Tensile Strength of Steel - The point when material breaks

Tensile strength or ultimate strength shows at what point a material breaks when a load is applied. This is important for industries like the construction, automotive, aerospace or engineering industry and depend for example on the composition of the steel grade.
Different alloys and alloy compositions can result in different tensile strengths. Tensile strength can be positively influenced by heat treatment such as annealing, since both the grain structure and internal stresses can be influenced by this. But other heat treatment steps also have a positive effect on tensile strength.
For construction elements such as bridges and buildings, it is particularly important to choose a high tensile strength, as the elements have to withstand many and high stresses, and a break in the material would have catastrophic consequences.
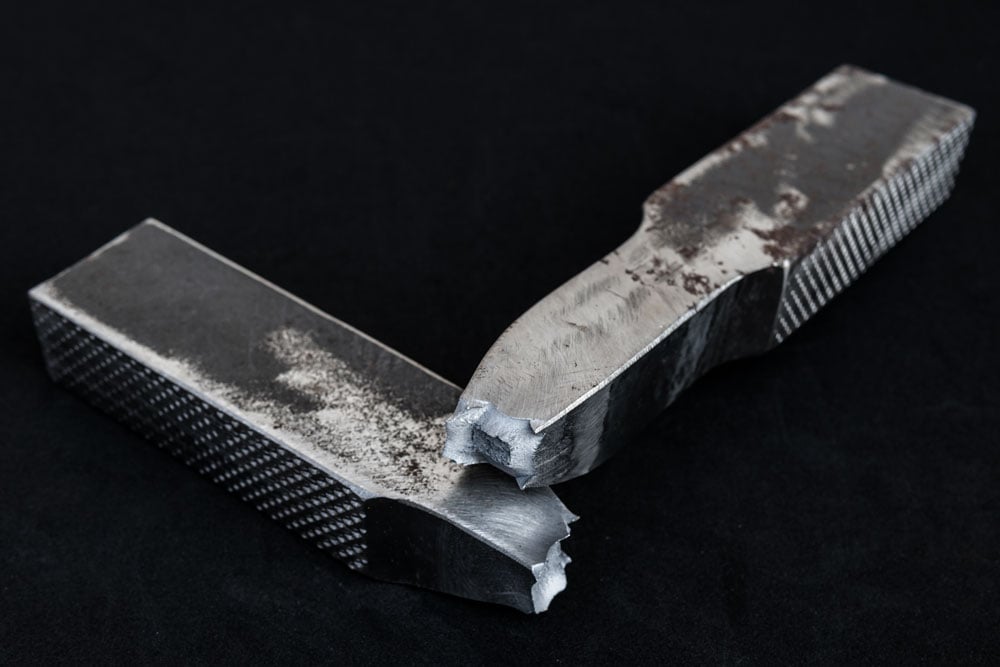

