changes over time at different temperatures which are important during heat treatment. They show the optimum conditions for the processes such as hardening, annealing and normalizing.
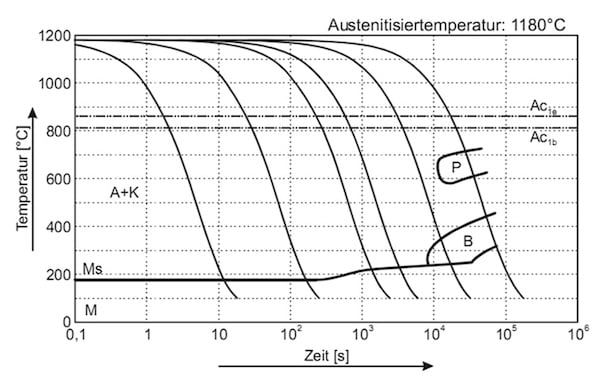
HSS PM M4 HC SURFACE TREATMENT
Treating the surface of HSS PM M4 HC can enhance wear, corrosion resistance and performance. Following are a few examples of surface treatments with their advantages and applications.
Coating the material grade PM M4 HC can increase its wear resistance and corrosion resistance and reduce friction. This method is commonly used for cutting tools or drills.
Nitriding enhances the surface hardness and therefore the wear resistance of components and tools by introducing nitrogen into the surface of the material. This process maintains dimensional stability and is often used for components where the dimensional accuracy is very important.
Carburizing also enhances hardness and wear resistance by introducing carbon into the material surface. This method is often used for components subjected to high contact stresses.
Carbonitriding introduces a mixture of carbon and nitrogen into the surface of the material. This can give components or tools improved wear resistance and a longer service life. This method is often used for gears or bearings which have to have a hard surface but a tough core.
This process layers the parts with a very thin layer improving the surface hardness and wear resistance. PVD can lower friction and is often used for tools with high cutting speeds.
HSS PM M4 HC PROCESSING
On a scale where 1 is weak and 6 is good, the machinability of D2 reaches a score of 1.
This grade is known for its high hardness and wear resistance. Those properties lend themselves to a variety of tool applications but also limits the machinability for this useful grade.
As a non contact, thermal energy based machining process it can be used for hard materials like the PM M4 HC. Electrodes, surface finish and heat affected zones should be considered before EDM is used for this material grade. Heat affected zones might need further heat treatment after EDM to align the microstructure in the workpiece and EDM may leave a rougher surface with a recast layer which can be removed by stoning and polishing.
VAs for other steels the PM M4 HC will display dimensional changes with heating and cooling the material. To reduce dimensional changes like distortion or warping it is important to control the heating and cooling rates or employ jigs and fixtures to restrain the material. It is always important to allow for those changes by giving an allowance on the material and always to be mindful when tight dimensions are needed.
Heat PM M4 HC slowly to a temperature of 2000 - 2100°F (1093 - 1149°C). Do not continue forging under the temperature of 1700°F (927°C), reheat as often as needed. When forging is finished, cool the parts down slowly in lime or ash.
When welding PM M4 HC the parts should be preheated and similar fillers to the base material should be used.
Local heat on the surface should be avoided during grinding as it may alter the temper of the workpiece.
HSS PM M4 HC APPLICATION OPTIONS
High Speed Steel a high alloyed tool steel, often used for drills, taps, turning tools and broaches, has a 3-4 times higher cutting speed without losing its hardness up to a temperature of 1112°F (600°C).
In comparison, ordinary cold work tool steel loses its hardness at about 392°F (200°C). The foundation for its abilities can be found in its alloys as well as its martensitic microstructure.
• Stamping tools
• Precision cutting tools
• Machining tools
• Broaching tools
• Rotary knives
• Woodworking tools
• Gear shaper cutters
• Circular saw segments
• Metal saws
• Screw dies
• Countersinks
• Chasers
• Cold extrusion punches
• Ceep drawing dies
• Plastic molds with high wear resistance

HSS PM M4 HC CONCLUSION
HSS PM M4 HC has a great combination of properties which can be assigned to its Powder Metallurgy process. It has great wear resistance, toughness, high hardness capabilities with a fine and uniform microstructure. Those properties make this material a great choice for tools and knives that need to keep an edge over a longer time, components like gears and bearing and for applications needing high speed.
- High-speed steel
- Powder metallurgical steel
- High toughness
- Very high wear resistance
- High purity
- Optimized homogeneity
- Uniform, fine carbide distribution
- Improved fracture resistance
- Improved edge stability
We offer this steel as PM M4 Flat Stock.

HSS PM M4 HC ALTERNATIVES
Are you looking for an alternative steel grade?
WE HAVE THE SOLUTION!
With the ABRAMS STEEL GUIDE, you can obtain an alternative or equivalent steel grade with just a few clicks.
HSS PM M4 HC DATASHEET
Download the technical data sheet in PDF format here.

The data shown here has been compiled with the greatest diligence and is regularly updated with regard to the correctness and completeness of its content. The content is indicative only and should not be taken as a warranty of specific properties of the product described or a warranty of suitability for a particular purpose. All information presented is given in good faith and no liability will be accepted for actions taken by third parties in reliance on this information. ABRAMS Industries reserves the right to change or amend the information given here in full or parts without prior notice.