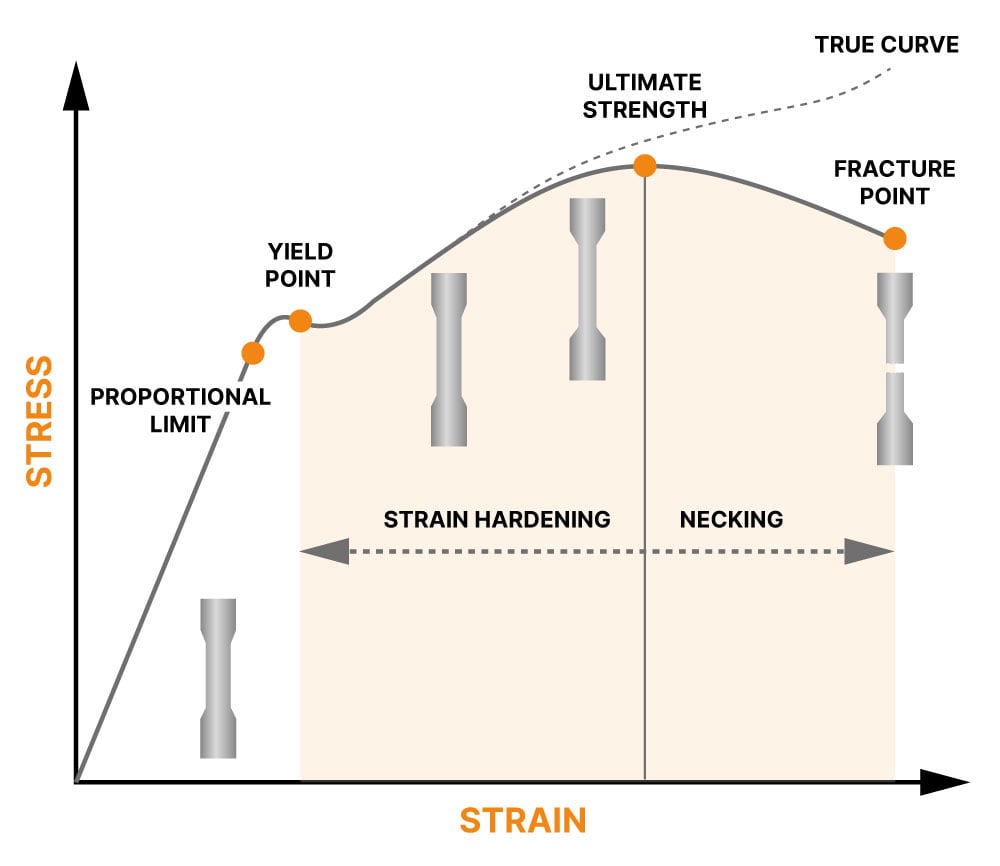
WHAT IS THE ULTIMATE STRENGTH / TENSILE STRENGTH
The force or stress a component can endure before it breaks is called tensile strength. The tensile strength is different for each material. The outside force applied to components can be named force, stress or load by which the tensile strength can be tested.
How is tensile strength measured and tested
A pulling force is applied to show the stress required to break the component, rendering it unusable.
Tensile strength is measured in Pounds per square inch. Tensile strength = maximum load that can be applied without breaking. This test gives the manufacturer the assurance that their components are safe and reliable.

WHAT IS THE ULTIMATE STRENGTH / TENSILE STRENGTH
The force or stress a component can endure before it breaks is called tensile strength. The tensile strength is different for each material. The outside force applied to components can be named force, stress or load by which the tensile strength can be tested.
How is tensile strength measured and tested
A pulling force is applied to show the stress required to break the component, rendering it unusable.
Tensile strength is measured in Pounds per square inch. Tensile strength = maximum load that can be applied without breaking. This test gives the manufacturer the assurance that their components are safe and reliable.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. YIELD STRENGTH
Yield strength indicates the force required before a material no longer returns to its original shape and undergoes permanent plastic deformation when pulled apart. Figuratively, it can be compared to a rubber band that is repeatedly stretched and, after the tension is released, returns to its original shape. If the rubber is stretched beyond that point, it will stretch out and not return to its actual shape. For steel, stretching beyond that point is called “necking”.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. FATIGUE STRENGTH
Fatigue strength shows the user how many cyclic stresses a material can withstand before it breaks and becomes unusable. External influences and environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and corrosion can shorten the lifespan of components and tools.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH
The main difference between tensile and compressive stresses is the direction of the force. Tensile stresses pull apart material, while compressive stresses push material together.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. YIELD STRENGTH
Yield strength indicates the force required before a material no longer returns to its original shape and undergoes permanent plastic deformation when pulled apart. Figuratively, it can be compared to a rubber band that is repeatedly stretched and, after the tension is released, returns to its original shape. If the rubber is stretched beyond that point, it will stretch out and not return to its actual shape. For steel, stretching beyond that point is called “necking”.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. FATIGUE STRENGTH
Fatigue strength shows the user how many cyclic stresses a material can withstand before it breaks and becomes unusable. External influences and environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and corrosion can shorten the lifespan of components and tools.
TENSILE STRENGTH VS. COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH
The main difference between tensile and compressive stresses is the direction of the force. Tensile stresses pull apart material, while compressive stresses push material together.
HOW TO ENHANCE TENSILE STRENGTH
1. Nitriding, case hardening or shot peening can enhance the resistance to tensile stresses of tools and components.
2. Composite materials like ceramic coatings or carbon fibers can also improve the tensile strength.
3. Manufacturing processes like thermomechanical processing where the microstructure is refined or hot isostatic pressing for enhanced density can be used to enhance the tensile strength of parts or tools.
When weld seams are needed the method of welding should be chosen as not to weaken but to enhance the strength of the pieces that are joint and done with much care as a weld seam is often the weakest point if not done properly.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF TENSILE STRENGTH?
Materials with a high tensile strength are able to withstand high loads, have a good wear resistance, good impact resistance and durability. All those properties give the material an improved reliability.
What disadvantages can a high tensile strength have?
A very high tensile strength can cause the material to become brittle and reduce its elasticity and flexibility. Understanding these limits is particularly important when the safety of buildings or bridges is at stake, as this is imperative for the health and safety of many people.
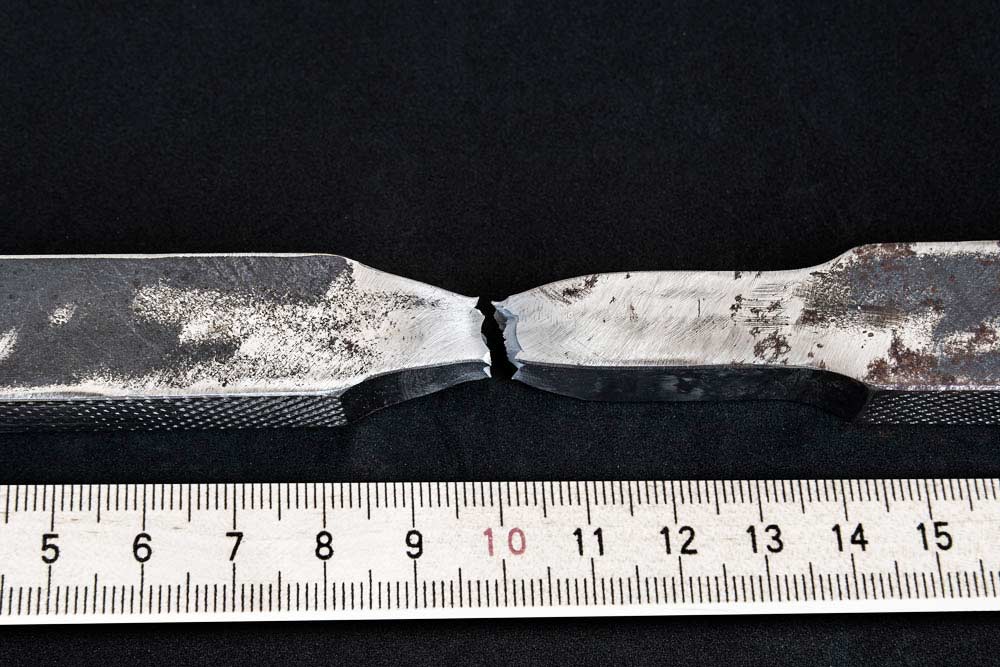

What stresses can affect the tensile strength
In addition to exceeding the maximum load, many different factors can influence the tensile strength. These include high or low temperatures, constantly changing load conditions, internal residual stresses, impact or shock loads, corrosion and concentrated loads in certain areas.
The cause of the acting load can therefore come from a variety of different factors, and it is very important to understand which factors influence components and tools in order to ensure complete safety. Quality control and regular maintenance can be used to assess whether the parts or tools can still be used safely.
CONCLUSION
Tensile strength is an important material property that indicates the tensile forces a material can withstand without breaking. It is a crucial factor in determining the suitability of materials for structural and operational applications across many industries. Material composition, manufacturing processes, heat treatment and environmental influences all have a significant impact upon a materials tensile strength.
It is important to develop an understanding of what tensile strength means so that advances in materials science, alloying techniques and processing methods can be utilized. Optimized tensile strength ensures that engineered structures are reliable and efficient.
Only by taking into account the stresses and challenges that materials face is it possible to develop innovative solutions that meet the demands of modern technology and infrastructure while ensuring sustainability and durability.

Dr. Jürgen Abrams
Founder, CEO
Experienced steel specialist
Dr. Jürgen Abrams is the founder and CEO of ABRAMS Industries®, a customer-oriented company specializing in premium steel and customized precision steel and aluminum.


